Pre-Infection Innate Immunity Attenuates SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Load in iPSC-Derived Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cells
Satish Kumar, Jose Granados, Miriam Aceves, Juan Peralta, Ana C Leandro, John Thomas, Sarah Williams-Blangero, Joanne E Curran, John Blangero
Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13050369
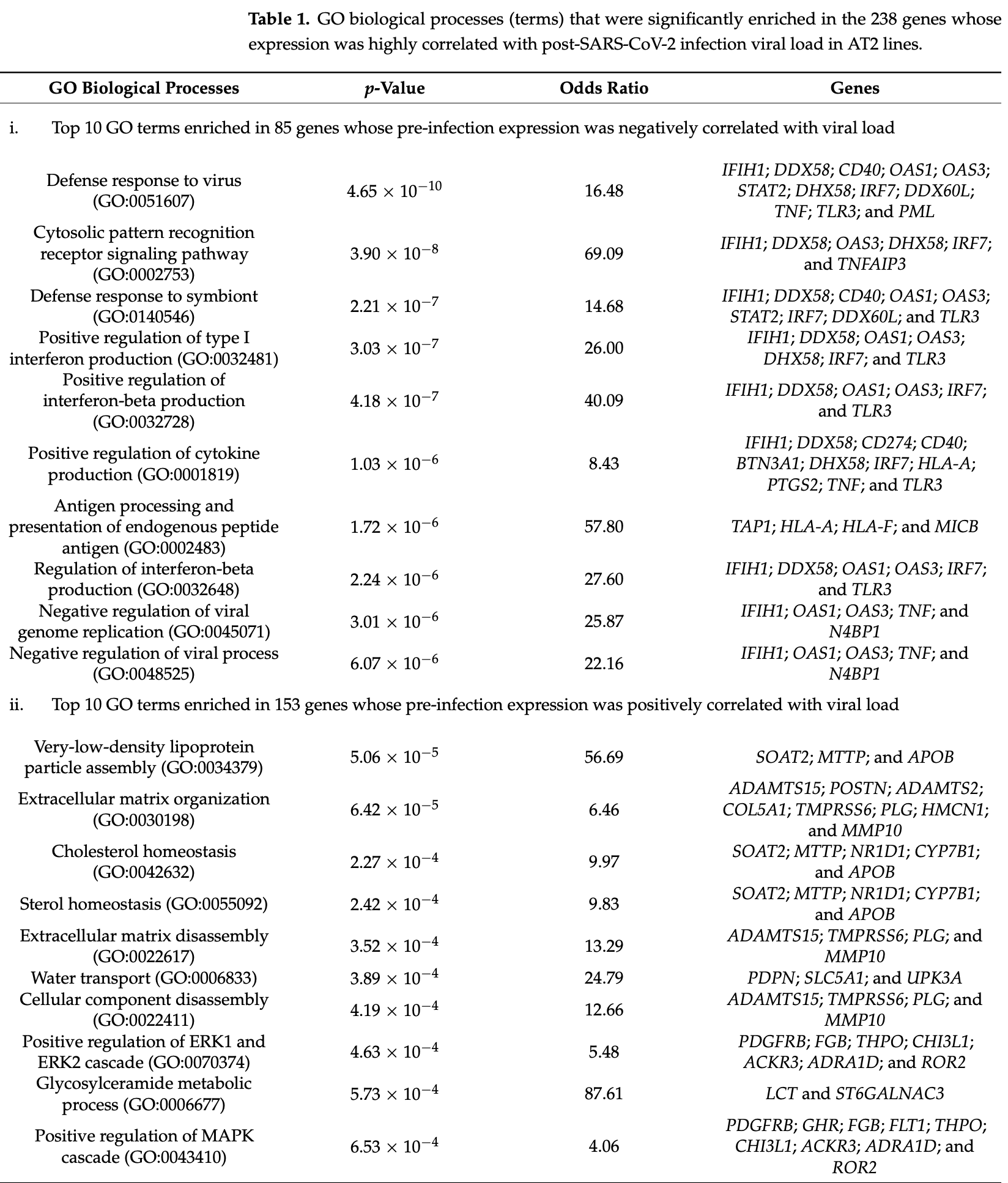
A large portion of the heterogeneity in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility and severity of illness (SOI) remains poorly understood. Recent evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection-associated damage to alveolar epithelial type 2 cells (AT2s) in the distal lung may directly contribute to disease severity and poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients. Our in vitro modeling of SARS-CoV-2 infection in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived AT2s from 10 different individuals showed interindividual variability in infection susceptibility and the postinfection cellular viral load. To understand the underlying mechanism of the AT2 ′ s capacity to regulate SARS-CoV-2 infection and cellular viral load, a genome-wide differential gene expression analysis between the mock and SARS-CoV-2 infection-challenged AT2s was performed. The 1393 genes, which were significantly (one-way ANOVA FDR-corrected p ≤ 0.05; FC abs ≥ 2.0) differentially expressed (DE), suggest significant upregulation of viral infection-related cellular innate immune response pathways (p-value ≤ 0.05; activation z-score ≥ 3.5), and significant downregulation of the cholesterol-and xenobiotic-related metabolic pathways (p-value ≤ 0.05; activation z-score ≤ -3.5). Whilst the effect of post-SARS-CoV-2 infection response on the infection susceptibility and postinfection viral load in AT2s is not clear, interestingly, pre-infection (mock-challenged) expression of 238 DE genes showed a high correlation with the postinfection SARS-CoV-2 viral load (FDR-corrected p-value ≤ 0.05 and r 2absolute ≥ 0.57). The 85 genes whose expression was negatively correlated with the viral load showed significant enrichment in viral recognition and cytokine-mediated innate immune GO biological processes (p-value range: 4.65 × 10 -10 to 2.24 × 10 -6 ). The 153 genes whose expression was positively correlated with the viral load showed significant enrichment in cholesterol homeostasis, extracellular matrix, and MAPK/ERK pathway-related GO biological processes (p-value range: 5.06 × 10 -5 to 6.53 × 10 -4 ). Overall, our results strongly suggest that AT2s' pre-infection innate immunity and metabolic state affect their susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and viral load.
Conflicts of Interest: The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
Abo, Ma, Matte, Huang, Alysandratos et al., Human iPSC-derived alveolar and airway epithelial cells can be cultured at air-liquid interface and express SARS-CoV-2 host factors, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.06.03.132639Aquino, Bisiaux, Li, O'neill, Mendoza-Revilla et al., Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06422-9Barkauskas, Cronce, Rackley, Bowie, Keene et al., Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung, J. Clin. Investig,
doi:10.1172/JCI68782Bastard, Michailidis, Hoffmann, Chbihi, Le Voyer et al., Auto-antibodies to type I IFNs can underlie adverse reactions to yellow fever live attenuated vaccine, J. Exp. Med,
doi:10.1084/jem.20202486Bastard, Zhang, Zhang, Jouanguy, Casanova, Type I interferons and SARS-CoV-2: From cells to organisms, Curr. Opin. Immunol,
doi:10.1016/j.coi.2022.01.003Bradley, Maioli, Johnston, Chaudhry, Fink et al., Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington State: A case series, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31305-2Béliveau, Tarkar, Dion, Désilets, Ghinet et al., Discovery and Development of TMPRSS6 Inhibitors Modulating Hepcidin Levels in Human Hepatocytes, Cell Chem. Biol,
doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.09.004Carcaterra, Caruso, Alveolar epithelial cell type II as main target of SARS-CoV-2 virus and COVID-19 development via NF-Kb pathway deregulation: A physio-pathological theory, Med. Hypotheses,
doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110412Cevik, Tate, Lloyd, Maraolo, Schafers et al., SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Microbe,
doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30172-5Cheemarla, Watkins, Mihaylova, Wang, Zhao et al., Dynamic innate immune response determines susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and early replication kinetics, J. Exp. Med,
doi:10.1084/jem.20210583Chen, Tan, Kou, Duan, Wang et al., Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool, BMC Bioinform,
doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-128Chen, Wu, He, Jiang, He, Metabolic alterations upon SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential therapeutic targets against coronavirus infection, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther,
doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01510-8Chen, Zheng, Understand variability of COVID-19 through population and tissue variations in expression of SARS-CoV-2 host genes, Inform. Med. Unlocked,
doi:10.1016/j.imu.2020.100443Costa, Júnior, Nascimento, De Brito, Antonangelo et al., COVID-19 induces more pronounced extracellular matrix deposition than other causes of ARDS, Respir. Res,
doi:10.1186/s12931-023-02555-7Daamen, Bachali, Owen, Kingsmore, Hubbard et al., Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of COVID-19 blood, lung, and airway, Sci. Rep,
doi:10.1038/s41598-021-86002-xDaniloski, Jordan, Wessels, Hoagland, Kasela et al., Identification of Required Host Factors for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Cells, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.030Desai, Brownfield, Krasnow, Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer, Nature,
doi:10.1038/nature12930Du, She, Gelbart, Truksa, Lee et al., The serine protease TMPRSS6 is required to sense iron deficiency, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.1157121Ehsani, COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: Distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein, Biol. Direct,
doi:10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2Ellinghaus, Degenhardt, Bujanda, Buti, Albillos et al., Genomewide Association Study of Severe COVID-19 with Respiratory Failure, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2020283Engler, Albers, Von Maltitz, Groß, Münch et al., ACE2-EGFR-MAPK signaling contributes to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Life Sci. Alliance,
doi:10.26508/lsa.202201880Ganz, Nemeth, Mitchell, Shawki, Mackenzie, Iron imports. IV. Hepcidin and regulation of body iron metabolism, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol,
doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00412.2005Gong, Wei, Xu, Miller, Thompson et al., Polymorphism in the surfactant protein-B gene, gender, and the risk of direct pulmonary injury and ARDS, Chest,
doi:10.1378/chest.125.1.203Gotoh, Ito, Nagasaki, Yamamoto, Konishi et al., Generation of alveolar epithelial spheroids via isolated progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells, Stem Cell Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.07.005Han, Yang, Duan, Duan, Nilsson-Payant et al., Identification of Candidate COVID-19 Therapeutics using hPSC-derived Lung Organoids, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.05.05.079095Harcourt, Tamin, Lu, Kamili, Sakthivel et al., Isolation and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 from the first US COVID-19 patient, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.03.02.972935Hou, Okuda, Edwards, Martinez, Asakura et al., SARS-CoV-2 Reverse Genetics Reveals a Variable Infection Gradient in the Respiratory Tract, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042Huang, Hume, Abo, Werder, Villacorta-Martin et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Lung Alveolar Type 2 Cells Elicits a Rapid Epithelial-Intrinsic Inflammatory Response, Cell Stem Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.013Hurley, Ding, Villacorta-Martin, Herriges, Jacob et al., Reconstructed Single-Cell Fate Trajectories Define Lineage Plasticity Windows during Differentiation of Human PSC-Derived Distal Lung Progenitors, Cell Stem Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.stem.2019.12.009Jacob, Morley, Hawkins, Mccauley, Jean et al., Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Functional Lung Alveolar Epithelial Cells, Cell Stem Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.stem.2017.08.014Jacob, Vedaie, Roberts, Thomas, Villacorta-Martin et al., Derivation of self-renewing lung alveolar epithelial type II cells from human pluripotent stem cells, Nat. Protoc,
doi:10.1038/s41596-019-0220-0Katsura, Sontake, Tata, Kobayashi, Edwards et al., Human Lung Stem Cell-Based Alveolospheres Provide Insights into SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Interferon Responses and Pneumocyte Dysfunction, Cell Stem Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.10.005Kulasinghe, Tan, Miggiolaro, Monkman, Sadeghirad et al., Profiling of lung SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection dissects virus-specific host responses and gene signatures, Eur. Respir. J,
doi:10.1183/13993003.01881-2021Kumar, Curran, Espinosa, Glahn, Blangero, Highly efficient induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming of cryopreserved lymphoblastoid cell lines, J. Biol. Methods,
doi:10.14440/jbm.2020.296Kumar, Curran, Glahn, Blangero, Utility of Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generation, Stem Cells Int,
doi:10.1155/2016/2349261Lee, Kim, Lee, Lee, Kim et al., Clinical Course and Molecular Viral Shedding Among Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Community Treatment Center in the Republic of Korea, JAMA Intern. Med,
doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3862Loske, Röhmel, Lukassen, Stricker, Magalhães et al., Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, Nat. Biotechnol,
doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01037-9Lu, Wang, Sakthivel, Whitaker, Murray et al., US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Emerg. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.3201/eid2608.201246Lukassen, Chua, Trefzer, Kahn, Schneider et al., SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are primarily expressed in bronchial transient secretory cells, EMBO J,
doi:10.15252/embj.20105114Nishino, Toyoda, Yamazaki-Inoue, Fukawatase, Chikazawa et al., DNA methylation dynamics in human induced pluripotent stem cells over time, PLoS Genet,
doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002085Noguchi-Sasaki, Sasaki, Shimonaka, Mori, Fujimoto-Ouchi, Treatment with anti-IL-6 receptor antibody prevented increase in serum hepcidin levels and improved anemia in mice inoculated with IL-6-producing lung carcinoma cells, BMC Cancer,
doi:10.1186/s12885-016-2305-2Rebendenne, Valadão, Tauziet, Maarifi, Bonaventure et al., SARS-CoV-2 triggers an MDA-5-dependent interferon response which is unable to control replication in lung epithelial cells, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.02415-20Rendeiro, Ravichandran, Bram, Chandar, Kim et al., The spatial landscape of lung pathology during COVID-19 progression, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03475-6Rouhani, Kumasaka, De Brito, Bradley, Vallier et al., Genetic background drives transcriptional variation in human induced pluripotent stem cells, PLoS Genet,
doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004432Schaefer, Padera, Solomon, Kanjilal, Hammer et al., In situ detection of SARS-CoV-2 in lungs and airways of patients with COVID-19, Mod. Pathol,
doi:10.1038/s41379-020-0595-zSisson, Mendez, Choi, Subbotina, Courey et al., Targeted injury of type II alveolar epithelial cells induces pulmonary fibrosis, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med,
doi:10.1164/rccm.200810-1615OCSoares-Schanoski, Sauerwald, Goforth, Periasamy, Weir et al., Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with Higher Levels of Serum IL-17C, Matrix Metalloproteinase 10 and Fibroblast Growth Factors Than Mild Symptomatic COVID-19, Front. Immunol,
doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.821730Strässler, Aalto-Setälä, Kiamehr, Landmesser, Kränkel, Age Is Relative-Impact of Donor Age on Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cell Functionality, Front. Cardiovasc. Med,
doi:10.3389/fcvm.2018.00004Sungnak, Huang, Becavin, Berg, Queen et al., SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes, Nat. Med,
doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6Wang, Simoneau, Kulsuptrakul, Bouhaddou, Travisano et al., Genetic Screens Identify Host Factors for SARS-CoV-2 and Common Cold Coronaviruses, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004Wang, Zhao, Yan, Wang, Sun et al., Viral and Host Transcriptomes in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Human Lung Cells, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00600-21Williams, Williams, Freidin, Freidin, Mangino et al., Self-Reported Symptoms of COVID-19, Including Symptoms Most Predictive of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Are Heritable, Twin Res. Hum. Genet,
doi:10.1017/thg.2020.85Wu, Shi, Li, Huang, Li et al., Viral RNA Load in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic COVID-19 Omicron Variant-Positive Patients, Can. Respir. J,
doi:10.1155/2022/5460400Yin, Riva, Pu, Martin-Sancho, Kanamune et al., MDA5 Governs the Innate Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Lung Epithelial Cells, Cell Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108628Ziegler, Allon, Nyquist, Mbano, Miao et al., SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035Zuo, Veldhuizen, Neumann, Petersen, Possmayer, Current perspectives in pulmonary surfactant-Inhibition, enhancement and evaluation, Biochim. Biophys. Acta,
doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.03.021DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells13050369",
"ISSN": [
"2073-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cells13050369",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A large portion of the heterogeneity in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility and severity of illness (SOI) remains poorly understood. Recent evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection-associated damage to alveolar epithelial type 2 cells (AT2s) in the distal lung may directly contribute to disease severity and poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients. Our in vitro modeling of SARS-CoV-2 infection in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived AT2s from 10 different individuals showed interindividual variability in infection susceptibility and the postinfection cellular viral load. To understand the underlying mechanism of the AT2′s capacity to regulate SARS-CoV-2 infection and cellular viral load, a genome-wide differential gene expression analysis between the mock and SARS-CoV-2 infection-challenged AT2s was performed. The 1393 genes, which were significantly (one-way ANOVA FDR-corrected p ≤ 0.05; FC abs ≥ 2.0) differentially expressed (DE), suggest significant upregulation of viral infection-related cellular innate immune response pathways (p-value ≤ 0.05; activation