Clinical Characteristics, Prognostic Factors, and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease Patients: A Retrospective Case–Control Study from Astana, Kazakhstan
Kristina Rutskaya-Moroshan, Saule Abisheva, Anilim Abisheva, Zhadra Amangeldiyeva, Tatyana Vinnik, Tansholpan Batyrkhan
Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina60091377
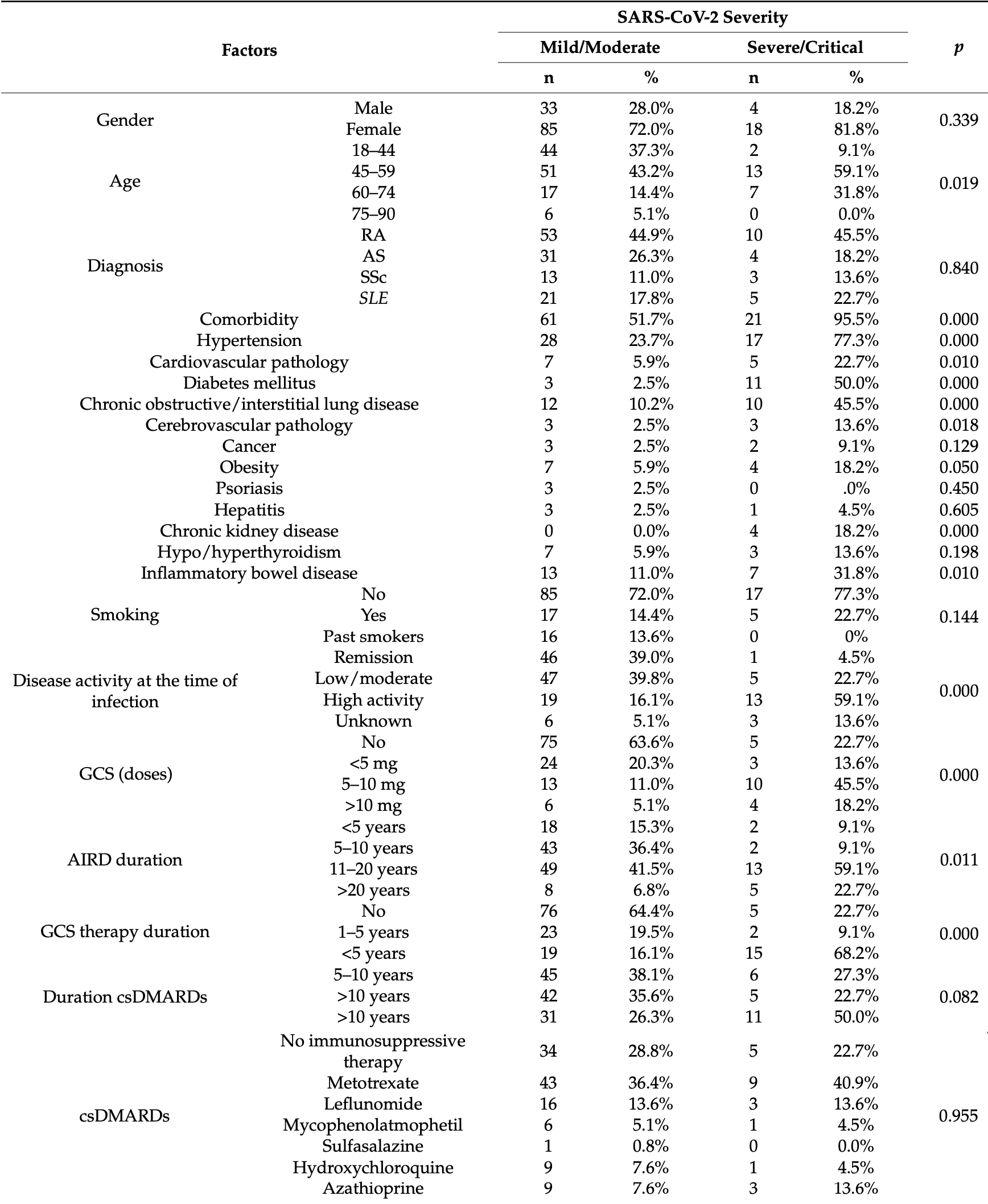
Background: Viral infections, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) tend to present more severe disease. This study aims to investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe infection in rheumatologic patients. Methods: We included patients with a diagnosis of AIRD and COVID-19 infection between January 2022 and July 2023. Patients with AIRDs infected with SARS-CoV-2 were matched with control patients of the general population according to age (±5 years) and sex in a 1:1 ratio. Confirmed infection was defined if a patient had a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. The severity was divided into mild, moderate, severe, and critical according to the guidelines of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). Results: A total of 140 individuals (37 males, 103 females; mean age 56.1 ± 11.3 years) with rheumatic disease diagnosed with COVID-19 infection were enrolled in the study. AIRDs included rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 63, 45%), ankylosing spondylitis (AS) (n = 35, 25%), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (n = 26, 8.6%), and systemic sclerosis (SSc) (n = 16, 11.4%). The AIRDs group had more SARS-CoV-2-related dyspnea (38.6%), arthralgia (45.7%), and depression (27.1%) than the control group (p = 0.004). The rate of lung infiltration on radiographic examination was higher in 58 (41.4%, p = 0.005) patients with rheumatic diseases than in those without them. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infection was more common in the AIRDs group than in the control group (22% vs. 12%; p = 0.043). Conclusions: Patients with AIRDs experienced more symptoms of arthralgia, depression, and dyspnea. There was a trend towards an increased severity of the disease in patients with AIRDs. Patients with arterial hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung, and kidney disease, treated with corticosteroids, had a longer duration, and high activity of autoimmune disease had an increased risk of severe COVID-19.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Amigues, Pearlman, Patel, Reid, Robinson et al., Coronavirus Disease 2019: Investigational Therapies in the Prevention and Treatment of Hyperinflammation, Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol,
doi:10.1080/1744666X.2021.1847084Battakova, Imasheva, Slazhneva, Imashev, Beloussov et al., Public Health Response Measures for COVID-19 in Kazakhstan, Disaster Med. Public Health Prep,
doi:10.1017/dmp.2023.181Briquez, Rouhani, Yu, Pyzer, Trujillo et al., Severe COVID-19 induces autoantibodies against angiotensin II that correlate with blood pressure dysregulation and disease severity, Sci. Adv,
doi:10.1126/sciadv.abn3777Bruce, Fries, Murtagh, Health status disparities in ethnic minority patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study, J. Rheumatol
Conway, Grimshaw, Konig, Putman, Duarte-García et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Outcomes in Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis, Arthritis Rheumatol,
doi:10.1002/art.42030Cordtz, Lindhardsen, Soussi, Vela, Uhrenholt et al., Incidence and Severeness of COVID-19 Hospitalisation in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Denmark, Rheumatology,
doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keaa897Dadras, Afsahi, Pashaei, Mojdeganlou, Karimi et al., The relationship between COVID-19 viral load and disease severity: A systematic review, Immun. Inflamm. Dis,
doi:10.1002/iid3.580Fleiss, Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, Formulas
Flook, Jackson, Vasileiou, Simpson, Muckian et al., Informing the public health response to COVID-19: A systematic review of risk factors for disease, severity, and mortality, BMC Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1186/s12879-021-05992-1Fonseca, Filgueiras, Marques, Vojdani, Halpert et al., Severe COVID-19 patients exhibit elevated levels of autoantibodies targeting cardiolipin and platelet glycoprotein with age: A systems biology approach, NPJ Aging,
doi:10.1038/s41514-023-00118-0Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Kursat Azkur et al., Risk Factors for Severe and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Review, Allergy,
doi:10.1111/all.14657Gastelum-Strozzi, Pascual, Hernández-Garduño, Moctezuma-Rios, Guaracha-Basañez et al., Perception of risk and impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with rheumatic diseases: A case-control study, Clin. Rheumatol,
doi:10.1007/s10067-022-06257-1Gianfrancesco, Hyrich, Al-Adely, Carmona, Danila et al., Characteristics Associated with Hospitalisation for COVID-19 in People with Rheumatic Disease: Data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Physician-Reported Registry, Ann. Rheum. Dis,
doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217871Gianfrancesco, Leykina, Izadi, Taylor, Sparks et al., Association of Race and Ethnicity With COVID-19 Outcomes in Rheumatic Disease: Data From the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Physician Registry, Arthritis Rheumatol,
doi:10.1002/art.41567Greenberg, Spruill, Shan, Reed, Kremer et al., Racial and ethnic disparities in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Am. J. Med,
doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.09.002Group; Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Haberman, Castillo, Chen, Yan, Ramirez et al., COVID-19 in Patients With Inflammatory Arthritis: A Prospective Study on the Effects of Comorbidities and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes, Arthritis Rheumatol,
doi:10.1002/art.41456Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J. Pathol,
doi:10.1002/path.1570Horwitz, Fahmy, Piccirillo, La Cava, Rebalancing Immune Homeostasis to Treat Autoimmune Diseases, Trends Immunol,
doi:10.1016/j.it.2019.08.003Jones, Faruqi, Sullivan, Calabrese, Calabrese, COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients Undergoing B Cell Depletion Therapy and Those with Humoral Immunodeficiency States: A Scoping Review, Pathog. Immun,
doi:10.20411/pai.v6i1.435Kastritis, Kitas, Vassilopoulos, Giannopoulos, Dimopoulos et al., Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, Anti-Rheumatic Therapies, COVID-19 Infection Risk and Patient Outcomes, Rheumatol. Int,
doi:10.1007/s00296-020-04629-xKelsey, Evans, Alice, Methods in Observational Epidemiology
Kokkotis, Kitsou, Xynogalas, Spoulou, Magiorkinis et al., Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients Receiving Anti-TNF Treatments, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther,
doi:10.1111/apt.16717Lassale, Gaye, Hamer, Gale, Batty, Ethnic disparities in hospitalisation for COVID-19 in England: The role of socioeconomic factors, mental health, and inflammatory and pro-inflammatory factors in a community-based cohort study, Brain Behav. Immun,
doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.074Leipe, Wilke, Ebert, Teufel, Reindl et al., Relapsing, and Atypical Symptomatic Course of COVID-19 in a B-Cell-Depleted Patient after Rituximab, Semin. Arthritis Rheum,
doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.06.013Li, Huang, Zou, Yang, Hui et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes, J. Med. Virol,
doi:10.1002/jmv.26424Liu, Gao, Zhang, Shi, Chen et al., The association between severe or dead COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta analysis, J. Infect,
doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.065Loarce-Martos, García-Fernández, López-Gutiérrez, García-García, Calvo-Sanz et al., High Rates of Severe Disease and Death Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Rheumatic Disease Patients Treated with Rituximab: A Descriptive Study, Rheumatol. Int,
doi:10.1007/s00296-020-04699-xLu, Chen, Ho, Wang, Autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and COVID-19 outcomes in South Korea: A nationwide cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol,
doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00151-XMahendra, Nuchin, Kumar, Shreedhar, Mahesh, Predictors of mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia-A retrospective study, Adv. Respir. Med,
doi:10.5603/arm.a2021.0036Mckeigue, Porter, Hollick, Ralston, Mcallister et al., Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Immunosuppressive Therapy in Scotland, Scand. J. Rheumatol,
doi:10.1080/03009742.2022.2063376Mikuls, Johnson, Fraenkel, Arasaratnam, Baden et al., American College of Rheumatology Guidance for the Management of Rheumatic Disease in Adult Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Version 2, Arthritis Rheumatol,
doi:10.1002/art.41437Mukusheva, Assylbekova, Poddighe, Management of pediatric rheumatic patients in Kazakhstan during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Rheumatol. Int,
doi:10.1007/s00296-020-04613-5Nas, Güçlü, Keskin, Dilek, Kalçık Unan et al., Clinical Course and Prognostic Factors of COVID-19 Infection in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory-Rheumatic Disease: A Retrospective, Case-Control Study, Arch. Rheumatol,
doi:10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2023.9289Pablos, Galindo, Carmona, Lledó, Retuerto et al., Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 and Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Multicentric Matched Cohort Study, Ann. Rheum. Dis,
doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218296Pijls, Jolani, Atherley, Derckx, Dijkstra et al., Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: A meta-analysis of 59 studies, BMJ Open,
doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044640Rodriguez-Perez, Labandeira, Pedrosa, Valenzuela, Suarez-Quintanilla et al., Autoantibodies against ACE2 and angiotensin type-1 receptors increase severity of COVID-19, J. Autoimmun,
doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102683Rorat, Zarębska-Michaluk, Kowalska, Kujawa, Rogalska et al., The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases, J. Clin. Med,
doi:10.3390/jcm11247342Rutskaya-Moroshan, Abisheva, Sarsenova, Ogay, Vinnik et al., Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and COVID-19 Vaccination: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study from Astana, Reumatologia,
