SARS-CoV-2 Syncytium under the Radar: Molecular Insights of the Spike-Induced Syncytia and Potential Strategies to Limit SARS-CoV-2 Replication
Hashim Ali, Asma Naseem, Zaheenul Islam Siddiqui
Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12186079
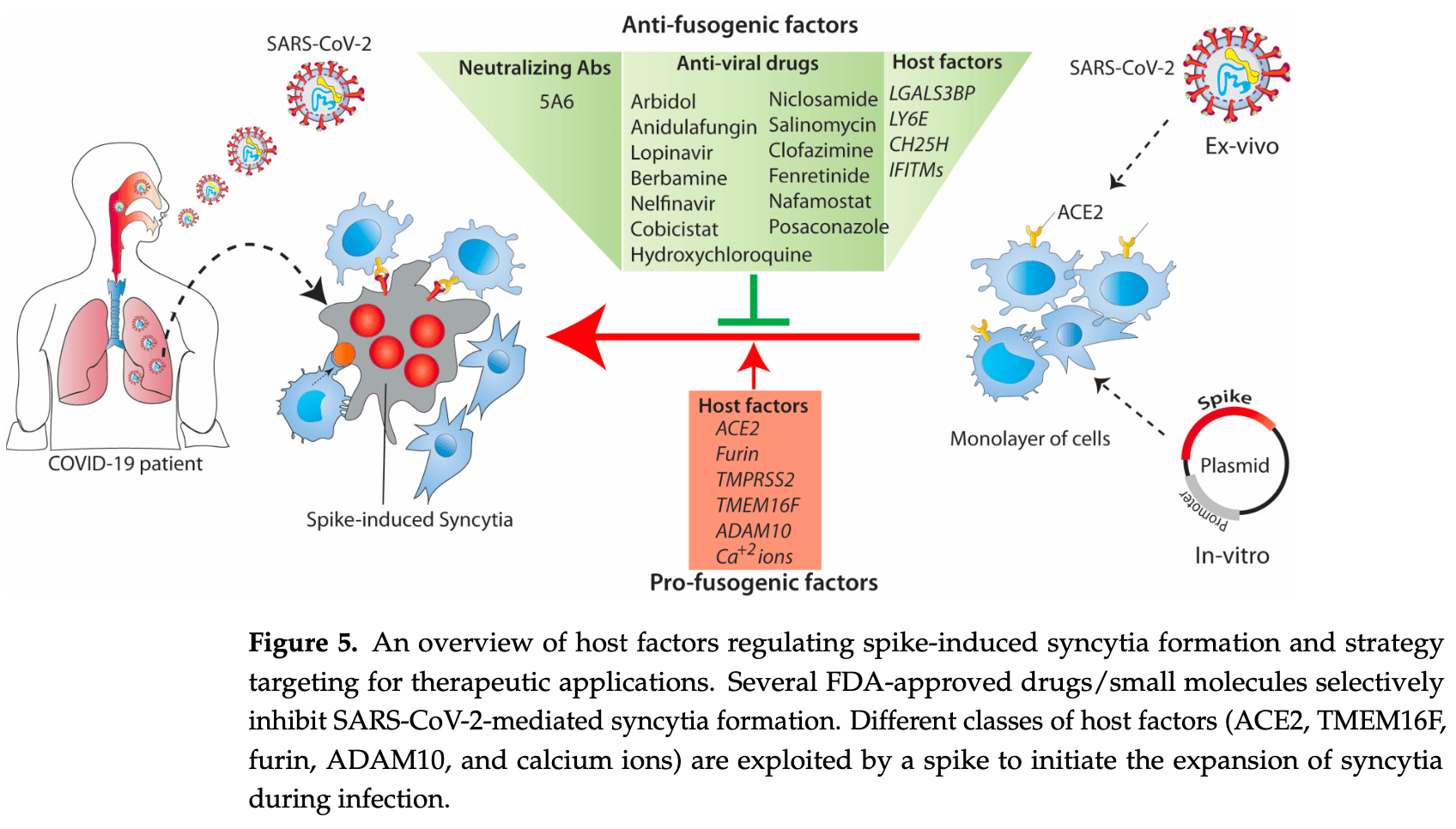
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces non-physiological syncytia when its spike fusogenic protein on the surface of the host cells interacts with the ACE2 receptor on adjacent cells. Spike-induced syncytia are beneficial for virus replication, transmission, and immune evasion, and contribute to the progression of COVID-19. In this review, we highlight the properties of viral fusion proteins, mainly the SARS-CoV-2 spike, and the involvement of the host factors in the fusion process. We also highlight the possible use of anti-fusogenic factors as an antiviral for the development of therapeutics against newly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and how the fusogenic property of the spike could be exploited for biomedical applications.
Author Contributions: H.A.: writing-original draft preparation, and illustration of images; A.N. and Z.I.S.: review and manuscript editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Funding: This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019, SARS-CoV: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, MERS-CoV: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, DPP4: transmembrane dipeptidyl peptidase 4, HA: hemagglutinin, gp41: glycoprotein 41, HIV-1: human immunodeficiency virus 1, VSVG: vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein, gB: glycoprotein B, FAST: fusion-associated small transmembrane, TM: transmembrane, ER: endoplasmic reticulum, RBD: receptor-binding domain, FP: fusion peptide, 6-HB: 6-helical bundle, HR heptapeptide repeat, VOCs: variants of concern, WHO: world health organisation, COPI: coatomer complex I, TMPRSS2: Transmembrane Serine Protease 2, ADAM: disintegrin and metalloprotease, SADS-CoV: swine acute diarrhoea syndrome coronavirus, IFITMs: Interferon-induced transmembrane proteins, ZMPSTE24: Zinc metallopeptidase STE24, CH25H: Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase, MHV-68: Murine gammaherpesvirus-68, LY6E: Lymphocyte antigen 6E, Gal-3BP: Galectin-3binding protein, SERCA: sarcoendoplamic reticulum Ca 2+ ATPase, HCQ: hydroxychloroquine, CYP3As: cytochrome P450-3As, CHIKV: Chikungunya virus,..
References
Abrams, Johnson, Perelman, Zhang, Endapally et al., Oxysterols provide innate immunity to bacterial infection by mobilizing cell surface accessible cholesterol, Nat. Microbiol,
doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0701-5Ahamad, Ali, Secco, Giacca, Gupta, Anti-Fungal Drug Anidulafungin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Induced Syncytia Formation by Targeting ACE2-Spike Protein Interaction, Front. Genet,
doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.866474Ali, Braga, Giacca, Cardiac regeneration and remodelling of the cardiomyocyte cytoarchitecture, FEBS J,
doi:10.1111/febs.15146Amini-Bavil-Olyaee, Choi, Lee, Shi, Huang et al., The antiviral effector IFITM3 disrupts intracellular cholesterol homeostasis to block viral entry, Cell Host Microbe,
doi:10.1016/j.chom.2013.03.006Appay, Sauce, Immune activation and inflammation in HIV-1 infection: Causes and consequences, J. Pathol,
doi:10.1002/path.2276Artini, Natoli, Tinari, Costanzo, Marinelli et al., Elevated serum levels of 90K/MAC-2 BP predict unresponsiveness to alpha-interferon therapy in chronic HCV hepatitis patients, J. Hepatol,
doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(96)80076-6Asarnow, Wang, Lee, Hu, Huang et al., Structural insight into SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and modulation of syncytia, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.033Avraham, Melamed, Achdout, Erez, Israeli et al., Antiviral activity of glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors in alphavirus infection of the central nervous system, Brain Commun,
doi:10.1093/braincomms/fcad086Azab, Gramatica, Herrmann, Osterrieder, Binding of alphaherpesvirus glycoprotein H to surface alpha4beta1integrins activates calcium-signaling pathways and induces phosphatidylserine exposure on the plasma membrane, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mBio.01552-15Benton, Wrobel, Xu, Roustan, Martin et al., Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2772-0Bertram, Dijkman, Habjan, Heurich, Gierer et al., TMPRSS2 activates the human coronavirus 229E for cathepsin-independent host cell entry and is expressed in viral target cells in the respiratory epithelium, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.03372-12Boehm, Kronig, Neher, Eckerle, Vetter et al., Geneva Centre for Emerging Viral Diseases. Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: The pandemics within the pandemic, Clin. Microbiol. Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022Bolze, Mommert, Mallet, Contribution of Syncytins and Other Endogenous Retroviral Envelopes to Human Placenta Pathologies, Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci,
doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.005Boson, Legros, Zhou, Siret, Mathieu et al., The SARS-CoV-2 envelope and membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the spike protein, allowing assembly of virus-like particles, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.RA120.016175Braga, Ali, Secco, Chiavacci, Neves et al., Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6Braun, Sauter, Furin-mediated protein processing in infectious diseases and cancer, Clin. Transl. Immunol,
doi:10.1002/cti2.1073Bullough, Hughson, Skehel, Wiley, Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion, Nature,
doi:10.1038/371037a0Bussani, Schneider, Zentilin, Collesi, Ali et al., Persistence of viral RNA, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology, EBioMedicine,
doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103104Calabrese, Sures, Pompetti, Natoli, Palka et al., The gene (LGALS3BP) encoding the serum protein 90K, associated with cancer and infection by the human immunodeficiency virus, maps at 17q25, Cytogenet. Cell Genet,
doi:10.1159/000133969Callahan, Popernack, Tsutsui, Truong, Schlegel et al., Phosphatidylserine on HIV envelope is a cofactor for infection of monocytic cells, J. Immunol,
doi:10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4840Cappelletto, Allan, Crescente, Schneider, Bussani et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein activates TMEM16F-mediated platelet procoagulant activity, Front. Cardiovasc. Med,
doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.1013262Casasampere, Ordonez, Pou, Casas, Inhibitors of dihydroceramide desaturase 1: Therapeutic agents and pharmacological tools to decipher the role of dihydroceramides in cell biology, Chem. Phys. Lipids,
doi:10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.07.025Cattin-Ortola, Welch, Maslen, Papa, James et al., Sequences in the cytoplasmic tail of SARS-CoV-2 Spike facilitate expression at the cell surface and syncytia formation, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25589-1Chan, Arthur, Morstein, Jin, Bhat et al., Evolutionarily related small viral fusogens hijack distinct but modular actin nucleation pathways to drive cell-cell fusion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.2007526118Chan, Son, Schmid, Fletcher, A viral fusogen hijacks the actin cytoskeleton to drive cell-cell fusion, Elife,
doi:10.7554/eLife.51358Chen, Skehel, Wiley, N-and C-terminal residues combine in the fusion-pH influenza hemagglutinin HA(2) subunit to form an N cap that terminates the triple-stranded coiled coil, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.96.16.8967Cheng, Chao, Li, Chiu, Kao et al., Furin Inhibitors Block SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Cleavage to Suppress Virus Production and Cytopathic Effects, Cell. Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108254Cheng, Chao, Li, Wang, Kao et al., D614G Substitution of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Increases Syncytium Formation and Virus Titer via Enhanced Furin-Mediated Spike Cleavage, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mBio.00587-21Clemens, Ye, Zhou, Kim, Pease et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cardiomyocyte fusion may contribute to increased arrhythmic risk in COVID-19, PLoS ONE,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282151Cohen, Melikyan, Implications of a fusion peptide structure, Nat. Struct. Biol,
doi:10.1038/90341Coutard, Valle, De Lamballerie, Canard, Seidah et al., The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade, Antiviral Res,
doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104742Cowley, Fuller, Rand, Parsegian, Measurement of repulsive forces between charged phospholipid bilayers, Biochemistry,
doi:10.1021/bi00608a034Das, Bulow, Diehl, Durham, Senjobe et al., Conformational changes in the Ebola virus membrane fusion machine induced by pH, Ca 2+ , and receptor binding, PLoS Biol,
doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000626Desai, Marin, Chin, Savidis, Brass et al., IFITM3 restricts influenza A virus entry by blocking the formation of fusion pores following virus-endosome hemifusion, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004048Dias, Soares, Ferreira, Sacramento, Fintelman-Rodrigues et al., Lipid droplets fuel SARS-CoV-2 replication and production of inflammatory mediators, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009127Dittmar, Lee, Whig, Segrist, Li et al., Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-CoV-2, Cell. Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959Drosten, Gunther, Preiser, Van Der Werf, Brodt et al., Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030747Dyall, Coleman, Hart, Venkataraman, Holbrook et al., Repurposing of clinically developed drugs for treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother,
doi:10.1128/AAC.03036-14Fenwick, Joo, Jacquier, Noto, Banga et al., T-cell exhaustion in HIV infection, Immunol. Rev,
doi:10.1111/imr.12823Filer, Bik, Parsonage, Fitton, Trebilcock et al., Galectin 3 induces a distinctive pattern of cytokine and chemokine production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via selective signaling pathways, Arthritis Rheum,
doi:10.1002/art.24574Frankel, Wenig, Burke, Mannan, Thompson et al., Replication of HIV-1 in dendritic cell-derived syncytia at the mucosal surface of the adenoid, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.272.5258.115Friedman, Manly, Mcmahon, Kerr, Stark, Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferoninduced gene expression in human cells, Cell,
doi:10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8Fu, Wang, Li, Dorf, ZMPSTE24 defends against influenza and other pathogenic viruses, J. Exp. Med,
doi:10.1084/jem.20161270Gall, Bobe, Reiss, Horiuchi, Niu et al., ADAMs 10 and 17 represent differentially regulated components of a general shedding machinery for membrane proteins such as transforming growth factor alpha, L-selectin, and tumor necrosis factor alpha, Mol. Biol. Cell,
doi:10.1091/mbc.e08-11-1135Gallo, Team, Gentile, Antonini, Iacobelli, Increased Gal-3BP plasma levels in hospitalized patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, Clin. Exp. Med,
doi:10.1007/s10238-021-00788-8Gauchotte, Venard, Segondy, Cadoz, Esposito-Fava et al., SARS-Cov-2 fulminant myocarditis: An autopsy and histopathological case study, Int. J. Legal Med,
doi:10.1007/s00414-020-02500-zGeyer, Arend, Doll, Louiset, Virreira Winter et al., High-resolution serum proteome trajectories in COVID-19 reveal patient-specific seroconversion, EMBO Mol. Med,
doi:10.15252/emmm.202114167Giansanti, Strating, Defourny, Cesonyte, Bottino et al., Dynamic remodelling of the human host cell proteome and phosphoproteome upon enterovirus infection, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18168-3Gopal, Padayatchi, Metcalfe, O'donnell, Systematic review of clofazimine for the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis, Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis,