z-score ≥ 3.5), and significant downregulation of the cholesterol- and xenobiotic-related metabolic pathways (p-value ≤ 0.05; activation z-score ≤ −3.5). Whilst the effect of post-SARS-CoV-2 infection response on the infection susceptibility and postinfection viral load in AT2s is not clear, interestingly, pre-infection (mock-challenged) expression of 238 DE genes showed a high correlation with the postinfection SARS-CoV-2 viral load (FDR-corrected p-value ≤ 0.05 and r2-absolute ≥ 0.57). The 85 genes whose expression was negatively correlated with the viral load showed significant enrichment in viral recognition and cytokine-mediated innate immune GO biological processes (p-value range: 4.65 × 10−10 to 2.24 × 10−6). The 153 genes whose expression was positively correlated with the viral load showed significant enrichment in cholesterol homeostasis, extracellular matrix, and MAPK/ERK pathway-related GO biological processes (p-value range: 5.06 × 10−5 to 6.53 × 10−4). Overall, our results strongly suggest that AT2s’ pre-infection innate immunity and metabolic state affect their susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and viral load.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"cells13050369"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1969-4431",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, McAllen, TX 78504, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Satish",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, McAllen, TX 78504, USA"
}
],
"family": "Granados",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1778-0213",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, McAllen, TX 78504, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aceves",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8811-5579",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, Brownsville, TX 78520, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Peralta",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7640-3469",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, Brownsville, TX 78520, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leandro",
"given": "Ana C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3816-584X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, McAllen, TX 78504, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, Brownsville, TX 78520, USA"
}
],
"family": "Williams-Blangero",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, Brownsville, TX 78520, USA"
}
],
"family": "Curran",
"given": "Joanne E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6250-5723",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Human Genetics and South Texas Diabetes and Obesity Institute, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley School of Medicine, Brownsville, TX 78520, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Blangero",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cells",
"container-title-short": "Cells",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T09:23:10Z",
"timestamp": 1708507390000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T10:15:33Z",
"timestamp": 1708510533000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"P01 HL045522"
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100022387",
"award": [
"510000000",
"U54 HG013247",
"U19 AG076581",
"RM1 GM149403"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Valley Baptist Legacy Foundation"
},
{
"award": [
"C06 RR020547"
],
"name": "NIH"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T01:01:41Z",
"timestamp": 1708563701800
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708473600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/5/369/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "369",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100443",
"article-title": "Understand variability of COVID-19 through population and tissue variations in expression of SARS-CoV-2 host genes",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100443",
"journal-title": "Inform. Med. Unlocked",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01091-0",
"article-title": "Innate immunity: The first line of defense against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Diamond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13199",
"article-title": "Insights into disparities observed with COVID-19",
"author": "Carethers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.20105114",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are primarily expressed in bronchial transient secretory cells",
"author": "Lukassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e105114",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes",
"author": "Sungnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3862",
"article-title": "Clinical Course and Molecular Viral Shedding Among Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Community Treatment Center in the Republic of Korea",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1447",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/5460400",
"article-title": "Viral RNA Load in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic COVID-19 Omicron Variant-Positive Patients",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5460400",
