Correct Use of HCQ Did Not Cause Extra Fatalities in COVID-19 Infection
Alberto Boretti, Bimal Banik
Coronaviruses, doi:10.2174/0126667975327612240902104505
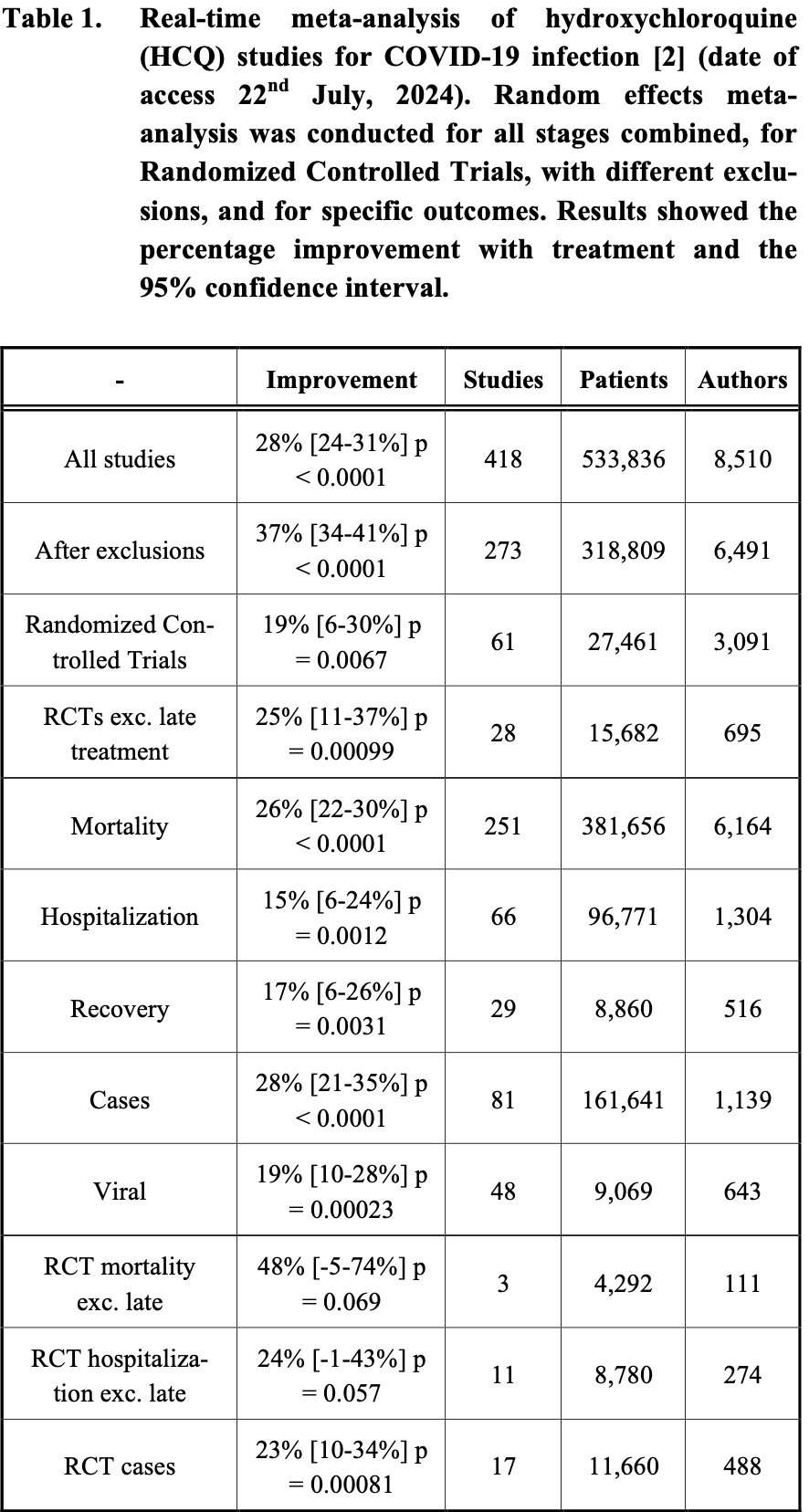
A recent study has claimed that nearly 17,000 people in the U.S. and five other countries died prematurely during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic due to the compassionate use of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) for treatment. However, this study's conclusions are contentious due to reliance on flawed data and the neglect of significant evidence supporting HCQ's efficacy in early outpatient treatment. Our critique challenges the validity of the study, highlighting its methodological weaknesses and the confounding factors it overlooked. By reviewing the comprehensive body of scientific literature, we demonstrate that treatment with HCQ, particularly in combination with zinc and antibiotics, consistently yielded positive outcomes, especially in the early stages. This work aims to provide a balanced and objective assessment of HCQ's impact on COVID-19, emphasizing the importance of early intervention and proper dosage.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
References
Agusti, Guillen, Ayora, Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine in healthcare professionals with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection: Prospective, non-randomized trial, Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin
Amaravadi, Giles, Carberry, Hydroxychloroquine for SARS-CoV-2 positive patients quarantined at home: The first interim analysis of a remotely conducted randomized clinical trial, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.02.22.21252228Ashraf, Shokouhi, Shirali, COVID-19 in Iran, a comprehensive investigation from exposure to treatment outcomes, MedRxiv
Atipornwanich, Kongsaengdao, Harnsomburana, darunavirritonavir, high-dose oseltamivir, and hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial (FIGHT-COVID-19 study)
Avezum, Oliveira, Oliveira, Hydroxychloroquine versus placebo in the treatment of non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19 (COPE-Coalition V): A double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial, The Lancet Reg Health-Americas
Azhar, Akram, Latif, Effectiveness of early pharmaceutical interventions in symptomatic COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial, Pak J Med Sci,
doi:10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757Bernabeu-Wittel, Vega, Nieto-Martín, Effectiveness of an on-site medicalization program for nursing homes with COVID-19 outbreaks, J Gerontol A
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, Mccoy, Early COVID-19 therapy with azithromycin plus nitazoxanide, ivermectin or hydroxychloroquine in outpatient settings significantly improved COVID-19 outcomes compared to known outcomes in untreated patients, New Microbes New Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100915Chechter, Da Silva, Costa, Evaluation of patients treated by telemedicine in the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in São Paulo, Brazil: A non-randomized clinical trial preliminary study, Heliyon,
doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15337PMID:37073324Corradini, Ventura, Ageno, Clinical factors associated with death in 3044 COVID-19 patients managed in internal medicine wards in Italy: Results from the SIMI-COVID-19 study of the Italian Society of Internal Medicine (SIMI), Intern Emerg Med,
doi:10.1007/s11739-021-02742-8PMID:33893976Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients: Early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low-dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective case series study, Int J Antimicrob Agents,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106214Esper, Da Silva, Oikawa, Empirical treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin for suspected cases of COVID-19 followed-up by telemedicine