doi:10.5114/reum/184335Sinha, Rosin, Arora, Labit, Jaffer et al., Dexamethasone Modulates Immature Neutrophils and Interferon Programming in Severe COVID-19, Nat. Med,
doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01576-3Strangfeld, Schäfer, Gianfrancesco, Lawson-Tovey, Liew et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry, Ann. Rheum. Dis,
doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219498Tepasse, Hafezi, Lutz, Kühn, Wilms et al., Persisting SARS-CoV-2 Viraemia after Rituximab Therapy: Two Cases with Fatal Outcome and a Review of the Literature, Br. J. Haematol,
doi:10.1111/bjh.16896Wang, Liu, Shao, Han, Su et al., Risk and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases compared with the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Rheumatol. Int,
doi:10.1007/s00296-021-04803-9Wang, Ma, Xu, Liu, Chen et al., Prevalence and risk of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Rheumatol,
doi:10.1007/s10067-022-06087-1Wei, Lin, Wei, Chen, He et al., Tocilizumab Treatment for COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Infect. Dis. Poverty,
doi:10.1186/s40249-021-00857-wWilliamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors Associated with COVID-19-Related Death Using OpenSAFELY, Nature,
doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA,
doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648Xu, Yi, Cai, Chen, Thong et al., Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global data, Autoimmun. Rev,
doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102778Yan, Ng, Nguyen, High Mortality from COVID-19 among Asian Americans in San Francisco
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Cui, Huang et al., In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin. Infect. Dis,
doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237Zhong, Shen, Yang, Huang, Chen et al., COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic disease in Hubei province, China: A multicentre retrospective observational study, Lancet Rheumatol,
doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30227-7DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina60091377",
"ISSN": [
"1648-9144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/medicina60091377",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Viral infections, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) tend to present more severe disease. This study aims to investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe infection in rheumatologic patients. Methods: We included patients with a diagnosis of AIRD and COVID-19 infection between January 2022 and July 2023. Patients with AIRDs infected with SARS-CoV-2 were matched with control patients of the general population according to age (±5 years) and sex in a 1:1 ratio. Confirmed infection was defined if a patient had a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. The severity was divided into mild, moderate, severe, and critical according to the guidelines of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). Results: A total of 140 individuals (37 males, 103 females; mean age 56.1 ± 11.3 years) with rheumatic disease diagnosed with COVID-19 infection were enrolled in the study. AIRDs included rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 63, 45%), ankylosing spondylitis (AS) (n = 35, 25%), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (n = 26, 8.6%), and systemic sclerosis (SSc) (n = 16, 11.4%). The AIRDs group had more SARS-CoV-2-related dyspnea (38.6%), arthralgia (45.7%), and depression (27.1%) than the control group (p = 0.004). The rate of lung infiltration on radiographic examination was higher in 58 (41.4%, p = 0.005) patients with rheumatic diseases than in those without them. Severe SARS-CoV-2 infection was more common in the AIRDs group than in the control group (22% vs. 12%; p = 0.043). Conclusions: Patients with AIRDs experienced more symptoms of arthralgia, depression, and dyspnea. There was a trend towards an increased severity of the disease in patients with AIRDs. Patients with arterial hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung, and kidney disease, treated with corticosteroids, had a longer duration, and high activity of autoimmune disease had an increased risk of severe COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"medicina60091377"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9324-8720",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rutskaya-Moroshan",
"given": "Kristina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6260-8220",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abisheva",
"given": "Saule",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
}
],
"family": "Abisheva",
"given": "Anilim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
}
],
"family": "Amangeldiyeva",
"given": "Zhadra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
},
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Biology, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel"
}
],
"family": "Vinnik",
"given": "Tatyana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine №1, NJSC «Astana Medical University», Astana 010000, Kazakhstan"