"journal-title": "Can. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30172-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cevik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20210583",
"article-title": "Dynamic innate immune response determines susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and early replication kinetics",
"author": "Cheemarla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20210583",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-021-01037-9",
"article-title": "Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children",
"author": "Loske",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "Nat. Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02415-20",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 triggers an MDA-5-dependent interferon response which is unable to control replication in lung epithelial cells",
"author": "Rebendenne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20202486",
"article-title": "Auto-antibodies to type I IFNs can underlie adverse reactions to yellow fever live attenuated vaccine",
"author": "Bastard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20202486",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coi.2022.01.003",
"article-title": "Type I interferons and SARS-CoV-2: From cells to organisms",
"author": "Bastard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108628",
"article-title": "MDA5 Governs the Innate Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Lung Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108628",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03475-6",
"article-title": "The spatial landscape of lung pathology during COVID-19 progression",
"author": "Rendeiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "593",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI68782",
"article-title": "Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung",
"author": "Barkauskas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3025",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.125.1.203",
"article-title": "Polymorphism in the surfactant protein-B gene, gender, and the risk of direct pulmonary injury and ARDS",
"author": "Gong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.03.021",
"article-title": "Current perspectives in pulmonary surfactant—Inhibition, enhancement and evaluation",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1947",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "1778",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12930",
"article-title": "Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer",
"author": "Desai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "507",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.200810-1615OC",
"article-title": "Targeted injury of type II alveolar epithelial cells induces pulmonary fibrosis",
"author": "Sisson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "254",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues",
"author": "Ziegler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1016",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110412",
"article-title": "Alveolar epithelial cell type II as main target of SARS-CoV-2 virus and COVID-19 development via NF-Kb pathway deregulation: A physio-pathological theory",
"author": "Carcaterra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110412",
"journal-title": "Med. Hypotheses",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/thg.2020.85",
"article-title": "Self-Reported Symptoms of COVID-19, Including Symptoms Most Predictive of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Are Heritable",
"author": "Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "316",
"journal-title": "Twin Res. Hum. Genet.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2023.105426",
"article-title": "Genetic susceptibility to severe COVID-19",
"author": "Cappadona",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105426",
"journal-title": "Infect. Genet. Evol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2020283",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Severe COVID-19 GWAS Group, Ellinghaus, D., Degenhardt, F., Bujanda, L., Buti, M., Albillos, A., Invernizzi, P., Fernandez, J., Prati, D., and Baselli, G. (2020). Genomewide Association Study of Severe COVID-19 with Respiratory Failure. N. Engl. J. Med., 383, 1522–1534."
},
{
"DOI": "10.14440/jbm.2020.296",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Kumar, S., Curran, J.E., Espinosa, E.C., Glahn, D.C., and Blangero, J. (2020). Highly efficient induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming of cryopreserved lymphoblastoid cell lines. J. Biol. Methods, 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2016/2349261",
"article-title": "Utility of Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Generation",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2349261",
"journal-title": "Stem Cells Int.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.07.005",
"article-title": "Generation of alveolar epithelial spheroids via isolated progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells",
