HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
5,900+ studies for
172 treatments. c19hcq.org
|
|
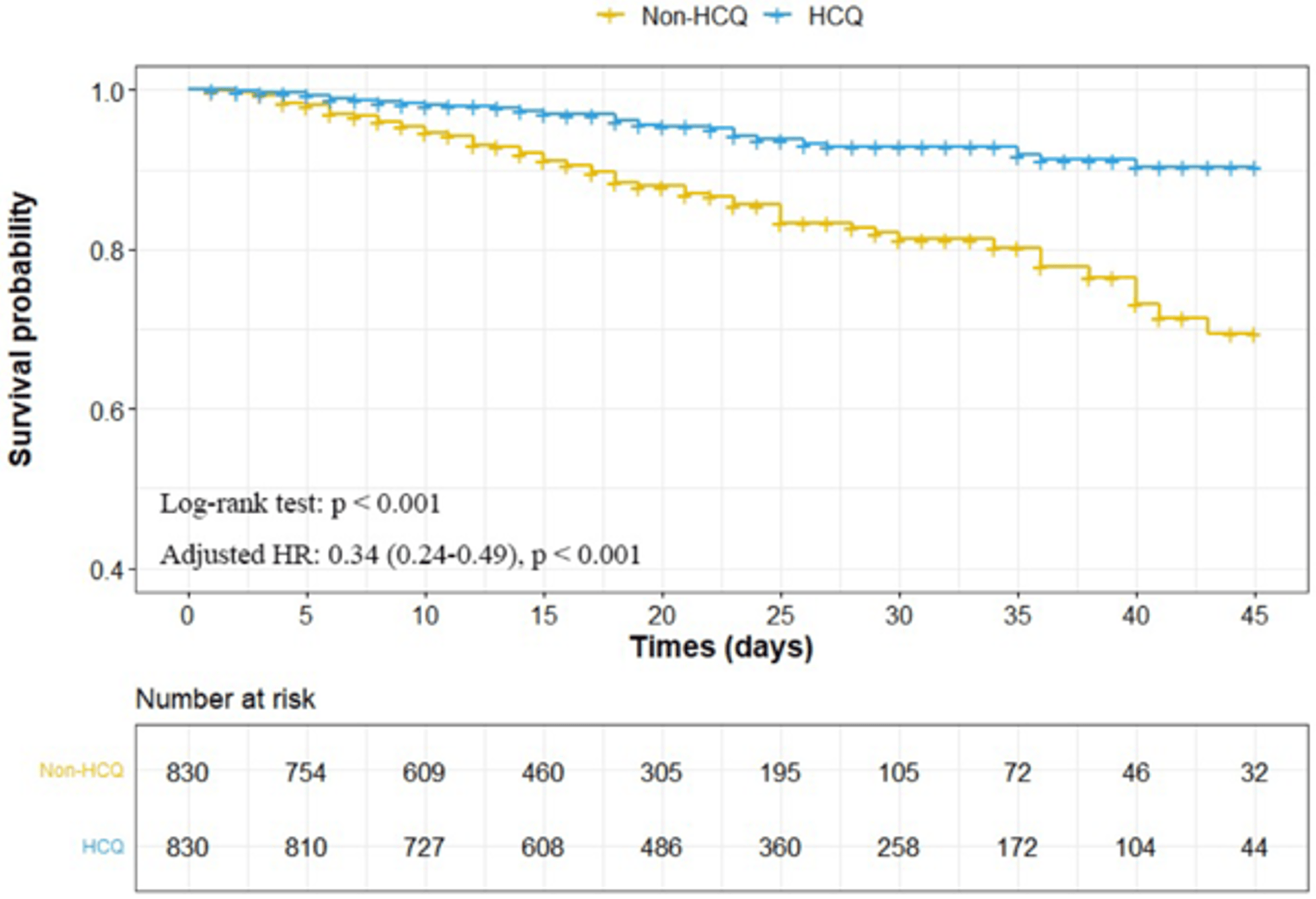
risk of death, 66.0% lower, HR 0.34, p < 0.001, treatment 830, control 830, all patients, propensity score matching, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
risk of death, 74.0% lower, HR 0.26, p < 0.001, treatment 800, control 800, low dose, propensity score matching, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 24.8% lower, HR 0.75, p = 0.05, treatment 841, control 52,189, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, all patients, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 27.0% lower, HR 0.73, p = 0.04, treatment 800, control 52,189, low dose, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
ARDS, 40.8% lower, HR 0.59, p = 0.21, treatment 841, control 52,189, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, all patients, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
ARDS, 49.0% lower, HR 0.51, p = 0.13, treatment 800, control 52,189, low dose, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
AKI, 31.0% lower, HR 0.69, p = 0.005, treatment 841, control 52,189, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, all patients, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
AKI, 30.0% lower, HR 0.70, p = 0.008, treatment 800, control 52,189, low dose, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
acute heart injury, 37.9% lower, HR 0.62, p = 0.03, treatment 841, control 52,189, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, all patients, Kaplan–Meier.
|
|
acute heart injury, 39.0% lower, HR 0.61, p = 0.02, treatment 800, control 52,189, low dose, Kaplan–Meier.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |