Clinical characteristics and risk factors for in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients in Hubei Province: A multicenter retrospective study
Wu He, Gen Li, Ke Xu, Bo Yu, Yang Sun, Kaineng Zhong, Da Zhou, Yongcui Yan, Junfang Wu, Dao Wen Wang
IJC Heart & Vasculature, doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574
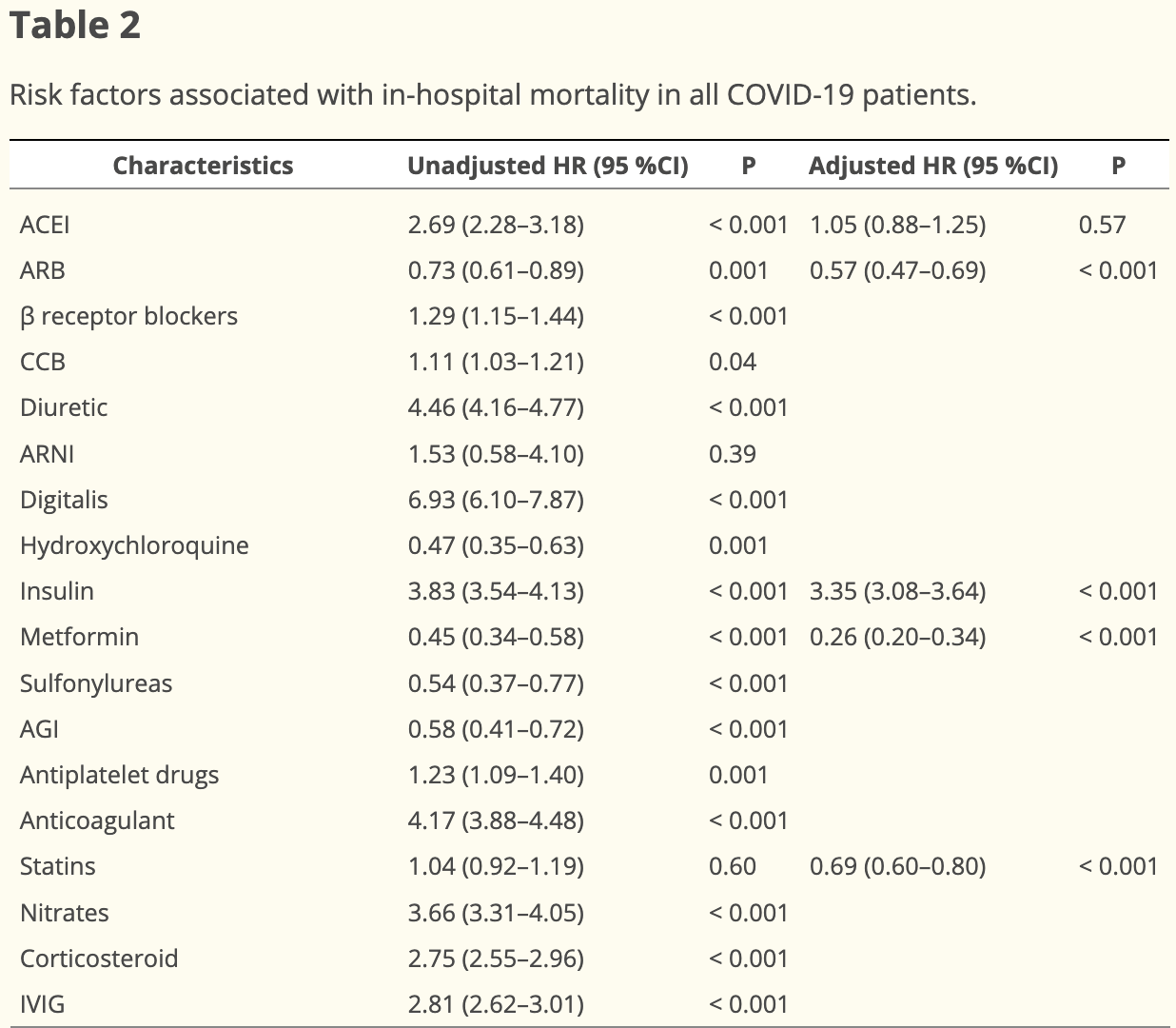
Background: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) remains one of the most significant factors threatening public health security worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic has been ongoing for more than 3 years; however, there are few studies on the clinical characteristics and mortality risk factors in patients with COVID-19 based on comprehensive data from multiple centers. Methods: A total of 53,030 patients with confirmed COVID-19 from 138 hospitals in Hubei Province were included in this study. We compared the clinical characteristics between survivors and non-survivors and analyzed the risk factors for in-hospital mortality. Results: Among the 53,030 patients with COVID-19, 49,320 (93.0 %) were discharged, and 3,710 (7.0 %) died during hospitalization. Cardiovascular disease was the most common comorbidity, followed by endocrine and digestive diseases. Male sex, >65-year-old, and high diastolic blood pressure, a series of abnormal laboratory test indicators and hyponatremia, hypokalemia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock, solid tumor, hematological tumor, and insulin use were independent risk factors for in-hospital mortality of patients with COVID-19. In addition, male sex, older age, and higher disease severity were associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19. Conclusion: Patients with early COVID-19 in Hubei Province had high mortality and a high proportion of severe cases and initial comorbidities. Cardiovascular disease was the most common comorbidity in patients with COVID-19. Male sex, older age, comorbidities, and abnormal laboratory data have been identified as independent risk factors for in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. Therefore, there should be an increased focus on patients with COVID-19 with these risk factors.