"author": "Gotoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "394",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2017.08.014",
"article-title": "Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Functional Lung Alveolar Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Jacob",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "472",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41596-019-0220-0",
"article-title": "Derivation of self-renewing lung alveolar epithelial type II cells from human pluripotent stem cells",
"author": "Jacob",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3303",
"journal-title": "Nat. Protoc.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.02.972935",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Harcourt, J., Tamin, A., Lu, X., Kamili, S., Sakthivel, S.K., Murray, J., Queen, K., Tao, Y., Paden, C.R., and Zhang, J. (2020). Isolation and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 from the first US COVID-19 patient. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2608.201246",
"article-title": "US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1654",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-14-128",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Chen, E.Y., Tan, C.M., Kou, Y., Duan, Q., Wang, Z., Meirelles, G.V., Clark, N.R., and Ma’Ayan, A. (2013). Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btz931",
"article-title": "ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants",
"author": "Ge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2628",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btt703",
"article-title": "Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis",
"author": "Green",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "523",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-86002-x",
"article-title": "Comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of COVID-19 blood, lung, and airway",
"author": "Daamen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7052",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.05.079095",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Han, Y., Yang, L., Duan, X., Duan, F., Nilsson-Payant, B.E., Yaron, T.M., Wang, P., Tang, X., Zhang, T., and Zhao, Z. (2020). Identification of Candidate COVID-19 Therapeutics using hPSC-derived Lung Organoids. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.10.005",
"article-title": "Human Lung Stem Cell-Based Alveolospheres Provide Insights into SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Interferon Responses and Pneumocyte Dysfunction",
"author": "Katsura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "890",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31305-2",
"article-title": "Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington State: A case series",
"author": "Bradley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Reverse Genetics Reveals a Variable Infection Gradient in the Respiratory Tract",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "429",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41379-020-0595-z",
"article-title": "In situ detection of SARS-CoV-2 in lungs and airways of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Schaefer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2104",
"journal-title": "Mod. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.03.132639",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Abo, K.M., Ma, L., Matte, T., Huang, J., Alysandratos, K.D., Werder, R.B., Mithal, A., Beermann, M.L., Lindstrom-Vautrin, J., and Mostoslavsky, G. (2020). Human iPSC-derived alveolar and airway epithelial cells can be cultured at air-liquid interface and express SARS-CoV-2 host factors. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2019.12.009",
"article-title": "Reconstructed Single-Cell Fate Trajectories Define Lineage Plasticity Windows during Differentiation of Human PSC-Derived Distal Lung Progenitors",
"author": "Hurley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1002085",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Nishino, K., Toyoda, M., Yamazaki-Inoue, M., Fukawatase, Y., Chikazawa, E., Sakaguchi, H., Akutsu, H., and Umezawa, A. (2011). DNA methylation dynamics in human induced pluripotent stem cells over time. PLoS Genet., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1004432",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Rouhani, F., Kumasaka, N., de Brito, M.C., Bradley, A., Vallier, L., and Gaffney, D. (2014). Genetic background drives transcriptional variation in human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS Genet., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2018.00004",
"article-title": "Age Is Relative—Impact of Donor Age on Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cell Functionality",
"author": "Kiamehr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Front. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.013",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Lung Alveolar Type 2 Cells Elicits a Rapid Epithelial-Intrinsic Inflammatory Response",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "962",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06422-9",