doi:10.5588/ijtld.12.0144Gutmann, Takov, Burnap, Singh, Ali et al., SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia and proteomic trajectories inform prognostication in COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23494-1Hayashi, Nemoto-Sasaki, Tanikawa, Oka, Tsuchiya et al., Sphingomyelin synthase 2, but not sphingomyelin synthase 1, is involved in HIV-1 envelope-mediated membrane fusion, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.574285Hayashi, Tsuchiya, Yamamoto, Nemoto-Sasaki, Tanigawa et al., N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) Retinamide Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion by a Dihydroceramide Delta4-Desaturase 1-Independent Mechanism, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00807-21He, Zhang, Chen, Li, Increased LGALS3 expression independently predicts shorter overall survival in patients with the proneural subtype of glioblastoma, Cancer Med,
doi:10.1002/cam4.2075Helm, Israelachvili, Mcguiggan, Molecular mechanisms and forces involved in the adhesion and fusion of amphiphilic bilayers, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.2814514Hepojoki, Strandin, Hetzel, Sironen, Klingstrom et al., Acute hantavirus infection induces galectin-3-binding protein, J. Gen. Virol,
doi:10.1099/vir.0.066837-0Herschke, Plumet, Duhen, Azocar, Druelle et al., Cell-cell fusion induced by measles virus amplifies the type I interferon response, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00078-07Heurich, Hofmann-Winkler, Gierer, Liepold, Jahn et al., TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.02202-13Hickford, Frankenberg, Shaw, Renfree, Evolution of vertebrate interferon inducible transmembrane proteins, BMC Genom,
doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-155Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Pohlmann, A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells, Mol. Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052Houri, Huang, Nalbantoglu, The Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor (CAR) undergoes ectodomain shedding and regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP), PLoS ONE,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073296Huang, Bailey, Weyer, Radoshitzky, Becker et al., Distinct patterns of IFITM-mediated restriction of filoviruses, SARS coronavirus, and influenza A virus, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001258Huang, Incognito, Cheng, Ulbrandt, Wu, Respiratory syncytial virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies motavizumab and palivizumab inhibit fusion, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.02699-09Inohara, Akahani, Koths, Raz, Interactions between galectin-3 and Mac-2-binding protein mediate cell-cell adhesion, Cancer Res
Izaguirre, The Proteolytic Regulation of Virus Cell Entry by Furin and Other Proprotein Convertases, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v11090837Jana, Bhattacharya, Mayilsamy, Banerjee, Bhattacharje et al., Targeting an evolutionarily conserved "E-L-L" motif in the spike protein to develop a small molecule fusion inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2022.03.16.484554Jang, Shin, Yoon, Go, Lee et al., Salinomycin Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection by Disrupting Endosomal Acidification and Viral Matrix Protein 2 Function, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01441-18Jangamreddy, Ghavami, Grabarek, Kratz, Wiechec et al., Salinomycin induces activation of autophagy, mitophagy and affects mitochondrial polarity: Differences between primary and cancer cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta,
doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.04.011Jia, Liu, Tian, Xiong, Xu et al., Potent neutralizing RBD-specific antibody cocktail against SARS-CoV-2 and its mutant, MedComm,
doi:10.1002/mco2.79Jiang, Li, Qaed, Zhang, Song et al., Salinomycin, as an autophagy modulator--a new avenue to anticancer: A review, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res,
doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0680-zJocher, Grass, Tschirner, Riepler, Breimann et al., ADAM10 and ADAM17 promote SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and spike protein-mediated lung cell fusion, EMBO Rep,
doi:10.15252/embr.202154305Johnson, Gonzales, Olson, Wright, Graham, The histopathology of fatal untreated human respiratory syncytial virus infection, Mod. Pathol,
doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800725Johnson, Xie, Bailey, Kalveram, Lokugamage et al., Loss of furin cleavage site attenuates SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03237-4Kanai, Kawagishi, Sakai, Nouda, Shimojima et al., Cell-cell fusion induced by reovirus FAST proteins enhances replication and pathogenicity of non-enveloped dsRNA viruses, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1007675Karki, Sharma, Tuladhar, Williams, Zalduondo et al., Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025Kielian, Rey, Virus membrane-fusion proteins: More than one way to make a hairpin, Nat. Rev. Microbiol,
doi:10.1038/nrmicro1326Kim, Yoon, Park, Furin cleavage is required for swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus spike protein-mediated cell-cell fusion, Emerg. Microbes Infect,
doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2114850Ko, Chang, Byun, Ianevski, Choi et al., Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs Using a MERS-CoV Clinical Isolate from South Korea Identifies Potential Therapeutic Options for COVID-19, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v13040651Koch, Manzur, Shan, Structure-based models of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion: The evolution continues, Cell. Mol. Life Sci,
doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4006-2Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Yoon, Theiler et al., Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat. Med,
doi:10.1038/nm1267Kusnierz-Cabala, Maziarz, Dumnicka, Dembinski, Kapusta et al., Diagnostic Significance of Serum Galectin-3 in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19-A Preliminary Study, Biomolecules,
doi:10.3390/biom11081136Lai, Millet, Daniel, Freed, Whittaker, The SARS-CoV Fusion Peptide Forms an Extended Bipartite Fusion Platform that Perturbs Membrane Order in a Calcium-Dependent Manner, J. Mol. Biol,
doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2017.10.017Lambert, Yarski, Warner, Thornhill, Parkin et al., Tumor necrosis factoralpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.M505111200Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5Lau, Luk, Wong, Li, Zhu et al., Possible Bat Origin of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Emerg. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.3201/eid2607.200092Li, Fu, Wang, Dorf, ZMPSTE24 Is Downstream Effector of Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Antiviral Activity, DNA Cell. Biol,
doi:10.1089/dna.2017.3791Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature,
doi:10.1038/nature02145Li, Wu, Nie, Zhang, Hao et al., The Impact of Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Spike on Viral Infectivity and Antigenicity, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.012Lin, Li, Wang, Shi, Syncytia formation during SARS-CoV-2 lung infection: A disastrous unity to eliminate lymphocytes, Cell. Death Differ,
doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00795-yLiu, Liu, Chen, Lin, Huang et al., Serum Galectin-9 and Galectin-3-Binding Protein in Acute Dengue Virus Infection, Int. J. Mol. Sci,
doi:10.3390/ijms17060832Liu, Sanchez, Aliyari, Lu, Cheng, Systematic identification of type I and type II interferon-induced antiviral factors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.1114981109Liu, Wei, Xu, Zhao, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced cell fusion activates the cGAS-STING pathway and the interferon response, Sci. Signal,
doi:10.1126/scisignal.abg8744Liu, Xiao, Chen, He, Niu et al., Interaction between heptad repeat 1 and 2 regions in spike protein of SARS-associated coronavirus: Implications for virus fusogenic mechanism and identification of fusion inhibitors, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15788-7Lozada, Barlow, Gonzalez, Lubin-Germain, Ballet, Identification and Characteristics of Fusion Peptides Derived From Enveloped Viruses, Front. Chem,
doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.689006Lu, Hu, Wang, Qi, Gao et al., Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26, Nature,
doi:10.1038/nature12328Lu, Huang, Yang, Chang, Lee et al., siRNA silencing of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 reduced severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus replications in Vero E6 cells, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1007/s10096-008-0495-5Lu, Liu, Zhu, Chan, Qin et al., Structure-based discovery of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus fusion inhibitor, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/ncomms4067Ma, Buckalew, Du, Kiyoshi, Alford et al., Gap junction coupling confers isopotentiality on astrocyte syncytium, Glia,
doi:10.1002/glia.22924Madu, Roth, Belouzard, Whittaker, Characterization of a highly conserved domain within the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein S2 domain with characteristics of a viral fusion peptide, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00079-09Mannar, Saville, Zhu, Srivastava, Berezuk et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein-ACE2 complex, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abn7760Martinez, Compounds with Therapeutic Potential against Novel Respiratory 2019 Coronavirus, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother,
doi:10.1128/AAC.00399-20Mcbride, Li, Machamer, The cytoplasmic tail of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein contains a novel endoplasmic reticulum retrieval signal that binds COPI and promotes interaction with membrane protein, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.02146-06Mcnamara, Smyth, The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus disease in childhood, Br. Med. Bull,
doi:10.1093/bmb/61.1.13Messner, Demichev, Wendisch, Michalick, White et al., Ultra-High-Throughput Clinical Proteomics Reveals Classifiers of COVID-19 Infection, Cell. Syst,
doi:10.1016/j.cels.2020.05.012Moss, Sklair-Tavron, Nudelman, Drug insight: Tumor necrosis factor-converting enzyme as a pharmaceutical target for rheumatoid arthritis, Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol,
doi:10.1038/ncprheum0797Mudhasani, Tran, Retterer, Radoshitzky, Kota et al., IFITM-2 and IFITM-3 but not IFITM-1 restrict Rift Valley fever virus, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.03382-12Musarrat, Chouljenko, Dahal, Nabi, Chouljenko et al., The anti-HIV drug nelfinavir mesylate (Viracept) is a potent inhibitor of cell fusion caused by the SARSCoV-2 spike (S) glycoprotein warranting further evaluation as an antiviral against COVID-19 infections, J. Med. Virol,
doi:10.1002/jmv.25985Nanbo, Maruyama, Imai, Ujie, Fujioka et al., Ebola virus requires a host scramblase for externalization of phosphatidylserine on the surface of viral particles, PLoS Pathog,
doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006848Nathan, Lai, Millet, Straus, Freed et al., Calcium Ions Directly Interact with the Ebola Virus Fusion Peptide To Promote Structure-Function Changes That Enhance Infection, ACS Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00296Natoli, Iacobelli, Ghinelli, Unusually high level of a tumor-associated antigen in the serum of human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals, J. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1093/infdis/164.3.616Navaratnarajah, Pease, Halfmann, Taye, Barkhymer et al., Highly Efficient SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Cardiomyocytes: Spike Protein-Mediated Cell Fusion and Its Inhibition, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01368-21Nishimura, Shimojima, Tano, Miyamura, Wakita et al., Human P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 is a functional receptor for enterovirus 71, Nat. Med,
doi:10.1038/nm.1961Osorio, Sfera, Anton, Thomas, Andronescu et al., Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion in Neurodegenerative Disorders, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol,
doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.845580Ostergaard, Nielsen, Iversen, Tanassi, Knudsen et al., Unique protein signature of circulating microparticles in systemic lupus erythematosus, Arthritis Rheum,
doi:10.1002/art.38065Peacock, Goldhill, Zhou, Baillon, Frise et al., The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets, Nat. Microbiol,
doi:10.1038/s41564-021-00908-wPfaender, Mar, Michailidis, Kratzel, Boys et al., LY6E impairs coronavirus fusion and confers immune control of viral disease, Nat. Microbiol,
doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0769-yPlanas, Veyer, Baidaliuk, Staropoli, Guivel-Benhassine et al., Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9Rajah, Hubert, Bishop, Saunders, Robinot et al., SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Beta, and Delta variants display enhanced Spike-mediated syncytia formation, EMBO J,
doi:10.15252/embj.2021108944Rea, Palmieri, Tinari, Natoli, Tagliaferri et al., 90k is a serum marker of poor-prognosis in non-hodgkins-lymphoma patients, Oncol. Rep,
doi:10.3892/or.1.4.723Riva, Yuan, Yin, Martin-Sancho, Matsunaga et al., Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1Rocheleau, Laroche, Fu, Stewart, Mohamud et al., Identification of a High-Frequency Intrahost SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variant with Enhanced Cytopathic and Fusogenic Effects, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mBio.00788-21Rockx, Kuiken, Herfst, Bestebroer, Lamers et al., Comparative pathogenesis of COVID-19, MERS, and SARS in a nonhuman primate model, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abb7314Romi, Gokhman, Wong, Antonovsky, Ludwig et al., ADAM metalloproteases promote a developmental switch in responsiveness to the axonal repellant Sema3A, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/ncomms5058Saito, Irie, Suzuki, Maemura, Nasser et al., Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04266-9Sakurai, Kolokoltsov, Chen, Tidwell, Bauta et al., Two-pore channels control Ebola virus host cell entry and are drug targets for disease treatment, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.1258758Sanders, Jumper, Ackerman, Bracha, Donlic et al., SARS-CoV-2 requires cholesterol for viral entry and pathological syncytia formation, Elife,
doi:10.7554/eLife.65962Sasaki, Brakebusch, Engel, Timpl, Mac-2 binding protein is a cell-adhesive protein of the extracellular matrix which self-assembles into ring-like structures and binds beta1 integrins, collagens and fibronectin, EMBO J,
doi:10.1093/emboj/17.6.1606Saurav, Tanwar, Ahuja, Motiani, Dysregulation of host cell calcium signaling during viral infections: Emerging paradigm with high clinical relevance, Mol. Aspects Med,
doi:10.1016/j.mam.2021.101004Schjoldager, Vester-Christensen, Goth, Petersen, Brunak et al., A systematic study of site-specific GalNAc-type O-glycosylation modulating proprotein convertase processing, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.287912Schoggins, Wilson, Panis, Murphy, Jones et al., A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response, Nature,
doi:10.1038/nature09907Shi, Kenney, Kudryashova, Zani, Zhang et al., Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection, EMBO J,
doi:10.15252/embj.2020106501Shilagardi, Spear, Abraham, Griffin, Michaelis, The Integral Membrane Protein ZMPSTE24 Protects Cells from SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Pseudovirus Infection and Syncytia Formation, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mbio.02543-22Shmulevitz, Epand, Epand, Duncan, Structural and functional properties of an unusual internal fusion peptide in a nonenveloped virus membrane fusion protein, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.78.6.2808-2818.2004Shytaj, Fares, Gallucci, Lucic, Tolba et al., The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir To Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters, mBio,
doi:10.1128/mbio.03705-21Singh, Mukherji, Basak, Hoffmann, Das, Dynamic Ca(2+) sensitivity stimulates the evolved SARS-CoV-2 spike strain-mediated membrane fusion for enhanced entry, Cell. Rep,
doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110694Siripanthong, Nazarian, Muser, Deo, Santangeli et al., Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management, Heart Rhythm,
doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.001Starr, Czudnochowski, Liu, Zatta, Park et al., SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies that maximize breadth and resistance to escape, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03807-6Straus, Bidon, Tang, Jaimes, Whittaker et al., Inhibitors of L-Type Calcium Channels Show Therapeutic Potential for Treating SARS-CoV-2 Infections by Preventing Virus Entry and Spread, ACS Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00023Straus, Tang, Lai, Flegel, Bidon et al., Ca(2+) Ions Promote Fusion of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus with Host Cells and Increase Infectivity, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00426-20Suzuki, Yamasoba, Kimura, Wang, Kishimoto et al., Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1Sylwester, Murphy, Shutt, Soll, HIV-induced T cell syncytia are self-perpetuating and the primary cause of T cell death in culture, J. Immunol,
doi:10.4049/jimmunol.158.8.3996Taylor, Adams, Hufford, De La Torre, Winthrop et al., Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Immunol,
doi:10.1038/s41577-021-00542-xTheken, Tang, Sengupta, Fitzgerald, The roles of lipids in SARS-CoV-2 viral replication and the host immune response, J. Lipid Res,
doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100129Thomas, Furin at the cutting edge: From protein traffic to embryogenesis and disease, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol,
doi:10.1038/nrm934V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol,
doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6Valdebenito, Bessis, Annane, Lorin De La Grandmaison, Cramer-Borde et al., COVID-19 Lung Pathogenesis in SARS-CoV-2 Autopsy Cases, Front. Immunol,
doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.735922Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, Beckmann, Nirenberg et al., An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat. Med,
doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9Verdoodt, Vogt, Schmitz, Liffers, Tannapfel et al., Salinomycin induces autophagy in colon and breast cancer cells with concomitant generation of reactive oxygen species, PLoS ONE,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044132Vitner, Achdout, Avraham, Politi, Cherry et al., Glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors prevent replication of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus, J. Biol. Chem,
doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100470Wall, Wu, Harvey, Kelly, Warchal et al., Neutralising antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs B.1.617.2 and B.1.351 by BNT162b2 vaccination, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01290-3Wang, Li, Hui, Tiwari, Zhang et al., Cholesterol 25-Hydroxylase inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by depleting membrane cholesterol, EMBO J,
doi:10.15252/embj.2020106057Wang, Yuan, Zhang, Min, Zhou et al., Impact of cell fusion in myeloma marrow microenvironment on tumor progression, Oncotarget,
doi:10.18632/oncotarget.25742Watanabe, Sakuragi, Noji, Nagata, Single-molecule analysis of phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.1717956115Weston, Czieso, White, Smith, Kellam et al., A membrane topology model for human interferon inducible transmembrane protein 1, PLoS ONE,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104341Wrensch, Winkler, Pohlmann, IFITM proteins inhibit entry driven by the MERS-coronavirus spike protein: Evidence for cholesterol-independent mechanisms, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v6093683Xia, Liu, Wang, Xu, Lan et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion, Cell. Res,
doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0305-xXia, Yan, Xu, Agrawal, Algaissi et al., A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike, Sci. Adv,
doi:10.1126/sciadv.aav4580Xia, Zhu, Liu, Lan, Xu et al., Fusion mechanism of 2019-nCoV and fusion inhibitors targeting HR1 domain in spike protein, Cell. Mol. Immunol,
doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0374-2Xing, Xu, Xu, Liu, Shen et al., A Five-Helix-Based SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Inhibitor Targeting Heptad Repeat 2 Domain against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants of Concern, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v14030597Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir. Med,
doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-XXu, Wu, Zhang, Manifestations and Mechanism of SARS-CoV2 Mediated Cardiac Injury, Int. J. Biol. Sci,
doi:10.7150/ijbs.69677Yamada, Liu, Proteolytic activation of the spike protein at a novel RRRR/S motif is implicated in furin-dependent entry, syncytium formation, and infectivity of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus in cultured cells, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.00613-09Yamamoto, Kiso, Sakai-Tagawa, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Imai et al., The Anticoagulant Nafamostat Potently Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S Protein-Mediated Fusion in a Cell Fusion Assay System and Viral Infection In Vitro in a Cell-Type-Dependent Manner, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v12060629Yamamoto, Matsuyama, Li, Takeda, Kawaguchi et al., Identification of Nafamostat as a Potent Inhibitor of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus S Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion Using the Split-Protein-Based Cell-Cell Fusion Assay, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother,
doi:10.1128/AAC.01043-16Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science,
doi:10.1126/science.abb2762Yang, Kim, David, Palmer, Jin et al., TMEM16F forms a Ca2+-activated cation channel required for lipid scrambling in platelets during blood coagulation, Cell,
doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.036Yu, Deng, Zou, Wang, Dai et al., A peptide-based viral inactivator inhibits Zika virus infection in pregnant mice and fetuses, Nat. Commun,
doi:10.1038/ncomms15672Zaitseva, Zaitsev, Melikov, Arakelyan, Marin et al., Fusion Stage of HIV-1 Entry Depends on Virus-Induced Cell Surface Exposure of Phosphatidylserine, Cell Host Microbe,
doi:10.1016/j.chom.2017.06.012Zaki, Van Boheemen, Bestebroer, Osterhaus, Fouchier, Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1211721Zang, Case, Yutuc, Ma, Shen et al., Cholesterol 25hydroxylase suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking membrane fusion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.2012197117Zeng, Evans, King, Zheng, Oltz et al., SARS-CoV-2 spreads through cell-to-cell transmission, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.2111400119Zhang, Le, Grabau, Mohseni, Kim et al., TMEM16F phospholipid scramblase mediates trophoblast fusion and placental development, Sci. Adv,
doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba0310Zhang, Mann, Syed, Reynolds, Tian et al., Furin cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike is modulated by O-glycosylation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.2109905118Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Li et al., Berbamine hydrochloride potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking S protein-mediated membrane fusion, PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis,
doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0010363Zhang, Zheng, Niu, Zhang, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination, Cell. Death Differ,
doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3Zhao, Chen, Li, Chen, Sun, Multifaceted Functions of CH25H and 25HC to Modulate the Lipid Metabolism, Immune Responses, and Broadly Antiviral Activities, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v12070727Zhao, Guo, Liu, Cuconati, Chang et al., Interferon induction of IFITM proteins promotes infection by human coronavirus OC43, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci,
doi:10.1073/pnas.1320856111Zhao, Meng, Peng, Lam, Zhang et al., Fusion-inhibition peptide broadly inhibits influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, including Delta and Omicron variants, Emerg. Microbes Infect,
doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2051753Zhao, Sehgal, Hou, Cheng, Shu et al., Identification of Residues Controlling Restriction versus Enhancing Activities of IFITM Proteins on Entry of Human Coronaviruses, J. Virol,
