DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbic.202400404",
"ISSN": [
"1439-4227",
"1439-7633"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202400404",
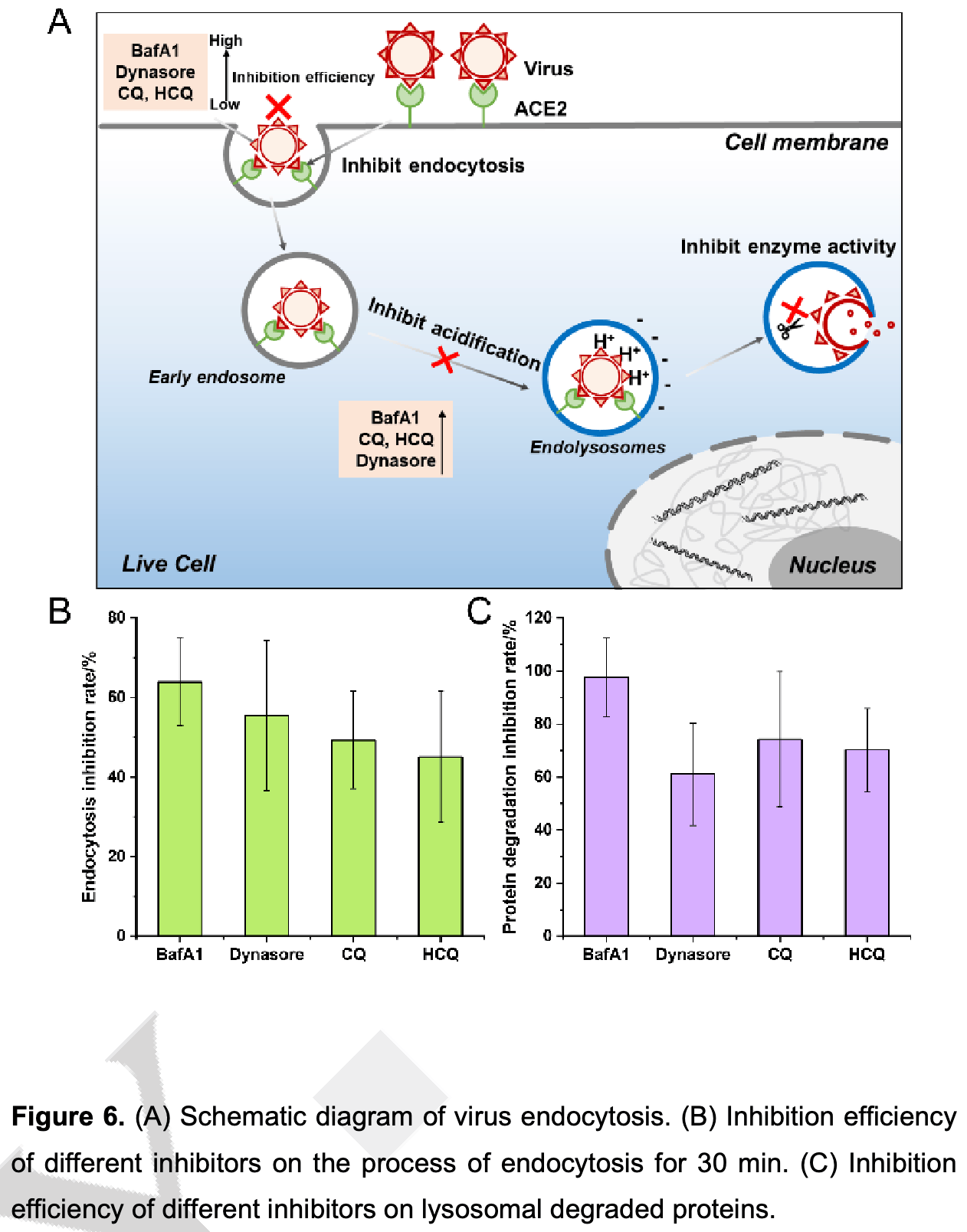
"abstract": "<jats:p>In this study, super‐resolution structured illumination microscope (SIM) was used to analyze molecular mechanism of endocytic acidification inhibitors in the SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic, such as Chloroquine (CQ), Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and Bafilomycin A1 (BafA1). We fluorescently labeled the SARS‐CoV‐2 RBD and its receptor ACE2 protein with small molecule dyes. Utilizing SIM imaging, the real‐time impact of inhibitors (BafA1, CQ, HCQ, Dynasore) on the RBD‐ACE2 endocytotic process was dynamically tracked in living cells. Initially, the protein activity of RBD and ACE2 was ensured after being labeled. And then our findings revealed that these inhibitors could inhibit the internalization and degradation of RBD‐ACE2 to varying degrees. Among them, 100 nM BafA1 exhibited the most satisfactory endocytotic inhibition (~63.9%) and protein degradation inhibition (~97.7%). And it could inhibit the fusion between endocytic vesicles in the living cells. Additionally, Dynasore, a widely recognized dynein inhibitor, also demonstrated cell acidification inhibition effects. Together, these inhibitors collectively hinder SARS‐CoV‐2 infection by inhibiting both the viral internalization and RNA release. The comprehensive evaluation of pharmacological mechanisms through super‐resolution fluorescence imaging has laid a crucial theoretical foundation for the development of potential drugs to treat COVID‐19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/cbic.202400404"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-05-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-06-14"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-06-14"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Chunyu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Xuelian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Qiao",
"given": "Qinglong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics department of biotechnology CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Miao",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics Department of Biotechnology Department of Biological Technology 457 Zhongshan Road 116023 Dalian CHINA"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Zhaochao",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "ChemBioChem",
"container-title-short": "ChemBioChem",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-15T03:10:25Z",
"timestamp": 1718421025000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-15T03:10:27Z",
"timestamp": 1718421027000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-16T00:19:30Z",
"timestamp": 1718497170381
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1718323200000
}
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cbic.202400404"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Super‐resolution imaging reveals the mechanism of endosomal acidification inhibitors against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}