Fonseca, De, Sousa, Wolkoff, Risk of hospitalization for Covid-19 outpatients treated with various drug regimens in Brazil: Comparative analysis, Travel Med Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101906Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949Guisado-Vasco, Valderas-Ortega, Clinical characteristics and outcomes among hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19 admitted to a tertiary medical center and receiving antiviral, antimalarials, glucocorticoids, or immunomodulation with tocilizumab or cyclosporine: A retrospective observational study (COQUIMA cohort), EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100591Guérin, Lévy, Thomas, Azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine accelerate recovery of outpatients with mild/moderate COVID-19
Hong, Jang, Hur, Early hydroxychloroquine administration for rapid severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 eradication, Infect Chemother,
doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.3.396Huang, Li, Xiao, Preliminary evidence from a multicenter prospective observational study of the safety and efficacy of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19, Natl Sci Rev,
doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa113PMID:34676087Ly, Zanini, Laforge, Pattern of SARS-CoV-2 infection among dependant elderly residents living in long-term care facilities in Marseille, France, March-June 2020, Int J Antimicrob Agents,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106219Million, Lagier, Tissot-Dupont, Early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in 10,429 COVID-19 outpatients: A monocentric retrospective cohort study, Rev Cardiovasc Med,
doi:10.31083/j.rcm2203116PMID:34565108Mitjà, Corbacho-Monné, Ubals, Tebe, Peñafiel et al., Hydroxychloroquine for early treatment of adults with mild Covid-19: A randomized-controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1009PMID:32674126Mokhtari, Mohraz, Gouya, Clinical outcomes of patients with mild COVID-19 following treatment with hydroxychloroquine in an outpatient setting, Int Immunopharmacol,
doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107636Omrani, Pathan, Thomas, Randomized doubleblinded placebo-controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin for virologic cure of non-severe Covid-19, EClinicalMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100645Pradelle, Mainbourg, Provencher, Massy, Grenet et al., Deaths induced by compassionate use of hydroxychloroquine during the first COVID-19 wave: An estimate, Biomed Pharmacother,
doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116055Rathod, Kargirwar, Patel, Kumar, Shalia et al., Risk factors associated with covid-19 patients in India: A single center retrospective cohort study, J Assoc Physicians India
Rodrigues, Freitas-Santos, Levi, Hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin early treatment of mild COVID-19 in an outpatient setting: A randomized, double-blinded, placebocontrolled clinical trial evaluating viral clearance, Int J Antimicrob Agents,
doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2021.106428Rouamba, Ouédraogo, Barry, Assessment of recovery time, worsening, and death among inpatients and outpatients with COVID-19, treated with hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine plus azithromycin combination in Burkina Faso, Int J Infect Dis,
doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.02.034Roy, Samajdar, Tripathi, Mukherjee, Bhattacharjee, Outcome of different therapeutic interventions in mild covid-19 patients in a single opd clinic of West Bengal: A retrospective study, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2021.03.08.21252883Roy-García, Moreno-Noguez, Rivas-Ruiz, Efficacy and safety of fixed combination of hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin versus hydroxychloroquine and placebo in patients with mild covid-19: Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2022.04.06.22273531Sawanpanyalert, Sirijatuphat, Sangsayunh, Assessement of outcomes following implementation of antiviral treatment guidelines for COVID-19 during the first wave in Thailand, Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health
Simova, Vekov, Krasnaliev, Kornovski, Bozhinov, Hydroxychloroquine for prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19 in health-care workers, New Microbes New Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100813Sobngwi, Zemsi, Guewo, Doxycycline vs hydroxychloroquine + azithromycin in the management of covid-19 patients: An open-label randomized clinical trial in Sub-Saharan Africa (DOXYCOV), Cureus,
doi:10.7759/cureus.45619PMID:37868535Su, Ling, Ma, Efficacy of early hydroxychloroquine treatment in preventing COVID-19 pneumonia aggravation, the experience from Shanghai, China, Biosci Trends,
doi:10.5582/bst.2020.03340PMID:33342929Sulaiman, Mohana, Alawdah, The effect of early hydroxychloroquine-based therapy in COVID-19 patients in ambulatory care settings: A nationwide prospective cohort study, MedRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.09.09.20184143DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0126667975327612240902104505",
"ISSN": [
"2666-7967"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/0126667975327612240902104505",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n<jats:title>Abstract:</jats:title>\n<jats:p>A recent study has claimed that nearly 17,000 people in the U.S. and five other countries\ndied prematurely during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic due to the compassionate use of\nhydroxychloroquine (HCQ) for treatment. However, this study's conclusions are contentious due to\nreliance on flawed data and the neglect of significant evidence supporting HCQ's efficacy in early\noutpatient treatment. Our critique challenges the validity of the study, highlighting its methodological\nweaknesses and the confounding factors it overlooked. By reviewing the comprehensive body of\nscientific literature, we demonstrate that treatment with HCQ, particularly in combination with zinc\nand antibiotics, consistently yielded positive outcomes, especially in the early stages. This work aims\nto provide a balanced and objective assessment of HCQ's impact on COVID-19, emphasizing the\nimportance of early intervention and proper dosage.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"LiveAll1"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Independent Scientist, Wellington, New Zealand"
}
],
"family": "Boretti",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, College of Sciences and Human Studies, Deanship of Research, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Al Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia"
}
],
"family": "Banik",
"given": "Bimal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Coronaviruses",
"container-title-short": "COVID",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-24T04:17:19Z",
"timestamp": 1727151439000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-24T04:17:39Z",
"timestamp": 1727151459000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-25T04:11:07Z",
"timestamp": 1727237467904
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.2174",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Bentham Science Publishers Ltd.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.eurekaselect.com/233910/article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Correct Use of HCQ Did Not Cause Extra Fatalities in COVID-19 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "05"
}