doi:10.1128/JVI.01535-17Zhu, Yu, Hu, Wu, Chong et al., SARS-CoV-2-derived fusion inhibitor lipopeptides exhibit highly potent and broad-spectrum activity against divergent human coronaviruses, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther,
doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00698-xZhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12186079",
"ISSN": [
"2077-0383"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186079",
"abstract": "<jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 infection induces non-physiological syncytia when its spike fusogenic protein on the surface of the host cells interacts with the ACE2 receptor on adjacent cells. Spike-induced syncytia are beneficial for virus replication, transmission, and immune evasion, and contribute to the progression of COVID-19. In this review, we highlight the properties of viral fusion proteins, mainly the SARS-CoV-2 spike, and the involvement of the host factors in the fusion process. We also highlight the possible use of anti-fusogenic factors as an antiviral for the development of therapeutics against newly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and how the fusogenic property of the spike could be exploited for biomedical applications.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"jcm12186079"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5056-845X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, Addenbrookes Hospital, Cambridge CB2 0QQ, UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Hashim",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection, Immunity and Inflammation Research and Teaching Department, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London WC1N 1DZ, UK"
}
],
"family": "Naseem",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7767-0158",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Diabetes and Obesity Research Center, NYU Grossman Long Island School of Medicine, New York, NY 11501, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Siddiqui",
"given": "Zaheenul Islam",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Clinical Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JCM",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-21T02:38:45Z",
"timestamp": 1695263925000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-22T06:29:50Z",
"timestamp": 1703226590000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-19T17:08:31Z",
"timestamp": 1724087311497
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1695168000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/12/18/6079/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "6079",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201901017",
"article-title": "How cells fuse",
"author": "Brukman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1436",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/glia.22924",
"article-title": "Gap junction coupling confers isopotentiality on astrocyte syncytium",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "Glia",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.aba0310",
"article-title": "TMEM16F phospholipid scramblase mediates trophoblast fusion and placental development",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eaba0310",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.005",
"article-title": "Contribution of Syncytins and Other Endogenous Retroviral Envelopes to Human Placenta Pathologies",
"author": "Bolze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1262/jrd.2016-108",
"article-title": "Male infertility-related molecules involved in sperm-oocyte fusion",
"author": "Mou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Reprod. Dev.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13395-017-0149-3",
"article-title": "Myoblast fusion confusion: The resolution begins",
"author": "Sampath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Skelet. Muscle",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.25742",
"article-title": "Impact of cell fusion in myeloma marrow microenvironment on tumor progression",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30997",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.272.5258.115",
"article-title": "Replication of HIV-1 in dendritic cell-derived syncytia at the mucosal surface of the adenoid",
"author": "Frankel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "272",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/modpathol.3800725",
"article-title": "The histopathology of fatal untreated human respiratory syncytial virus infection",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Mod. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103104",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Bussani, R., Schneider, E., Zentilin, L., Collesi, C., Ali, H., Braga, L., Volpe, M.C., Colliva, A., Zanconati, F., and Berlot, G. (2020). Persistence of viral RNA, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology. EBioMedicine, 61."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6",
"article-title": "Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "594",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2022.1013262",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein activates TMEM16F-mediated platelet procoagulant activity",
"author": "Cappelletto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1013262",
"journal-title": "Front. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.65962",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 requires cholesterol for viral entry and pathological syncytia formation",
"author": "Sanders",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e65962",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-021-00782-3",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein dictates syncytium-mediated lymphocyte elimination",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2765",
"journal-title": "Cell. Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb7314",
"article-title": "Comparative pathogenesis of COVID-19, MERS, and SARS in a nonhuman primate model",
"author": "Rockx",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1012",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.2276",
"article-title": "Immune activation and inflammation in HIV-1 infection: Causes and consequences",
"author": "Appay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imr.12823",
"article-title": "T-cell exhaustion in HIV infection",
"author": "Fenwick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "292",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2111400119",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spreads through cell-to-cell transmission",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2111400119",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00078-07",
"article-title": "Cell-cell fusion induced by measles virus amplifies the type I interferon response",
"author": "Herschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12859",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scisignal.abg8744",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced cell fusion activates the cGAS-STING pathway and the interferon response",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabg8744",
"journal-title": "Sci. Signal.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00414-020-02500-z",
"article-title": "SARS-Cov-2 fulminant myocarditis: An autopsy and histopathological case study",
"author": "Gauchotte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Legal Med.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.001",
"article-title": "Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management",
"author": "Siripanthong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1463",
"journal-title": "Heart Rhythm.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.69677",
"article-title": "Manifestations and Mechanism of SARS-CoV2 Mediated Cardiac Injury",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2703",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01368-21",
"article-title": "Highly Efficient SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Cardiomyocytes: Spike Protein-Mediated Cell Fusion and Its Inhibition",
"author": "Navaratnarajah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0136821",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0282151",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Clemens, D.J., Ye, D., Zhou, W., Kim, C.S.J., Pease, D.R., Navaratnarajah, C.K., Barkhymer, A., Tester, D.J., Nelson, T.J., and Cattaneo, R. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated cardiomyocyte fusion may contribute to increased arrhythmic risk in COVID-19. PLoS ONE, 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15146",
"article-title": "Cardiac regeneration and remodelling of the cardiomyocyte cytoarchitecture",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "417",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa030747",
"article-title": "Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Drosten",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1967",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2607.200092",
"article-title": "Possible Bat Origin of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2",
"author": "Lau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1542",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1211721",
"article-title": "Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia",
"author": "Zaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1814",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12328",
"article-title": "Molecular basis of binding between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "500",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"article-title": "Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Kratzel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022",
"article-title": "A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12070693",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Barrett, C.T., and Dutch, R.E. (2020). Viral Membrane Fusion and the Transmembrane Domain. Viruses, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/90341",
"article-title": "Implications of a fusion peptide structure",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "653",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015523",
"article-title": "Fusogenic Reoviruses and Their Fusion-Associated Small Transmembrane (FAST) Proteins",
"author": "Duncan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Virol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fchem.2021.689006",
"article-title": "Identification and Characteristics of Fusion Peptides Derived From Enveloped Viruses",
"author": "Lozada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "689006",
"journal-title": "Front. Chem.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21249644",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Leroy, H., Han, M., Woottum, M., Bracq, L., Bouchet, J., Xie, M., and Benichou, S. (2020). Virus-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1326",
"article-title": "Virus membrane-fusion proteins: More than one way to make a hairpin",
"author": "Kielian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.043",
"article-title": "Viral membrane fusion",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "479–480",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122422",
"article-title": "Virus and cell fusion mechanisms",
"author": "Podbilewicz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sbi.2009.02.012",
"article-title": "Class III viral membrane fusion proteins",
"author": "Backovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/371037a0",
"article-title": "Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion",
"author": "Bullough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "371",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.96.16.8967",
"article-title": "N- and C-terminal residues combine in the fusion-pH influenza hemagglutinin HA(2) subunit to form an N cap that terminates the triple-stranded coiled coil",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8967",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "96",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1007675",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Kanai, Y., Kawagishi, T., Sakai, Y., Nouda, R., Shimojima, M., Saijo, M., Matsuura, Y., and Kobayashi, T. (2019). Cell-cell fusion induced by reovirus FAST proteins enhances replication and pathogenicity of non-enveloped dsRNA viruses. PLoS Pathog., 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2014.08.005",
