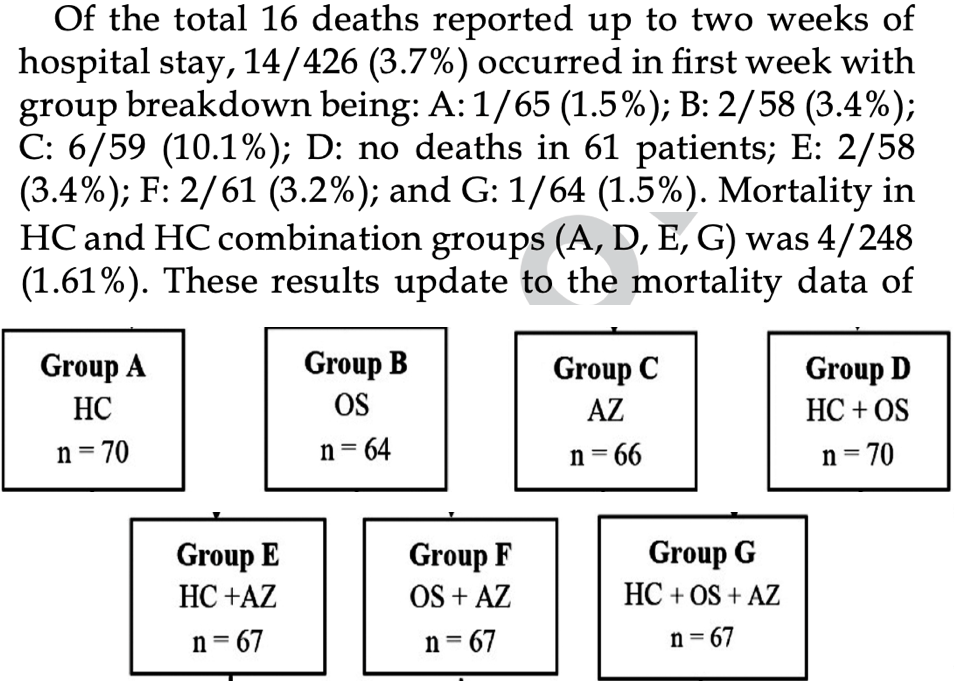Effectiveness of early pharmaceutical interventions in symptomatic COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial
Shehnoor Azhar, Javed Akram, Waqas Latif, Naomi Cano Ibanez, Samiullah Mumtaz, Ali Rafi, Usman Aftab, Somia Iqtadar, Muhammad Shahzad, Fibhaa Syed, Bilal Zafar, Nighat Fatima, Saleh Saadat Afridi, Shehla Javed Akram, Muhammad Afzal Chaudhary, Farah Sadiq, Saifullah Goraya, Muhammad Hanif, Verda Ashraf, Saadia Ashraf, Humaira Akram, Tanwir Khaliq
doi:10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757
Objective: We assessed the effectiveness of oral Hydroxychloroquine (HC), Azithromycin (AZ) and Oseltamivir (OS), alone or combined, among patients hospitalized with mildly symptomatic coronavirus infectious disease (COVID-19). Methods: Following the approval of the National Bioethics Committee and prospective registration (clinicaltrials.gov NCT04338698), a multicenter randomized clinical trial of adaptive design was conducted at 10 multispecialty hospitals in Pakistan. Patients were randomized into seven treatment groups. Starting April 15, 2020, consenting, eligible, otherwise healthy adult patients or those with co-morbidities under control, were recruited if they presented with mildly symptomatic COVID-19 (scored 3 on a 7-point ordinal scale anchored between 1 = not hospitalized, able to undertake normal activities, to 7 = death) confirmed by quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). Two primary outcomes were assessed by day seven: Turning qRT-PCR negative; and clinical improvement of two points from the baseline. Outcome rates were compared using a chi-square test. Multiple imputations were applied to handle missing data. An interim data analysis was carried out on July 19, 2020, following which the study continued without treatment group changes. Data Safety and Monitoring Board advised to stop recruitment due to its futility on January 18, 2021. Results: Of 471 patients randomized, a total of 426 (90.4%) completed the follow-up for primary outcomes. Based on imputed data analyses at day seven: Total qRT-PCR negative cases were 137/471 (29%, 95% CI 25.0 -33.4). By day seven, a total of 111/471 (23.5%, 95% CI 19.8 -27.6) showed clinical improvement. No serious or non-serious adverse event was reported. Conclusions: Among patients with mild COVID-19, there was no statistically significant difference in the effectiveness of oral antimalarial, antiviral, or antibiotic treatments.