}
],
"family": "Batyrkhan",
"given": "Tansholpan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina",
"container-title-short": "Medicina",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T16:38:43Z",
"timestamp": 1724431123000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T19:19:19Z",
"timestamp": 1724440759000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-24T00:23:20Z",
"timestamp": 1724459000862
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1724371200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/60/9/1377/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1377",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2024, June 29). COVID-19 Cases|WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001077",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Maddur, M.S., Vani, J., Lacroix-Desmazes, S., Kaveri, S., and Bayry, J. (2010). Autoimmunity as a Predisposition for Infectious Diseases. PLoS Pathog., 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/rheumatology/keaa897",
"article-title": "Incidence and Severeness of COVID-19 Hospitalisation in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study from Denmark",
"author": "Cordtz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "SI59",
"journal-title": "Rheumatology",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1744666X.2021.1847084",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019: Investigational Therapies in the Prevention and Treatment of Hyperinflammation",
"author": "Amigues",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1185",
"journal-title": "Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors Associated with COVID-19-Related Death Using OpenSAFELY",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217871",
"article-title": "Characteristics Associated with Hospitalisation for COVID-19 in People with Rheumatic Disease: Data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Physician-Reported Registry",
"author": "Gianfrancesco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "859",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01576-3",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone Modulates Immature Neutrophils and Interferon Programming in Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-021-00857-w",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab Treatment for COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Poverty",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.16717",
"article-title": "Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients Receiving Anti-TNF Treatments",
"author": "Kokkotis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-020-04613-5",
"article-title": "Management of pediatric rheumatic patients in Kazakhstan during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic",
"author": "Mukusheva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1351",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/dmp.2023.181",
"article-title": "Public Health Response Measures for COVID-19 in Kazakhstan",
"author": "Battakova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e524",
"journal-title": "Disaster Med. Public Health Prep.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "(2024, June 29). Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan Bureau of National Statistics—Main, Available online: https://stat.gov.kz/en/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30177-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 response in central Asia",
"author": "Balakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e281",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5114/reum/184335",
"article-title": "Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and COVID-19 Vaccination: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study from Astana",
"author": "Abisheva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "Reumatologia",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-021-04803-9",
"article-title": "Risk and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases compared with the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "851",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/ARM.a2021.0036",
"article-title": "Predictors of mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia—A retrospective study",
"author": "Mahendra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Adv. Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-05992-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Flook, M., Jackson, C., Vasileiou, E., Simpson, C.R., Muckian, M.D., Agrawal, U., McCowan, C., Jia, Y., Murray, J.L.K., and Ritchie, L.D. (2021). Informing the public health response to COVID-19: A systematic review of risk factors for disease, severity, and mortality. BMC Infect. Dis., 21."
},
{
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Kelsey, J.L., Evans, A.S., and Alice, S. (1996). Methods in Observational Epidemiology, Oxford University Press. [2nd ed.]."
},
{
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "(2003). Fleiss, Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, Formulas 3.18 &3.19, John Wiley & Sons."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-022-06087-1",
