Hydroxychloroquine attenuates double‐stranded RNA‐stimulated hyper‐phosphorylation of tristetraprolin/ZFP36 and AU‐rich mRNA stabilization
Edward G Hitti, Zeyad Muazzen, Walid Moghrabi, Suhad Al‐yahya, Khalid S A Khabar
Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13835
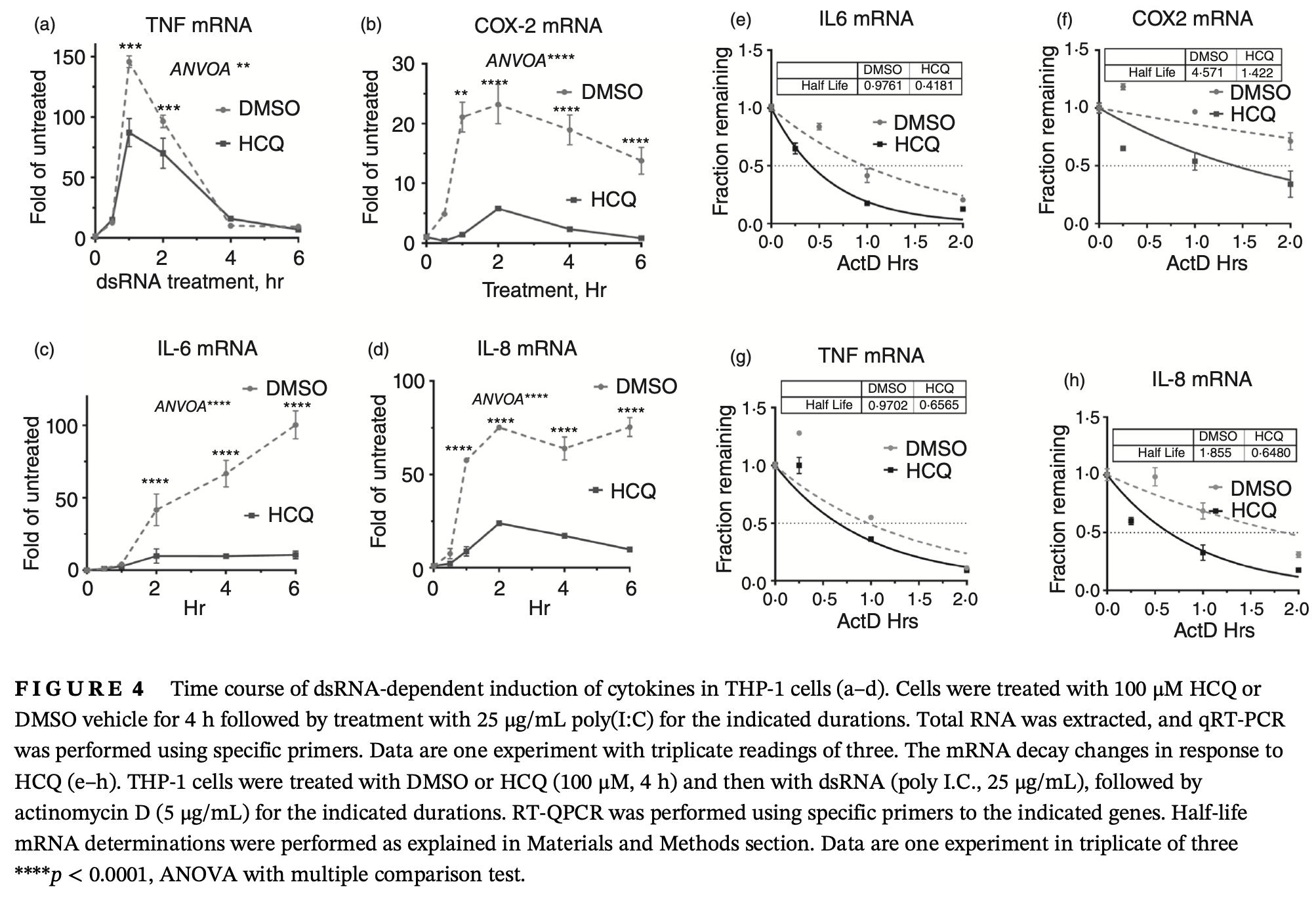
The human innate immune system recognizes dsRNA as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern that induces a potent inflammatory response. The primary source of pathogenic dsRNA is cells infected with replicating viruses, but can also be released from uninfected necrotic cells. Here, we show that the dsRNA poly(I:C) challenge in human macrophages activates the p38 MAPK-MK2 signalling pathway and subsequently the phosphorylation of tristetraprolin (TTP/ZFP36). The latter is an mRNA decaypromoting protein that controls the stability of AU-rich mRNAs (AREs) that code for many inflammatory mediators. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), a common anti-malaria drug, is used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune disorders and, controversially, during acute COVID-19 disease. We found that HCQ reduced the dsRNA-dependent phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and its downstream kinase MK2. Subsequently, HCQ reduced the abundance and protein stability of the inactive (phosphorylated) form of TTP. HCQ reduced the levels and the mRNA stability of poly (I:C)-induced cytokines and inflammatory mRNAs like TNF, IL-6, COX-2, and IL-8 in THP-1 and primary blood monocytes. Our results demonstrate a new mechanism of the anti-inflammatory role of HCQ at post-transcriptional level (TTP phosphorylation) in a model of dsRNA activation, which usually occurs in viral infections or RNA release from necrotic tissue.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Concept, Design, Data analysis, and Writing: (E. Hitti, K. Khabar); Performance of experiments and data acquisition (Z. Muazzen, W. Moghrabi, S. Al-Yahya). All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors report no conflicts of interest.