References
Abduljabbar, Alghamdi, Althobaiti, Althubaiti, Alharthi et al., The length of hospital stays and clinical and therapeutic characteristics of patients with COVID-19 early in the pandemic in Taif City, KSA: A retrospective study, Medicine (Baltimore),
doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000032386Aftab, None
Afzal, None
Akram, Azhar, Shahzad, Latif, Khan, Pakistan Randomized and Observational Trial to Evaluate Coronavirus Treatment (PROTECT) of Hydroxychloroquine, Oseltamivir and Azithromycin to treat newly diagnosed patients with COVID-19 infection who have no comorbidities like diabetes mellitus: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04616-4Akram, Mbbs, Frcp, None
Akram, None
Angus, Berry, Lewis, Al-Beidh, Arabi et al., The REMAP-CAP (Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community-acquired Pneumonia) Study. Rationale and Design, Ann Am Thorac Soc,
doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-192SDAranda, Loureiro-Amigo, Murgadella, Vazquez, Feria et al., Changing Trends in the Global Consumption of Treatments Used in Hospitalized Patients for COVID-19: A Time Series Multicentre Study, Antibiotics,
doi:10.3390/antibiotics12050809Ashraf, None
Ashraf, None
Axfors, Schmitt, Janiaud, Van't Hooft, Abd-Elsalam et al., Mortality outcomes with hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 from an international collaborative metaanalysis of randomized trials, Nat Commun,
doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22446-zAzhar, Akram, Shahzad, Latif, Khan, Protocol of Pakistan randomized and observational trial to evaluate coronavirus treatment among newly diagnosed patients with COVID-19: Azithromycin, Oseltamivir, and Hydroxychloquine, Pak J Med Sci,
doi:10.12669/pjms.38.5.5512Azhar, Bds, Doctoral candidate in Epidemiology and Public Health
Babaei, Mirzababaei, Nassiri-Asl, Hosseinzadeh, Review of registered clinical trials for the treatment of COVID-19, Drug Dev Res,
doi:10.1002/ddr.21762Bhatti, Hospital, ABSTH) Gujrat
Bull-Otterson, Gray, Budnitz, Strosnider, Schieber et al., Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine Prescribing Patterns by Provider Specialty Following Initial Reports of Potential Benefit for COVID-19 Treatment -United States, January-June 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep,
doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6935a4Burgess, Rennie, Moodley, Key ethical issues encountered during COVID-19 research: a thematic analysis of perspectives from South African research ethics committees, BMC Med Ethics,
doi:10.1186/s12910-023-00888-yCano, None
Clair, Chan, Paiero, Fraser, Gunvaldsen et al., One Health response to SARS-CoV-2-associated risk from mink farming in British Columbia, Canada, October 2020 to October 2021, Can Commun Dis Rep,
doi:10.14745/ccdr.v48i06a04Curnow, Carpenter, Heron, Cornish, Rach et al., Multiple imputation of missing data under missing at random: compatible imputation models are not sufficient to avoid bias if they are mis-specified, J Clin Epidemiol,
doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2023.06.011Dai, Gao, Tao, Hadinegoro, Erkin et al., Efficacy and Safety of the RBD-Dimer-Based Covid-19 Vaccine ZF2001 in Adults, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJ-Moa2202261Diallo, Ndejjo, Leye, Egbende, Tusubira et al., Unintended consequences of implementing nonpharmaceutical interventions for the COVID-19 response in Africa: experiences from DRC, Nigeria, Senegal, and Uganda, Global Health,
doi:10.1186/s12992-023-00937-6Dunajcik, Haire, Thomas, Moriarty, Springer et al., Travel history among persons infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the United States, December 2020-February 2021, PLOS Glob Public Health,
doi:10.1371/journal.pgph.0001252Dutka, Bonello, Integrating a Research Protocol into a Health Care Setting, Nephrol Nurs J
Farlow, Torreele, Gray, Ruxrungtham, Rees et al., The Future of Epidemic and Pandemic Vaccines to Serve Global Public Health Needs, Vaccines,
doi:10.3390/vaccines11030690Fatima, None
Faucheux, Alves, Chevret, Rocha, Comparison of characteristics and laboratory tests of COVID-19 hematological patients from France and Brazil during the pre-vaccination period: identification of prognostic profiles for survival, Hematol Transfus Cell Ther,
doi:10.1016/j.htct.2022.05.003Fricke-Galindo, Valencia, Pharmacogenetics Approach for the Improvement of COVID-19 Treatment, Viruses,
doi:10.3390/v13030413Halperin, Ye, Mackinnon-Cameron, Smith, Cahn et al., Final efficacy analysis, interim safety analysis, and immunogenicity of a single dose of recombinant novel coronavirus vaccine (adenovirus type 5 vector) in adults 18 years and older: an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet,
doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02753-7Hanif, None
Hashem, Abufaraj, Tbakhi, Sultan, Obstacles and Considerations Related to Clinical Trial Research During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Front Med,
doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.598038Hong Nguyen, Ou, Huy, Shih, Chang et al., A global analysis of COVID-19 infection fatality rate and its associated factors during the Delta and Omicron variant periods: an ecological study, Front Public Health,
doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145138Husayn, Brown, Presley, Boghean, Waller, Hydroxychloroquine Alternatives for Chronic Disease: Response to a Growing Shortage Amid the Global COVID-19 Pandemic, J Pharm Pract,
doi:10.1177/0897190020942658Iqtadar, None
Jabeen, Rabbani, Telehealth as a public health approach to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan: A narrative review, J Med Access,
doi:10.1177/27550834231181299Janssen, Schakel, Fokou, Krisam, Stermann et al., A Randomized Open label Phase-II Clinical Trial with or without Infusion of Plasma from Subjects after Convalescence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in High-Risk Patients with Confirmed Severe SARS-CoV-2 Disease (RECOVER): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials,
doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04735-yJaved Akram, Mbbs, Dtm&h, Dch, None
Khaliq, None, FRCS) Professor of Surgery and Vice Chancellor SZABMU Islamabad
Latif, Phil Statistics) Data Analyst
Lauffenburger, Choudhry, Russo, Glynn, Ventz et al., Designing and conducting adaptive trials to evaluate interventions in health services and implementation research: practical considerations, BMJ Med,
doi:10.1136/bm-jmed-2022-000158Medical, World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2013.281053Miyazaki, Hosogaya, Fukushige, Takemori, Morimoto et al., A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial To Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Nelfinavir in Patients with Mild COVID-19, Microbiol Spectr,
doi:10.1128/spectrum.04311-22Mol, Lai, Rahim, Bordewijk, Wang et al., Checklist to assess Trustworthiness in RAndomised Controlled Trials (TRACT checklist): concept proposal and pilot, Res Integr Peer Rev,
doi:10.1186/s41073-023-00130-8Moorthy, Karam, Vannice, Kieny, Rationale for WHO's new position calling for prompt reporting and public disclosure of interventional clinical trial results, PLoS Med,
doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001819Mukhopadhyay, Paul, Samanta, Hydroxychloroquine in the prophylaxis of COVID 19: A survey of safety on the healthcare workers in India, Perspect Clin Res,
doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_310_20Mumtaz, None
Munblit, Nicholson, Akrami, Apfelbacher, Chen et al., A core outcome set for post-COVID-19 condition in adults for use in clinical practice and research: an international Delphi consensus study, Lancet Respir Med,
doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00169-2Murray, Babiker, Baker, Barkauskas, Brown et al., Design and implementation of an international, multi-arm, multi-stage platform master protocol for trials of novel SARS-CoV-2 antiviral agents: Therapeutics for Inpatients with COVID-19 (TICO/ACTIV-3), Clin Trials,
doi:10.1177/17407745211049829Navaei, Taleizadeh, Goodarzian, Designing a new sustainable Test Kit supply chain network utilizing Internet of Things, Eng Appl Artif Intell,
doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106585Quan, Taylor-Robinson, Vietnam's Evolving Healthcare System: Notable Successes and Significant Challenges, Cureus,
doi:10.7759/cureus.40414Rafi, None
Saadat, None
Sadiq, None
Saifullah Goraya, None
Samaras, Bekiaridou, Papazoglou, Moysidis, Tsoumakas et al., Artificial intelligence-based mining of electronic health record data to accelerate the digital transformation of the national cardiovascular ecosystem: design protocol of the Car-dioMining study, BMJ Open,
doi:10.1136/bmjo-pen-2022-068698AuthorsShahzad, None
Syed, None
Van Kessel, Kyriopoulos, Wong, Mossialos, The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Digital Health-Seeking Behavior: Big Data Interrupted Time-Series Analysis of Google Trends, J Med Internet Res,
doi:10.2196/42401Yadav, Chowdhury, Effectivity of repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infections, A hope for COVID 19: inhibitor modelling studies by docking and molecular dynamics, Heliyon,
doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12327Zafar, None
Zekarias, Watson, Vidlin, Grundmark, Sex Differences in Reported Adverse Drug Reactions to COVID-19 Drugs in a Global Database of Individual Case Safety Reports, Drug Saf,
doi:10.1007/s40264-020-01000-8DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757",
"ISSN": [
"1681-715X",
"1682-024X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Objective: We assessed the effectiveness of oral Hydroxychloroquine (HC), Azithromycin (AZ) and Oseltamivir (OS), alone or combined, among patients hospitalized with mildly symptomatic coronavirus infectious disease (COVID-19).