"article-title": "Prevalence and risk of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2213",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00151-X",
"article-title": "Autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and COVID-19 outcomes in South Korea: A nationwide cohort study",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e698",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102778",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global data",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102778",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.065",
"article-title": "The association between severe or dead COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e93",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2019.08.003",
"article-title": "Rebalancing Immune Homeostasis to Treat Autoimmune Diseases",
"author": "Horwitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "888",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.580",
"article-title": "The relationship between COVID-19 viral load and disease severity: A systematic review",
"author": "Dadras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e580",
"journal-title": "Immun. Inflamm. Dis.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30227-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in patients with rheumatic disease in Hubei province, China: A multicentre retrospective observational study",
"author": "Zhong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e557",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219498",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death in people with rheumatic diseases: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician-reported registry",
"author": "Strangfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "930",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.42030",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Outcomes in Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Conway",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-022-06257-1",
"article-title": "Perception of risk and impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with rheumatic diseases: A case-control study",
"author": "Pascual",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3211",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ard-2023-223974",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "(2024, June 29). Outcomes Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Individuals with and without Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study|Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. Available online: https://ard.bmj.com/content/82/10/1359."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11247342",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Rorat, M., Zarębska-Michaluk, D., Kowalska, J., Kujawa, K., Rogalska, M., Kozielewicz, D., Lorenc, B., Sikorska, K., Czupryna, P., and Bolewska, B. (2022). The Course of COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. J. Clin. Med., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218296",
"article-title": "Clinical Outcomes of Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 and Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Multicentric Matched Cohort Study",
"author": "Pablos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1544",
"journal-title": "Ann. Rheum. Dis.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-020-04629-x",
"article-title": "Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, Anti-Rheumatic Therapies, COVID-19 Infection Risk and Patient Outcomes",
"author": "Kastritis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1353",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "American College of Rheumatology Guidance for the Management of Rheumatic Disease in Adult Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Version 2",
"author": "Mikuls",
"first-page": "e1",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2023.9289",
"article-title": "Clinical Course and Prognostic Factors of COVID-19 Infection in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory-Rheumatic Disease: A Retrospective, Case-Control Study",
"author": "Nas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Arch. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-0418-0",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance: Collecting data in a pandemic",
"author": "Robinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102683",
"article-title": "Autoantibodies against ACE2 and angiotensin type-1 receptors increase severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Labandeira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102683",
"journal-title": "J. Autoimmun.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abn3777",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 induces autoantibodies against angiotensin II that correlate with blood pressure dysregulation and disease severity",
"author": "Briquez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabn3777",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.41456",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Patients With Inflammatory Arthritis: A Prospective Study on the Effects of Comorbidities and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes",
