SIM imaging resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells
Lu Miao, Chunyu Yan, Yingzhu Chen, Wei Zhou, Xuelian Zhou, Qinglong Qiao, Zhaochao Xu
Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001
Highlights d RBD endocytosis is resolved by imaging the location and ratio of ACE2/RBD fluorescence d Exploring the initiation and influencing factors of RBD internalization d The movement and maturation of ACE2/RBD co-localized vesicles are tracked by SIM imaging
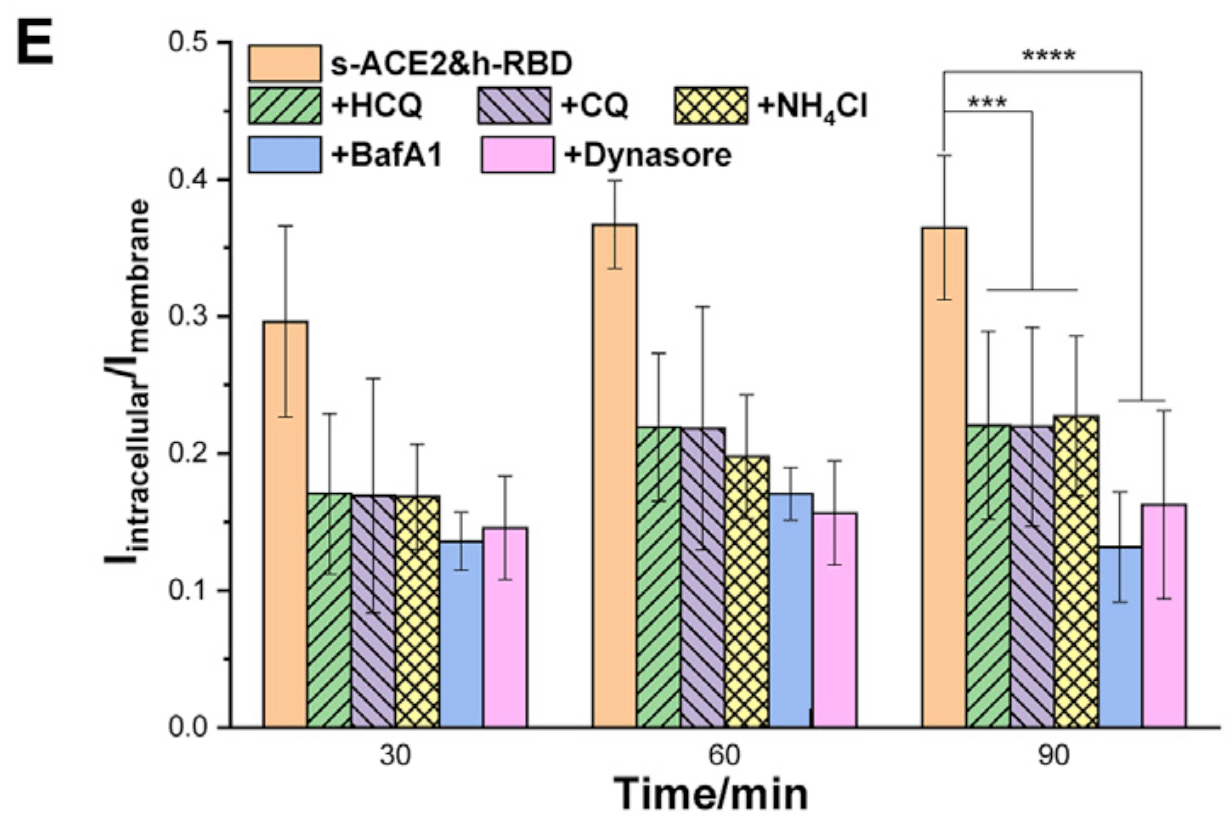
enlightenment on the pathogenic mechanism of COVID-19 and the development of antiviral drugs, but the molecular mechanism remains to be further analyzed.