"article-title": "Reovirus FAST proteins: Virus-encoded cellular fusogens",
"author": "Ciechonska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Salsman, J., Top, D., Barry, C., and Duncan, R. (2008). A virus-encoded cell-cell fusion machine dependent on surrogate adhesins. PLoS Pathog., 4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.78.6.2808-2818.2004",
"article-title": "Structural and functional properties of an unusual internal fusion peptide in a nonenveloped virus membrane fusion protein",
"author": "Shmulevitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2808",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.51358",
"article-title": "A viral fusogen hijacks the actin cytoskeleton to drive cell-cell fusion",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e51358",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi00608a034",
"article-title": "Measurement of repulsive forces between charged phospholipid bilayers",
"author": "Cowley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3163",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.2814514",
"article-title": "Molecular mechanisms and forces involved in the adhesion and fusion of amphiphilic bilayers",
"author": "Helm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "919",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "246",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2007526118",
"article-title": "Evolutionarily related small viral fusogens hijack distinct but modular actin nucleation pathways to drive cell-cell fusion",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2007526118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-004-4006-2",
"article-title": "Structure-based models of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion: The evolution continues",
"author": "Koch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1884",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03372-12",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 activates the human coronavirus 229E for cathepsin-independent host cell entry and is expressed in viral target cells in the respiratory epithelium",
"author": "Bertram",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6150",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.777",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of viral membrane fusion and its inhibition",
"author": "Eckert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nsmb.1456",
"article-title": "Viral membrane fusion",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "690",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25589-1",
"article-title": "Sequences in the cytoplasmic tail of SARS-CoV-2 Spike facilitate expression at the cell surface and syncytia formation",
"author": "Welch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5333",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.79",
"article-title": "Potent neutralizing RBD-specific antibody cocktail against SARS-CoV-2 and its mutant",
"author": "Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "MedComm",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03807-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies that maximize breadth and resistance to escape",
"author": "Starr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "597",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2772-0",
"article-title": "Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion",
"author": "Benton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "588",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00079-09",
"article-title": "Characterization of a highly conserved domain within the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein S2 domain with characteristics of a viral fusion peptide",
"author": "Madu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7411",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms15672",
"article-title": "A peptide-based viral inactivator inhibits Zika virus infection in pregnant mice and fetuses",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15672",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15788-7",
"article-title": "Interaction between heptad repeat 1 and 2 regions in spike protein of SARS-associated coronavirus: Implications for virus fusogenic mechanism and identification of fusion inhibitors",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "938",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "363",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.012",
"article-title": "The Impact of Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Spike on Viral Infectivity and Antigenicity",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1284",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.07.027",
"article-title": "Coronavirus RNA Proofreading: Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Targeting",
"author": "Robson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "710",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043",
"article-title": "Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus",
"author": "Korber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00587-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_72",
"unstructured": "Cheng, Y.W., Chao, T.L., Li, C.L., Wang, S.H., Kao, H.C., Tsai, Y.M., Wang, H.Y., Hsieh, C.L., Lin, Y.Y., and Chen, P.J. (2021). D614G Substitution of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Increases Syncytium Formation and Virus Titer via Enhanced Furin-Mediated Spike Cleavage. mBio, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03944-y",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion",
"author": "Mlcochova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "599",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021108944",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Beta, and Delta variants display enhanced Spike-mediated syncytia formation",
"author": "Rajah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e108944",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1",
"article-title": "Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant",
"author": "Suzuki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "700",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01397-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are emerging in India",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1131",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04266-9",
"article-title": "Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation",
"author": "Saito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"article-title": "Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization",
"author": "Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01290-3",
"article-title": "Neutralising antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs B.1.617.2 and B.1.351 by BNT162b2 vaccination",
"author": "Wall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2331",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022",
"article-title": "Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: The pandemics within the pandemic",
"author": "Boehm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.287912",
"article-title": "A systematic study of site-specific GalNAc-type O-glycosylation modulating proprotein convertase processing",
"author": "Schjoldager",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "40122",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2109905118",
"article-title": "Furin cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike is modulated by O-glycosylation",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2109905118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-00121-z",
"article-title": "Fast-spreading COVID variant can elude immune responses",
"author": "Callaway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "500",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "589",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abn7760",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein-ACE2 complex",
"author": "Mannar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "760",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02146-06",
"article-title": "The cytoplasmic tail of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein contains a novel endoplasmic reticulum retrieval signal that binds COPI and promotes interaction with membrane protein",
"author": "McBride",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2418",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA120.016175",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_86",
"unstructured": "Boson, B., Legros, V., Zhou, B., Siret, E., Mathieu, C., Cosset, F.L., Lavillette, D., and Denolly, S. (2021). The SARS-CoV-2 envelope and membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the spike protein, allowing assembly of virus-like particles. J. Biol. Chem., 296."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00788-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_87",
"unstructured": "Rocheleau, L., Laroche, G., Fu, K., Stewart, C.M., Mohamud, A.O., Cote, M., Giguere, P.M., Langlois, M.A., and Pelchat, M. (2021). Identification of a High-Frequency Intrahost SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variant with Enhanced Cytopathic and Fusogenic Effects. mBio, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"article-title": "A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-00908-w",
"article-title": "The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets",
"author": "Peacock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-008-0495-5",
"article-title": "siRNA silencing of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 reduced severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus replications in Vero E6 cells",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "709",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm934",
"article-title": "Furin at the cutting edge: From protein traffic to embryogenesis and disease",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol.",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cti2.1073",
"article-title": "Furin-mediated protein processing in infectious diseases and cancer",
"author": "Braun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1073",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11090837",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_95",
"unstructured": "Izaguirre, G. (2019). The Proteolytic Regulation of Virus Cell Entry by Furin and Other Proprotein Convertases. Viruses, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00613-09",
"article-title": "Proteolytic activation of the spike protein at a novel RRRR/S motif is implicated in furin-dependent entry, syncytium formation, and infectivity of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus in cultured cells",
"author": "Yamada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8744",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104742",
"article-title": "The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furin-like cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade",
"author": "Coutard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104742",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03237-4",
"article-title": "Loss of furin cleavage site attenuates SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2114850",
"article-title": "Furin cleavage is required for swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus spike protein-mediated cell-cell fusion",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2176",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108254",
"article-title": "Furin Inhibitors Block SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Cleavage to Suppress Virus Production and Cytopathic Effects",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108254",
"journal-title": "Cell. Rep.",
"key": "ref_100",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1004048",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_101",
"unstructured": "Desai, T.M., Marin, M., Chin, C.R., Savidis, G., Brass, A.L., and Melikyan, G.B. (2014). IFITM3 restricts influenza A virus entry by blocking the formation of fusion pores following virus-endosome hemifusion. PLoS Pathog., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001258",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_102",