"author": "Haberman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1981",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00005-9",
"article-title": "Divergent Effects of Acute versus Chronic Glucocorticoids in COVID-19",
"author": "Robinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e168",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41514-023-00118-0",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 patients exhibit elevated levels of autoantibodies targeting cardiolipin and platelet glycoprotein with age: A systems biology approach",
"author": "Fonseca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "NPJ Aging.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753466621995050",
"article-title": "Respiratory viral infections in the elderly",
"author": "Watson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1753466621995050",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26424",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1449",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044640",
"article-title": "Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: A meta-analysis of 59 studies",
"author": "Pijls",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e044640",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.074",
"article-title": "Ethnic disparities in hospitalisation for COVID-19 in England: The role of socioeconomic factors, mental health, and inflammatory and pro-inflammatory factors in a community-based cohort study",
"author": "Lassale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Yan, B., Ng, F., and Nguyen, T. (2024, April 20). High Mortality from COVID-19 among Asian Americans in San Francisco. Asian American Research Center on Health. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=SbnK3p8AAAAJ&citation_for_view=SbnK3p8AAAAJ:eQOLeE2rZwMC."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.41567",
"article-title": "Association of Race and Ethnicity With COVID-19 Outcomes in Rheumatic Disease: Data From the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Physician Registry",
"author": "Gianfrancesco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "374",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Health status disparities in ethnic minority patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study",
"author": "Bruce",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.09.002",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Greenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1089",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218310",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_53",
"unstructured": "FAI2R/SFR/SNFMI/SOFREMIP/CRI/IMIDIATE consortium and contributors (2021). Severity of COVID-19 and survival in patients with rheumatic and inflammatory diseases: Data from the French RMD COVID-19 cohort of 694 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis., 80, 527–538."
},
{
"DOI": "10.20411/pai.v6i1.435",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients Undergoing B Cell Depletion Therapy and Those with Humoral Immunodeficiency States: A Scoping Review",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Pathog. Immun.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-020-04699-x",
"article-title": "High Rates of Severe Disease and Death Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Rheumatic Disease Patients Treated with Rituximab: A Descriptive Study",
"author": "Boteanu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2015",
"journal-title": "Rheumatol. Int.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.16896",
"article-title": "Persisting SARS-CoV-2 Viraemia after Rituximab Therapy: Two Cases with Fatal Outcome and a Review of the Literature",
"author": "Tepasse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Haematol.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.06.013",
"article-title": "Long, Relapsing, and Atypical Symptomatic Course of COVID-19 in a B-Cell-Depleted Patient after Rituximab",
"author": "Leipe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1087",
"journal-title": "Semin. Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03009742.2022.2063376",
"article-title": "Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Immunosuppressive Therapy in Scotland",
"author": "McKeigue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"article-title": "Risk Factors for Severe and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Review",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_60",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby, P., Lim, W.S., Emberson, J.R., Mafham, M., Bell, J.L., Linsell, L., Staplin, N., Brightling, C., and Ustianowski, A. (2021). Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med., 384, 693–704."
}
],
"reference-count": 60,
"references-count": 60,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/60/9/1377"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical Characteristics, Prognostic Factors, and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease Patients: A Retrospective Case–Control Study from Astana, Kazakhstan",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "60"
}