STAR+METHODS Detailed methods are provided in the online version of this paper and include the following:
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Concepts were conceived by Z.X. and L.M.; L.M. designed the experiments and analyzed the data; C.Y., X.Z., and L.M. performed live-cell experiments; W.Z. and Q.Q. performed compound synthesis; L.M. and Z.X. wrote the manuscript.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
STAR+METHODS KEY RESOURCES
References
Angeli, Zappa, Reboldi, Trapasso, Cavallini et al., The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection: one year later, Eur. J. Intern. Med,
doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.09.007Bayati, Kumar, Francis, Mcpherson, SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306Bright, Gratian, Luzio, Endocytic delivery to lysosomes mediated by concurrent fusion and kissing events in living cells, Curr. Biol,
doi:10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.049Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Djannatian, Franz et al., Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abd2985Chen, Liu, Fang, Qiao, Xu, BODIPY 493 acts as a bright buffering fluorogenic probe for super-resolution imaging of lipid droplet dynamics, Chin. Chem. Lett,
doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.120Chen, Wang, Liu, Qiao, Qi et al., Stable super-resolution imaging of lipid droplet dynamics through a buffer strategy with a hydrogen-bond sensitive fluorogenic probe, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl,
doi:10.1002/ange.202111052Chi, Qiao, Wang, Zheng, Zhou et al., Descriptor DG(C-O) enables the quantitative design of spontaneously blinking rhodamines for live-cell super-resolution imaging, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl,
doi:10.1002/ange.202010169Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on cellular heparan sulfate and ACE2, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033Deshotels, Xia, Sriramula, Lazartigues, Filipeanu, Angiotensin II mediates angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 internalization and degradation through an angiotensin ii type i receptordependent mechanism, Hypertension,
doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03743Fang, Geng, Hao, Chen, Liu et al., Simultaneous Zn 2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20309-7Ghosh, Dellibovi-Ragheb, Kerviel, Pak, Qiu et al., Beta-coronaviruses use lysosomes for egress instead of the biosynthetic secretory pathway, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.039Gourdelier, Swain, Arone, Mouttou, Bracquemond et al., Optimized production and fluorescent labeling of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles, Sci. Rep,
doi:10.1038/s41598-022-18681-zGuo, Li, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Visualizing intracellular organelle and cytoskeletal interactions at nanoscale resolution on millisecond timescales, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.057Han, Li, Qiu, Zhang, Zhang, Cell-permeable organic fluorescent probes for live-cell long-term super-resolution imaging reveal lysosome-mitochondrion interactions, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-017-01503-6Harada, Sakisaka, Yoshitake, Kin, Ohishi et al., Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPases, inhibits the receptor-mediated endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins in isolated rat hepatocytes, J. Hepatol,
doi:10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80146-2Huang, Fan, Li, Liu, Wu et al., Fast, long-term, super-resolution imaging with Hessian structured illumination microscopy, Nat. Biotechnol,
doi:10.1038/nbt.4115Karthika, Joseph, Das, Nair, Charulekha et al., SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry is independent of the ACE2 cytoplasmic domain signaling, Cells,
doi:10.3390/cells10071814Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptorbinding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5Lazartigues, Feng, Lavoie, The two fACEs of the tissue renin-angiotensin systems: implication in cardiovascular diseases, Curr. Pharm. Des,
doi:10.2174/138161207780618911Leng, Qiao, Miao, Deng, Cui et al., A washfree SNAP-tag fluorogenic probe based on the additive effects of quencher release and environmental sensitivity, Chem. Commun,
doi:10.1039/C7CC01483JLiu, Qiao, Zheng, Chen, Zhou et al., An assembly-regulated SNAP-tag fluorogenic probe for long-term super-resolution imaging of mitochondrial dynamics, Biosens. Bioelectron,
doi:10.1016/j.bios.2020.112886Liu, Wang, Xie, Liu, Lamb et al., Single-virus tracking: from imaging methodologies to virological applications, Chem. Rev,
doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00692Liu, Zhang, Sun, Zheng, Zhang et al., Simultaneous visualization of parental and prog-eny viruses by a capsid-specific HaloTag labeling strategy, ACS Nano,
doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b06438Los, Encell, Mcdougall, Hartzell, Karassina et al., HaloTag: a novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis, ACS Chem. Biol,
doi:10.1021/cb800025kLukinavi Cius, Umezawa, Olivier, Honigmann, Yang et al., A near-infrared fluorophore for live-cell super-resolution microscopy of cellular proteins, Nat. Chem,
doi:10.1038/nchem.1546Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04474-xOu, Liu, Lei, Li, Mi et al., Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9Portales, Mustafa, Mccarthy, Cornejo, Couto et al., ACE2 internalization induced by a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein is modulated by angiotensin II type 1 and bradykinin 2 receptors, Life Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120284Prabhakara, Godbole, Sil, Jahnavi, Gulzar et al., Strategies to target SARS-CoV-2 entry and infection using dual mechanisms of inhibition by acidification inhibitors, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009706Qi, Chi, Li, Qiao, Chen et al., A H-bond strategy to develop acid-resistant photoswitchable rhodamine spirolactams for super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy, Chem. Sci,
doi:10.1039/C9SC01284BQiao, Liu, Chen, Zhou, Yin et al., A naphthalimide-derived fluorogenic probe for SNAP-tag with a fast record labeling rate, Dyes Pigm,
doi:10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.08.032Trivedi, Bartlett, Pulinilkunnil, Lysosomal biology and function: modern view of cellular debris bin, Cells,
doi:10.3390/cells9051131Verdecchia, Cavallini, Spanevello, Angeli, The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Intern. Med,
doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037Vickers, Hales, Kaushik, Dick, Gavin et al., Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.M200581200Wang, Frei, Salim, Johnsson, Small-molecule fluorescent probes for live-cell super-resolution microscopy, J. Am. Chem. Soc,
doi:10.1021/jacs.8b11134Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res,
doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00460-yWrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abb2507Yan, Gao, Comparison of the binding characteristics of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 RBDs to ACE2 at different temperatures by MD simulations, Brief. Bioinform,
doi:10.1093/bib/bbab044Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abb2762Yang, Shen, Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19, Int. J. Biol. Sci,
doi:10.7150/ijbs.45498Yeung, Teng, Jia, Zhang, Huang et al., Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053Yuan, Pavel, Wang, Kwachukwu, Mediouni et al., Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture, Commun. Biol,
doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8Zhang, Wada, Hida, Tsuchiyama, Hiragushi et al., Collectrin, a collecting duct-specific transmembrane glycoprotein, is a novel homolog of ACE2 and is developmentally regulated in embryonic kidneys, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.M006723200DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001",
"ISSN": [
"2451-9456"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001",
"alternative-id": [