"unstructured": "Huang, I.C., Bailey, C.C., Weyer, J.L., Radoshitzky, S.R., Becker, M.M., Chiang, J.J., Brass, A.L., Ahmed, A.A., Chi, X., and Dong, L. (2011). Distinct patterns of IFITM-mediated restriction of filoviruses, SARS coronavirus, and influenza A virus. PLoS Pathog., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8",
"article-title": "Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells",
"author": "Friedman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "745",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_103",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2164-13-155",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_104",
"unstructured": "Hickford, D., Frankenberg, S., Shaw, G., and Renfree, M.B. (2012). Evolution of vertebrate interferon inducible transmembrane proteins. BMC Genom., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03382-12",
"article-title": "IFITM-2 and IFITM-3 but not IFITM-1 restrict Rift Valley fever virus",
"author": "Mudhasani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8451",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0104341",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_106",
"unstructured": "Weston, S., Czieso, S., White, I.J., Smith, S.E., Kellam, P., and Marsh, M. (2014). A membrane topology model for human interferon inducible transmembrane protein 1. PLoS ONE, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v6093683",
"article-title": "IFITM proteins inhibit entry driven by the MERS-coronavirus spike protein: Evidence for cholesterol-independent mechanisms",
"author": "Wrensch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3683",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref_107",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1320856111",
"article-title": "Interferon induction of IFITM proteins promotes infection by human coronavirus OC43",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6756",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_108",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01535-17",
"article-title": "Identification of Residues Controlling Restriction versus Enhancing Activities of IFITM Proteins on Entry of Human Coronaviruses",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01535-17",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_109",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106501",
"article-title": "Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106501",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_110",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2013.03.006",
"article-title": "The antiviral effector IFITM3 disrupts intracellular cholesterol homeostasis to block viral entry",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_111",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-031413-085537",
"article-title": "IFITM-Family Proteins: The Cell’s First Line of Antiviral Defense",
"author": "Bailey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Virol.",
"key": "ref_112",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40588-018-0103-0",
"article-title": "Antiviral Protection by IFITM3 In Vivo",
"author": "Zani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_113",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106267",
"article-title": "Syncytia formation by SARS-CoV-2-infected cells",
"author": "Buchrieser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106267",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_114",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20161270",
"article-title": "ZMPSTE24 defends against influenza and other pathogenic viruses",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "919",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_115",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/dna.2017.3791",
"article-title": "ZMPSTE24 Is Downstream Effector of Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Antiviral Activity",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "DNA Cell. Biol.",
"key": "ref_116",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.02543-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_117",
"unstructured": "Shilagardi, K., Spear, E.D., Abraham, R., Griffin, D.E., and Michaelis, S. (2022). The Integral Membrane Protein ZMPSTE24 Protects Cells from SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Pseudovirus Infection and Syncytia Formation. mBio, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12060629",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_118",
"unstructured": "Yamamoto, M., Kiso, M., Sakai-Tagawa, Y., Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K., Imai, M., Takeda, M., Kinoshita, N., Ohmagari, N., Gohda, J., and Semba, K. (2020). The Anticoagulant Nafamostat Potently Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 S Protein-Mediated Fusion in a Cell Fusion Assay System and Viral Infection In Vitro in a Cell-Type-Dependent Manner. Viruses, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01043-16",
"article-title": "Identification of Nafamostat as a Potent Inhibitor of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus S Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion Using the Split-Protein-Based Cell-Cell Fusion Assay",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6532",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_119",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e08-11-1135",
"article-title": "ADAMs 10 and 17 represent differentially regulated components of a general shedding machinery for membrane proteins such as transforming growth factor alpha, L-selectin, and tumor necrosis factor alpha",
"author": "Bobe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1785",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell.",
"key": "ref_120",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02202-13",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein",
"author": "Heurich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1293",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_121",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M505111200",
"article-title": "Tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2)",
"author": "Lambert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30113",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_122",
"volume": "280",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms5058",
"article-title": "ADAM metalloproteases promote a developmental switch in responsiveness to the axonal repellant Sema3A",
"author": "Romi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4058",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_123",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0073296",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_124",
"unstructured": "Houri, N., Huang, K.C., and Nalbantoglu, J. (2013). The Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor (CAR) undergoes ectodomain shedding and regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP). PLoS ONE, 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.1961",
"article-title": "Human P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 is a functional receptor for enterovirus 71",
"author": "Nishimura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "794",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_125",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.202154305",
"article-title": "ADAM10 and ADAM17 promote SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and spike protein-mediated lung cell fusion",
"author": "Jocher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e54305",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep.",
"key": "ref_126",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"article-title": "An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1636",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_127",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025",
"article-title": "Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes",
"author": "Karki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_128",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncprheum0797",
"article-title": "Drug insight: Tumor necrosis factor-converting enzyme as a pharmaceutical target for rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Moss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_129",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138161209788682398",
"article-title": "ADAM17 as a therapeutic target in multiple diseases",
"author": "Arribas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2319",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Des.",
"key": "ref_130",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18168-3",
"article-title": "Dynamic remodelling of the human host cell proteome and phosphoproteome upon enterovirus infection",
"author": "Giansanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4332",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_131",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12070727",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_132",
"unstructured": "Zhao, J., Chen, J., Li, M., Chen, M., and Sun, C. (2020). Multifaceted Functions of CH25H and 25HC to Modulate the Lipid Metabolism, Immune Responses, and Broadly Antiviral Activities. Viruses, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0701-5",
"article-title": "Oxysterols provide innate immunity to bacterial infection by mobilizing cell surface accessible cholesterol",
"author": "Abrams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_133",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1114981109",
"article-title": "Systematic identification of type I and type II interferon-induced antiviral factors",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4239",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_134",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106057",
"article-title": "Cholesterol 25-Hydroxylase inhibits SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses by depleting membrane cholesterol",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106057",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_135",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012197117",
"article-title": "Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication by blocking membrane fusion",
"author": "Zang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "32105",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_136",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0769-y",
"article-title": "LY6E impairs coronavirus fusion and confers immune control of viral disease",
"author": "Pfaender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_137",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature09907",
"article-title": "A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response",
"author": "Schoggins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "481",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_138",
"volume": "472",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.036",
"article-title": "TMEM16F forms a Ca2+-activated cation channel required for lipid scrambling in platelets during blood coagulation",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_139",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00052",
"article-title": "Broad Spectrum Antiviral Agent Niclosamide and Its Therapeutic Potential",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "909",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_140",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1717956115",
"article-title": "Single-molecule analysis of phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F",
"author": "Watanabe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3066",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_141",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03287-13",
"article-title": "Role of phosphatidylserine receptors in enveloped virus infection",
"author": "Morizono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4275",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_142",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100411",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_143",
"unstructured": "Whitlock, J.M., and Chernomordik, L.V. (2021). Flagging fusion: Phosphatidylserine signaling in cell-cell fusion. J. Biol. Chem., 296."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.170.9.4840",