"article-title": "Dissecting human population variation in single-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Aquino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "621",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01881-2021",
"article-title": "Profiling of lung SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection dissects virus-specific host responses and gene signatures",
"author": "Kulasinghe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2101881",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-023-01510-8",
"article-title": "Metabolic alterations upon SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential therapeutic targets against coronavirus infection",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.791267",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Infection and Cholesterol Metabolism",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "791267",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-020-00324-0",
"article-title": "HDL-scavenger receptor B type 1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1391",
"journal-title": "Nat. Metab.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.030",
"article-title": "Identification of Required Host Factors for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Cells",
"author": "Daniloski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004",
"article-title": "Genetic Screens Identify Host Factors for SARS-CoV-2 and Common Cold Coronaviruses",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00600-21",
"article-title": "Viral and Host Transcriptomes in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Human Lung Cells",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0060021",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-023-02555-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19 induces more pronounced extracellular matrix deposition than other causes of ARDS",
"author": "Costa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Respir. Res.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.73",
"article-title": "Role of the extracellular matrix in COVID-19",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "World J. Clin. Cases",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112970",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Dias, I.R.d.S.R., Cao, Z., and Kwok, H.F. (2022). Adamalysins in COVID-19—Potential mechanisms behind exacerbating the disease. Biomed. Pharmacother., 150."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.821730",
"article-title": "Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Associated with Higher Levels of Serum IL-17C, Matrix Metalloproteinase 10 and Fibroblast Growth Factors Than Mild Symptomatic COVID-19",
"author": "Sauerwald",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "821730",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.09.004",
"article-title": "Discovery and Development of TMPRSS6 Inhibitors Modulating Hepcidin Levels in Human Hepatocytes",
"author": "Tarkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1559",
"journal-title": "Cell Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1401038",
"article-title": "Iron-deficiency anemia",
"author": "Camaschella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1832",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1157121",
"article-title": "The serine protease TMPRSS6 is required to sense iron deficiency",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "320",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13062-020-00275-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Ehsani, S. (2020). COVID-19 and iron dysregulation: Distant sequence similarity between hepcidin and the novel coronavirus spike glycoprotein. Biol. Direct, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00412.2005",
"article-title": "Iron imports. IV. Hepcidin and regulation of body iron metabolism",
"author": "Ganz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "G199",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12885-016-2305-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_65",
"unstructured": "Noguchi-Sasaki, M., Sasaki, Y., Shimonaka, Y., Mori, K., and Fujimoto-Ouchi, K. (2016). Treatment with anti-IL-6 receptor antibody prevented increase in serum hepcidin levels and improved anemia in mice inoculated with IL-6–producing lung carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.26508/lsa.202201880",
"article-title": "ACE2-EGFR-MAPK signaling contributes to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Engler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e202201880",
"journal-title": "Life Sci. Alliance",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 66,
"references-count": 66,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/5/369"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Pre-Infection Innate Immunity Attenuates SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Viral Load in iPSC-Derived Alveolar Epithelial Type 2 Cells",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}