"S2451945623000326"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "SIM imaging resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Cell Chemical Biology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miao",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Chunyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yingzhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Xuelian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qiao",
"given": "Qinglong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Zhaochao",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cell Chemical Biology",
"container-title-short": "Cell Chemical Biology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-07T18:14:27Z",
"timestamp": 1678212867000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-17T09:07:44Z",
"timestamp": 1710666464000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"22078314",
"22225806",
"22278394"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002979",
"award": [
"DICPI202142",
"DICPI202227"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-25T01:20:30Z",
"timestamp": 1711329630497
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 381,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1710547200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451945623000326?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451945623000326?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "248-260.e4",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053",
"article-title": "Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib1",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib2",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib3",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib4",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.045",
"article-title": "Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib5",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib6",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"article-title": "Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation",
"author": "Wrapp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1260",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib7",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201108131",
"article-title": "The cell biology of receptor-mediated virus entry",
"author": "Grove",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib8",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib9",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2003138117",
"article-title": "Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11727",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib10",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009706",
"article-title": "Strategies to target SARS-CoV-2 entry and infection using dual mechanisms of inhibition by acidification inhibitors",
"author": "Prabhakara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1009706",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib11",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"article-title": "Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV",
"author": "Ou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1620",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib12",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis",
"author": "Bayati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100306",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib13",
"volume": "296",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on cellular heparan sulfate and ACE2",
"author": "Clausen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1043",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib14",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10071814",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry is independent of the ACE2 cytoplasmic domain signaling",
"author": "Karthika",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1814",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbab044",
"article-title": "Comparison of the binding characteristics of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 RBDs to ACE2 at different temperatures by MD simulations",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1122",
"journal-title": "Brief. Bioinform.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib16",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00692",
"article-title": "Single-virus tracking: from imaging methodologies to virological applications",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1936",
"journal-title": "Chem. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib17",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00218",
"article-title": "Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy",
"author": "Heintzmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13890",
"journal-title": "Chem. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib18",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt.4115",
"article-title": "Fast, long-term, super-resolution imaging with Hessian structured illumination microscopy",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nat. Biotechnol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib19",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.057",
"article-title": "Visualizing intracellular organelle and cytoskeletal interactions at nanoscale resolution on millisecond timescales",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1430",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib20",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-01503-6",
"article-title": "Cell-permeable organic fluorescent probes for live-cell long-term super-resolution imaging reveal lysosome-mitochondrion interactions",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib21",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20309-7",
"article-title": "Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/anie.202111052",
"article-title": "Stable super-resolution imaging of lipid droplet dynamics through a buffer strategy with a hydrogen-bond sensitive fluorogenic probe",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25104",
"journal-title": "Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib23",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.120",
"article-title": "BODIPY 493 acts as a bright buffering fluorogenic probe for super-resolution imaging of lipid droplet dynamics",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5042",
"journal-title": "Chin. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib24",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jacs.8b11134",
"article-title": "Small-molecule fluorescent probes for live-cell super-resolution microscopy",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2770",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Chem. Soc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib25",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cclet.2021.02.003",
"article-title": "Quantitative assessment of rhodamine spectra",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "943",
"journal-title": "Chin. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib26",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/anie.202010169",
"article-title": "Descriptor ΔG(C-O) enables the quantitative design of spontaneously blinking rhodamines for live-cell super-resolution imaging",
"author": "Chi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20215",
"journal-title": "Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib27",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C9SC01284B",
"article-title": "A H-bond strategy to develop acid-resistant photoswitchable rhodamine spirolactams for super-resolution single-molecule localization microscopy",
"author": "Qi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4914",
"journal-title": "Chem. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib28",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.01.007",
"article-title": "An engineered protein tag for multiprotein labeling in living cells",
"author": "Gautier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib29",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/cb800025k",
"article-title": "HaloTag: a novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis",
"author": "Los",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib30",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C7CC01483J",
"article-title": "A wash-free SNAP-tag fluorogenic probe based on the additive effects of quencher release and environmental sensitivity",