"article-title": "Phosphatidylserine on HIV envelope is a cofactor for infection of monocytic cells",
"author": "Callahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4840",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_144",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2017.06.012",
"article-title": "Fusion Stage of HIV-1 Entry Depends on Virus-Induced Cell Surface Exposure of Phosphatidylserine",
"author": "Zaitseva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_145",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006848",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_146",
"unstructured": "Nanbo, A., Maruyama, J., Imai, M., Ujie, M., Fujioka, Y., Nishide, S., Takada, A., Ohba, Y., and Kawaoka, Y. (2018). Ebola virus requires a host scramblase for externalization of phosphatidylserine on the surface of viral particles. PLoS Pathog., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01552-15",
"article-title": "Binding of alphaherpesvirus glycoprotein H to surface alpha4beta1-integrins activates calcium-signaling pathways and induces phosphatidylserine exposure on the plasma membrane",
"author": "Azab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01552-15",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "ref_147",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000133969",
"article-title": "The gene (LGALS3BP) encoding the serum protein 90K, associated with cancer and infection by the human immunodeficiency virus, maps at 17q25",
"author": "Calabrese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Cytogenet. Cell Genet.",
"key": "ref_148",
"volume": "69",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/emboj/17.6.1606",
"article-title": "Mac-2 binding protein is a cell-adhesive protein of the extracellular matrix which self-assembles into ring-like structures and binds beta1 integrins, collagens and fibronectin",
"author": "Sasaki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1606",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_149",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cam4.2075",
"article-title": "Increased LGALS3 expression independently predicts shorter overall survival in patients with the proneural subtype of glioblastoma",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2031",
"journal-title": "Cancer Med.",
"key": "ref_150",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.38065",
"article-title": "Unique protein signature of circulating microparticles in systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Ostergaard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2680",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "ref_151",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "90k is a serum marker of poor-prognosis in non-hodgkins-lymphoma patients",
"author": "Rea",
"first-page": "723",
"journal-title": "Oncol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_152",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0168-8278(96)80076-6",
"article-title": "Elevated serum levels of 90K/MAC-2 BP predict unresponsiveness to alpha-interferon therapy in chronic HCV hepatitis patients",
"author": "Artini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "212",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_153",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.066837-0",
"article-title": "Acute hantavirus infection induces galectin-3-binding protein",
"author": "Hepojoki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2356",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "ref_154",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms17060832",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_155",
"unstructured": "Liu, K.T., Liu, Y.H., Chen, Y.H., Lin, C.Y., Huang, C.H., Yen, M.C., and Kuo, P.L. (2016). Serum Galectin-9 and Galectin-3-Binding Protein in Acute Dengue Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/164.3.616",
"article-title": "Unusually high level of a tumor-associated antigen in the serum of human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals",
"author": "Natoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_156",
"volume": "164",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.24574",
"article-title": "Galectin 3 induces a distinctive pattern of cytokine and chemokine production in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via selective signaling pathways",
"author": "Filer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1604",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "ref_157",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Interactions between galectin-3 and Mac-2-binding protein mediate cell-cell adhesion",
"author": "Inohara",
"first-page": "4530",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "ref_158",
"volume": "56",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"article-title": "Increased Gal-3BP plasma levels in hospitalized patients infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gallo",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_159",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202114167",
"article-title": "High-resolution serum proteome trajectories in COVID-19 reveal patient-specific seroconversion",
"author": "Geyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14167",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_160",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11081136",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_161",
"unstructured": "Kusnierz-Cabala, B., Maziarz, B., Dumnicka, P., Dembinski, M., Kapusta, M., Bociaga-Jasik, M., Winiarski, M., Garlicki, A., Grodzicki, T., and Kukla, M. (2021). Diagnostic Significance of Serum Galectin-3 in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19-A Preliminary Study. Biomolecules, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cels.2020.05.012",
"article-title": "Ultra-High-Throughput Clinical Proteomics Reveals Classifiers of COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Messner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Cell. Syst.",
"key": "ref_162",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23494-1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia and proteomic trajectories inform prognostication in COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care",
"author": "Gutmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3406",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_163",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009127",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_164",
"unstructured": "Dias, S.S.G., Soares, V.C., Ferreira, A.C., Sacramento, C.Q., Fintelman-Rodrigues, N., Temerozo, J.R., Teixeira, L., Nunes da Silva, M.A., Barreto, E., and Mattos, M. (2020). Lipid droplets fuel SARS-CoV-2 replication and production of inflammatory mediators. PLoS Pathog., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a004820",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_165",
"unstructured": "Lorizate, M., and Krausslich, H.G. (2011). Role of lipids in virus replication. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100129",
"article-title": "The roles of lipids in SARS-CoV-2 viral replication and the host immune response",
"author": "Theken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100129",
"journal-title": "J. Lipid Res.",
"key": "ref_166",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100470",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_167",
"unstructured": "Vitner, E.B., Achdout, H., Avraham, R., Politi, B., Cherry, L., Tamir, H., Yahalom-Ronen, Y., Paran, N., Melamed, S., and Erez, N. (2021). Glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors prevent replication of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus. J. Biol. Chem., 296."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/braincomms/fcad086",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors in alphavirus infection of the central nervous system",
"author": "Avraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "fcad086",
"journal-title": "Brain Commun.",
"key": "ref_168",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M114.574285",
"article-title": "Sphingomyelin synthase 2, but not sphingomyelin synthase 1, is involved in HIV-1 envelope-mediated membrane fusion",
"author": "Hayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30842",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_169",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2015.07.025",
"article-title": "Inhibitors of dihydroceramide desaturase 1: Therapeutic agents and pharmacological tools to decipher the role of dihydroceramides in cell biology",
"author": "Casasampere",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Chem. Phys. Lipids",
"key": "ref_170",
"volume": "197",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00807-21",
"article-title": "N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) Retinamide Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion by a Dihydroceramide Delta4-Desaturase 1-Independent Mechanism",
"author": "Hayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0080721",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_171",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.embor.7400921",
"article-title": "Calcium: A fundamental regulator of intracellular membrane fusion?",
"author": "Hay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep.",
"key": "ref_172",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_1",
"article-title": "Calcium Signaling: From Basic to Bedside",
"author": "Islam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_173",
"volume": "1131",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9010094",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_174",
"unstructured": "Chen, X., Cao, R., and Zhong, W. (2019). Host Calcium Channels and Pumps in Viral Infections. Cells, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2021.101004",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of host cell calcium signaling during viral infections: Emerging paradigm with high clinical relevance",
"author": "Saurav",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101004",
"journal-title": "Mol. Aspects Med.",
"key": "ref_175",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ceca.2009.05.005",
"article-title": "Viral calciomics: Interplays between Ca2+ and virus",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Calcium",
"key": "ref_176",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.845580",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_177",
"unstructured": "Osorio, C., Sfera, A., Anton, J.J., Thomas, K.G., Andronescu, C.V., Li, E., Yahia, R.W., Avalos, A.G., and Kozlakidis, Z. (2022). Virus-Induced Membrane Fusion in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000626",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_178",
"unstructured": "Das, D.K., Bulow, U., Diehl, W.E., Durham, N.D., Senjobe, F., Chandran, K., Luban, J., and Munro, J.B. (2020). Conformational changes in the Ebola virus membrane fusion machine induced by pH, Ca2+, and receptor binding. PLoS Biol., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1004530",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_179",
"unstructured": "Dube, M., Rey, F.A., and Kielian, M. (2014). Rubella virus: First calcium-requiring viral fusion protein. PLoS Pathog., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00296",
"article-title": "Calcium Ions Directly Interact with the Ebola Virus Fusion Peptide To Promote Structure-Function Changes That Enhance Infection",
"author": "Nathan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_180",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1258758",
"article-title": "Ebola virus. Two-pore channels control Ebola virus host cell entry and are drug targets for disease treatment",
"author": "Sakurai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_181",
"volume": "347",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2017.10.017",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV Fusion Peptide Forms an Extended Bipartite Fusion Platform that Perturbs Membrane Order in a Calcium-Dependent Manner",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3875",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_182",
"volume": "429",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00426-20",
"article-title": "Ca(2+) Ions Promote Fusion of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus with Host Cells and Increase Infectivity",