\nMethods: Following the approval of the National Bioethics Committee and prospective registration (clinicaltrials.gov NCT04338698), a multicenter randomized clinical trial of adaptive design was conducted at 10 multispecialty hospitals in Pakistan. Patients were randomized into seven treatment groups. Starting April 15, 2020, consenting, eligible, otherwise healthy adult patients or those with co-morbidities under control, were recruited if they presented with mildly symptomatic COVID-19 (scored 3 on a 7-point ordinal scale anchored between 1 = not hospitalized, able to undertake normal activities, to 7 = death) confirmed by quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). Two primary outcomes were assessed by day seven: Turning qRT-PCR negative; and clinical improvement of two points from the baseline. Outcome rates were compared using a chi-square test. Multiple imputations were applied to handle missing data. An interim data analysis was carried out on July 19, 2020, following which the study continued without treatment group changes. Data Safety and Monitoring Board advised to stop recruitment due to its futility on January 18, 2021.
\nResults: Of 471 patients randomized, a total of 426 (90.4%) completed the follow-up for primary outcomes. Based on imputed data analyses at day seven: Total qRT-PCR negative cases were 137/471 (29%, 95% CI 25.0 - 33.4). By day seven, a total of 111/471 (23.5%, 95% CI 19.8 - 27.6) showed clinical improvement. No serious or non-serious adverse event was reported.
\nConclusions: Among patients with mild COVID-19, there was no statistically significant difference in the effectiveness of oral antimalarial, antiviral, or antibiotic treatments.
\nClinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT04338698.
\ndoi: https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757
\nHow to cite this: Azhar S, Akram J, Latif W, Ibanez NC, Mumtaz S, Rafi A, et al. Effectiveness of early pharmaceutical interventions in symptomatic COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial. Pak J Med Sci. 2024;40(5):---------. doi: https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.40.5.8757
\nThis is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azhar",
"given": "Shehnoor",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akram",
"given": "Javed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latif",
"given": "Waqas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cano Ibanez",
"given": "Naomi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mumtaz",
"given": "Samiullah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafi",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aftab",
"given": "Usman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqtadar",
"given": "Somia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahzad",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syed",
"given": "Fibhaa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafar",
"given": "Bilal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatima",
"given": "Nighat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saadat Afridi",
"given": "Saleh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javed Akram",
"given": "Shehla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afzal Chaudhary",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadiq",
"given": "Farah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goraya",
"given": "Saifullah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haneef",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraf",
"given": "Verda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraf",
"given": "Saadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akrma",
"given": "Humaira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khaliq",
"given": "Tanwir",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Pak J Med Sci",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-06T21:20:36Z",
"timestamp": 1712438436000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-06T21:20:37Z",
"timestamp": 1712438437000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-07T00:40:16Z",
"timestamp": 1712450416408
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
]
}
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.pjms.org.pk/index.php/pjms/article/download/8757/2126",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.pjms.org.pk/index.php/pjms/article/download/8757/2126",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4935",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.12669",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.pjms.org.pk/index.php/pjms/article/view/8757"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effectiveness of early pharmaceutical interventions in symptomatic COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "40"
}