References
Bakheet, Hitti, Khabar, ARED-plus: an updated and expanded database of AU-rich element-containing mRNAs and pre-mRNAs, Nucleic Acids Res
Brentano, Schorr, Gay, Gay, Kyburz et al., Hydroxychloroquine attenuates double-stranded RNA-stimulated hyper-phosphorylation of tristetraprolin/ZFP36 and AU-rich mRNA stabilization, Arthritis Rheum
Canovas, Nebreda, Diversity and versatility of p38 kinase signalling in health and disease, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Cao, Deterding, Blackshear, Phosphorylation site analysis of the anti-inflammatory and mRNA-destabilizing protein tristetraprolin, Expert Rev Proteomics
Circu, Cardelli, Barr, Byrne, Mills et al., Modulating lysosomal function through lysosome membrane permeabilization or autophagy suppression restores sensitivity to cisplatin in refractory non-small-cell lung cancer cells, PLoS One
Clement, Scheckel, Stoecklin, Lykke-Andersen, Phosphorylation of tristetraprolin by MK2 impairs AU-rich element mRNA decay by preventing deadenylase recruitment, Mol Cell Biol
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hoang, Meddeb et al., Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label nonrandomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Zucker, Baldwin et al., Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Gies, Bekaddour, Dieudonne, Guffroy, Frenger et al., Beyond anti-viral effects of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine, Front Immunol
Hashem, Alghamdi, Algaissi, Alshehri, Bukhari et al., Therapeutic use of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 and other viral infections: a narrative review, Travel Med Infect Dis
Hitti, Iakovleva, Brook, Deppenmeier, Gruber et al., Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 regulates tumor necrosis factor mRNA stability and translation mainly by altering tristetraprolin expression, stability, and binding to adenine/uridine-rich element, Mol Cell Biol
Hitti, Khabar, Sequence variations affecting AU-rich element function and disease, Front Biosci
Jang, Choi, Byun, Jue, Chloroquine inhibits production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes/macrophages by different modes, Rheumatology
Johnsen, Nguyen, Bergstrom, Anthonsen, Toll-like receptor 3-elicited MAPK activation induces stabilization of interferon-beta mRNA, Cytokine
Khabar, Post-transcriptional control during chronic inflammation and cancer: a focus on AU-rich elements, Cell Mol Life Sci
Khabar, Post-transcriptional control of cytokine gene expression in health and disease, J Interferon Cytokine Res
Kuznik, Bencina, Svajger, Jeras, Rozman et al., Mechanism of endosomal TLR inhibition by antimalarial drugs and imidazoquinolines, J Immunol
Kyburz, Brentano, Gay, Mode of action of hydroxychloroquine in RA-evidence of an inhibitory effect on toll-like receptor signaling, Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol
Li, Wu, Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Liu, Cao, Xu, Wang, Zhang et al., Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discov
Mahmoud, Abdulkarim, Kutbi, Moghrabi, Altwijri et al., Post-transcriptional inflammatory response to intracellular bacterial c-di-AMP, Front Immunol
Mahmoud, Al-Enezi, Al-Saif, Warsy, Khabar et al., Sustained stabilization of Interleukin-8 mRNA in human macrophages, RNA Biol
Marchese, Aubareda, Tudor, Saklatvala, Clark et al., MAPKAP kinase 2 blocks tristetraprolin-directed mRNA decay by inhibiting CAF1 deadenylase recruitment, J Biol Chem
Mogensen, Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses, Clin Microbiol Rev
Moghrabi, Al-Yahya, Al-Haj, Al-Saif, Kinome inhibition reveals a role for polo-like kinase 1 in targeting post-transcriptional control in cancer, Mol Oncol
Nguyen, Smith, Tate, Belz, Barrios et al., SIDT2 transports extracellular dsRNA into the cytoplasm for innate immune recognition, Immunity
Olsen, Schleich, Karp, Multifaceted effects of hydroxychloroquine in human disease, Semin Arthritis Rheum
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging, J Clin Invest
Ponticelli, Moroni, Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Expert Opin Drug Saf
Reddin, Fenton, Wass, Michaelis, Large inherent variability in data derived from highly standardised cell culture experiments, Pharmacol Res
Ronkina, Shushakova, Tiedje, Yakovleva, Tollenaere et al., The role of TTP phosphorylation in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine production by MK2/3, J Immunol
Sato, Imaizumi, Aizawa, Watanabe, Tsugawa et al., Inhibitory effect of anti-malarial agents on the expression of proinflammatory chemokines via toll-like receptor 3 signaling in human glomerular endothelial cells, Ren Fail
Schrezenmeier, Dorner, Mechanisms of action of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine: implications for rheumatology, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Self, Semler, Leither, Casey, Angus et al., Network, effect of hydroxychloroquine on clinical status at 14 days in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Steer, Moran, Christmann, Lb, Corbett, Role of MAPK in the regulation of double-stranded RNA-and encephalomyocarditis virus-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression by macrophages, J Immunol
Sun, Stoecklin, Van Way, Hinkovska-Galcheva, Guo et al., Tristetraprolin (TTP)-14-3-3 complex formation protects TTP from dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase 2a and stabilizes tumor necrosis factor-α mRNA, J Biol Chem
Tatematsu, Funami, Seya, Matsumoto, Extracellular RNA sensing by pattern recognition receptors, J Innate Immun
Thwaites, Chamberlain, Sacre, Emerging role of endosomal toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis, Front Immunol
Tiedje, Diaz-Muñoz, Trulley, Ahlfors, Laaß et al., The RNA-binding protein TTP is a global post-transcriptional regulator of feedback control in inflammation, Nucleic Acids Res
Zhang, Zhao, Zhang, Wang, Li et al., The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): the experience of clinical immunologists from China, Clin Immunol