"author": "Straus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00426-20",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_183",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00023",
"article-title": "Inhibitors of L-Type Calcium Channels Show Therapeutic Potential for Treating SARS-CoV-2 Infections by Preventing Virus Entry and Spread",
"author": "Straus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2807",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_184",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110694",
"article-title": "Dynamic Ca(2+) sensitivity stimulates the evolved SARS-CoV-2 spike strain-mediated membrane fusion for enhanced entry",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110694",
"journal-title": "Cell. Rep.",
"key": "ref_185",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13238-020-00806-7",
"article-title": "Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors as the hope for today and tomorrow",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "84",
"journal-title": "Protein Cell",
"key": "ref_186",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.aav4580",
"article-title": "A pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting the HR1 domain of human coronavirus spike",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eaav4580",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_187",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0374-2",
"article-title": "Fusion mechanism of 2019-nCoV and fusion inhibitors targeting HR1 domain in spike protein",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_188",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030597",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_189",
"unstructured": "Xing, L., Xu, X., Xu, W., Liu, Z., Shen, X., Zhou, J., Xu, L., Pu, J., Yang, C., and Huang, Y. (2022). A Five-Helix-Based SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Inhibitor Targeting Heptad Repeat 2 Domain against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants of Concern. Viruses, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00698-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-derived fusion inhibitor lipopeptides exhibit highly potent and broad-spectrum activity against divergent human coronaviruses",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_190",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867326666190805151654",
"article-title": "Antiviral Activities of Human Host Defense Peptides",
"author": "Brice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1420",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_191",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2051753",
"article-title": "Fusion-inhibition peptide broadly inhibits influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, including Delta and Omicron variants",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "926",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_192",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms4067",
"article-title": "Structure-based discovery of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus fusion inhibitor",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3067",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_193",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pnasnexus/pgac198",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_194",
"unstructured": "Jana, I.D., Bhattacharya, P., Mayilsamy, K., Banerjee, S., Bhattacharje, G., Das, S., Aditya, S., Ghosh, A., McGill, A.R., and Srikrishnan, S. (2022). Targeting an evolutionarily conserved “E-L-L” motif in the spike protein to develop a small molecule fusion inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv, pgac198."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13040651",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_195",
"unstructured": "Ko, M., Chang, S.Y., Byun, S.Y., Ianevski, A., Choi, I., Pham Hung d’Alexandry d’Orengiani, A.L., Ravlo, E., Wang, W., Bjoras, M., and Kainov, D.E. (2021). Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs Using a MERS-CoV Clinical Isolate from South Korea Identifies Potential Therapeutic Options for COVID-19. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00399-20",
"article-title": "Compounds with Therapeutic Potential against Novel Respiratory 2019 Coronavirus",
"author": "Martinez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00399-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_196",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03431-4",
"article-title": "Clofazimine broadly inhibits coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_197",
"volume": "593",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5588/ijtld.12.0144",
"article-title": "Systematic review of clofazimine for the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis",
"author": "Gopal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1001",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis.",
"key": "ref_198",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2577-1",
"article-title": "Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing",
"author": "Riva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_199",
"volume": "586",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03036-14",
"article-title": "Repurposing of clinically developed drugs for treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection",
"author": "Dyall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4885",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_200",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Dittmar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108959",
"journal-title": "Cell. Rep.",
"key": "ref_201",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01441-18",
"article-title": "Salinomycin Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection by Disrupting Endosomal Acidification and Viral Matrix Protein 2 Function",
"author": "Jang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01441-18",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_202",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.04.011",
"article-title": "Salinomycin induces activation of autophagy, mitophagy and affects mitochondrial polarity: Differences between primary and cancer cells",
"author": "Jangamreddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2057",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta",
"key": "ref_203",
"volume": "1833",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13046-018-0680-z",
"article-title": "Salinomycin, as an autophagy modulator-- a new avenue to anticancer: A review",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.",
"key": "ref_204",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0044132",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_205",
"unstructured": "Verdoodt, B., Vogt, M., Schmitz, I., Liffers, S.T., Tannapfel, A., and Mirmohammadsadegh, A. (2012). Salinomycin induces autophagy in colon and breast cancer cells with concomitant generation of reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE, 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fgene.2022.866474",
"article-title": "Anti-Fungal Drug Anidulafungin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Induced Syncytia Formation by Targeting ACE2-Spike Protein Interaction",
"author": "Ahamad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "866474",
"journal-title": "Front. Genet.",
"key": "ref_206",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0010363",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_207",
"unstructured": "Zhang, Z.R., Zhang, Y.N., Zhang, H.Q., Zhang, Q.Y., Li, N., Li, Q., Deng, C.L., Zhang, B., Li, X.D., and Ye, H.Q. (2022). Berbamine hydrochloride potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking S protein-mediated membrane fusion. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis., 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Cell. Res.",
"key": "ref_208",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25985",
"article-title": "The anti-HIV drug nelfinavir mesylate (Viracept) is a potent inhibitor of cell fusion caused by the SARSCoV-2 spike (S) glycoprotein warranting further evaluation as an antiviral against COVID-19 infections",
"author": "Musarrat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2087",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_209",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1358/dot.2013.49.4.1947288",
"article-title": "Cobicistat, a pharmacoenhancer for HIV treatments",
"author": "Temesgen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Drugs Today",
"key": "ref_210",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.03705-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_211",
"unstructured": "Shytaj, I.L., Fares, M., Gallucci, L., Lucic, B., Tolba, M.M., Zimmermann, L., Adler, J.M., Xing, N., Bushe, J., and Gruber, A.D. (2022). The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir To Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters. mBio, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bmb/61.1.13",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus disease in childhood",
"author": "McNamara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Br. Med. Bull.",
"key": "ref_212",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-118-9-199305010-00004",
"article-title": "Prognostic value of HIV-1 syncytium-inducing phenotype for rate of CD4+ cell depletion and progression to AIDS",
"author": "Koot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_213",
"volume": "118",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.158.8.3996",
"article-title": "HIV-induced T cell syncytia are self-perpetuating and the primary cause of T cell death in culture",
"author": "Sylwester",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3996",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_214",
"volume": "158",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00428-021-03053-1",
"article-title": "The pulmonary pathology of COVID-19",
"author": "Bosmuller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Virchows. Arch.",
"key": "ref_215",
"volume": "478",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-021-00795-y",
"article-title": "Syncytia formation during SARS-CoV-2 lung infection: A disastrous unity to eliminate lymphocytes",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2019",
"journal-title": "Cell. Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_216",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.735922",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Lung Pathogenesis in SARS-CoV-2 Autopsy Cases",
"author": "Valdebenito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735922",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_217",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02699-09",
"article-title": "Respiratory syncytial virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies motavizumab and palivizumab inhibit fusion",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8132",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_218",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005",
"article-title": "Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "Corti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3086",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_219",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042420-113838",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies for COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Med.",
"key": "ref_220",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00542-x",
"article-title": "Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "382",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_221",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.033",
"article-title": "Structural insight into SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and modulation of syncytia",
"author": "Asarnow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3192",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_222",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 222,
"references-count": 222,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/12/18/6079"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Syncytium under the Radar: Molecular Insights of the Spike-Induced Syncytia and Potential Strategies to Limit SARS-CoV-2 Replication",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}