"author": "Leng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6448",
"journal-title": "Chem. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib31",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.08.032",
"article-title": "A naphthalimide-derived fluorogenic probe for SNAP-tag with a fast record labeling rate",
"author": "Qiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Dyes Pigm.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib32",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.5b06438",
"article-title": "Simultaneous visualization of parental and progeny viruses by a capsid-specific HaloTag labeling strategy",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1147",
"journal-title": "ACS Nano",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib33",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bios.2020.112886",
"article-title": "An assembly-regulated SNAP-tag fluorogenic probe for long-term super-resolution imaging of mitochondrial dynamics",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112886",
"journal-title": "Biosens. Bioelectron.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib34",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.121",
"article-title": "A TICS-fluorophore based probe for dual-color GSH imaging",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4943",
"journal-title": "Chin. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib35",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M006723200",
"article-title": "Collectrin, a collecting duct-specific transmembrane glycoprotein, is a novel homolog of ACE2 and is developmentally regulated in embryonic kidneys",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17132",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib36",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm.2017.132",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of clathrin-mediated endocytosis",
"author": "Kaksonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "313",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib37",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nchem.1546",
"article-title": "A near-infrared fluorophore for live-cell super-resolution microscopy of cellular proteins",
"author": "Lukinavičius",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib38",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M200581200",
"article-title": "Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase",
"author": "Vickers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14838",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib39",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45498",
"article-title": "Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1724",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib40",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.043",
"article-title": "Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes",
"author": "Rink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib41",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0955-0674(03)00081-4",
"article-title": "Insider information: what viruses tell us about endocytosis",
"author": "Pelkmans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138161207780618911",
"article-title": "The two fACEs of the tissue renin-angiotensin systems: implication in cardiovascular diseases",
"author": "Lazartigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1231",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Des.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03743",
"article-title": "Angiotensin II mediates angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 internalization and degradation through an angiotensin ii type i receptor–dependent mechanism",
"author": "Deshotels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1368",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib44",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y",
"article-title": "AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib45",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd2985",
"article-title": "Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity",
"author": "Cantuti-Castelvetri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib46",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "958",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib47",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41565-020-0674-9",
"article-title": "Insights from nanomedicine into chloriquine efficacy against COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Nat. Nanotechnol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib48",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0168-8278(96)80146-2",
"article-title": "Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPases, inhibits the receptor-mediated endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins in isolated rat hepatocytes",
"author": "Harada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "594",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib49",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9051131",
"article-title": "Lysosomal biology and function: modern view of cellular debris bin",
"author": "Trivedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1131",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib50",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tcb.2019.05.003",
"article-title": "Lysosome fission: planning for an exit",
"author": "Saffi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "635",
"journal-title": "Trends Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib51",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tcb.2017.12.001",
"article-title": "Increasing diversity of biological membrane fission mechanisms",
"author": "Renard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "274",
"journal-title": "Trends Cell Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib52",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.049",
"article-title": "Endocytic delivery to lysosomes mediated by concurrent fusion and kissing events in living cells",
"author": "Bright",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "360",
"journal-title": "Curr. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib53",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.039",
"article-title": "Beta-coronaviruses use lysosomes for egress instead of the biosynthetic secretory pathway",
"author": "Ghosh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1520",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib54",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0000000000002859",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection and ACE2 inhibition",
"author": "Angeli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1555",
"journal-title": "J. Hypertens.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib55",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2021.09.007",
"article-title": "The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection: one year later",
"author": "Angeli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib56",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037",
"article-title": "The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Verdecchia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib57",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120284",
"article-title": "ACE2 internalization induced by a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein is modulated by angiotensin II type 1 and bradykinin 2 receptors",
"author": "Portales",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120284",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib58",
"volume": "293",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-18681-z",
"article-title": "Optimized production and fluorescent labeling of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles",
"author": "Gourdelier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14651",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001_bib59",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2451945623000326"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmacology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SIM imaging resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "30"
}