Trial registration number ClinicalTrials.gov NCT05615792.
CRediT authorship contribution statement Wu
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574 .
References
Bergman, Ballin, Nordström, Nordström, Risk factors for COVID-19 diagnosis, hospitalization, and subsequent all-cause mortality in Sweden: a nationwide study, Eur J Epidemiol
Chen, Klein, Garibaldi, Li, Wu et al., Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, immunity and intervention, Ageing Res Rev
Chen, Wu, Chen, Yan, Yang et al., Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study, BMJ
Clift, Coupland, Keogh, Diaz-Ordaz, Williamson et al., Living risk prediction algorithm (QCOVID) for risk of hospital admission and mortality from coronavirus 19 in adults: national derivation and validation cohort study, BMJ
Del Rio, Omer, Malani, Winter of omicron-the evolving COVID-19 pandemic, JAMA
Dessie, Zewotir, Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients, BMC Infect Dis
Du, Han, Li, Zhang, Epidemic update of COVID-19 in Hubei Province compared with other regions in China, Int J Infect Dis
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Kursat Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review, Allergy
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Albano, Antonelli et al., Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in lombardy, italy, JAMA Intern Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in china, N Engl J Med
Kim, Garg, O'halloran, Whitaker, Pham et al., Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the US coronavirus disease, COVID-19)associated hospitalization surveillance network (COVID-NET, Clin Infect Dis
Li, Tian, Yang, Lv, Yu et al., Clinical characteristics of 225 patients with COVID-19 in a tertiary Hospital near Wuhan, China, J Clin Virol
Li, Wang, Tian, Pang, Yang et al., COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Liang, Liang, Ou, Chen, Chen et al., Development and validation of a clinical risk score to predict the occurrence of critical illness in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, JAMA Intern Med
Liu, Yang, Liao, Wan, Lin et al., Risk factors for COVID-19 progression and mortality in hospitalized patients without pre-existing comorbidities, J Infect Public Health
Myers, Parodi, Escobar, Liu, Characteristics of hospitalized adults with COVID-19 in an integrated health care system in california, JAMA
O'driscoll, Ribeiro Dos Santos, Wang, Cummings, Azman et al., Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Rajagopalan, O'donnell et al., Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the new york city area, JAMA
Saravolatz, Depcinski, Sharma, Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs, Clin Infect Dis
Singanayagam, Chalmers, Severity assessment scores to guide empirical use of antibiotics in community acquired pneumonia, Lancet Respir Med
Team, Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) -United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19, Lancet
Xu, Wei, Giunta, Zhou, Xia, Do inflammaging and coagul-aging play a role as conditions contributing to the co-occurrence of the severe hyperinflammatory state and deadly coagulopathy during COVID-19 in older people?, Exp Gerontol
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes, Cell Metab
Zhang, Dong, Liu, Gao, Risk and protective factors for COVID-19 morbidity, severity, and mortality, Clin Rev Allergy Immunol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in china, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574",
"ISSN": [
"2352-9067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574",
"alternative-id": [
"S2352906724002409"
],
"article-number": "101574",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Clinical characteristics and risk factors for in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients in Hubei Province: A multicenter retrospective study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "IJC Heart & Vasculature"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Wu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Gen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Ke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Kaineng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Yongcui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Junfang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Dao Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "IJC Heart & Vasculature",
"container-title-short": "IJC Heart & Vasculature",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-30T18:52:41Z",
"timestamp": 1732992761000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-04T10:31:36Z",
"timestamp": 1733308296000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-05T05:21:31Z",
"timestamp": 1733376091004,
"version": "3.30.1"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1732579200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2352906724002409?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2352906724002409?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101574",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in china",
"author": "Zhu",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "2020",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0005",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0010",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00996-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine development: milestones, lessons and prospects",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0015",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"first-page": "165",
"issue": "2023",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0020",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.24315",
"article-title": "Winter of omicron-the evolving COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Del Rio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0025",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in lombardy, italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0030",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the US coronavirus disease, COVID-19)-associated hospitalization surveillance network (COVID-NET",
"author": "Kim",
"first-page": "e206",
"issue": "2021",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0035",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-021-00732-w",
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19 diagnosis, hospitalization, and subsequent all-cause mortality in Sweden: a nationwide study",
"author": "Bergman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0040",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Living risk prediction algorithm (QCOVID) for risk of hospital admission and mortality from coronavirus 19 in adults: national derivation and validation cohort study",
"author": "Clift",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0045",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in china",
"author": "Guan",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "2020",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0050",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.031",
"article-title": "Epidemic update of COVID-19 in Hubei Province compared with other regions in China",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0055",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70084-5",
"article-title": "Severity assessment scores to guide empirical use of antibiotics in community acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Singanayagam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "653",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0060",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the new york city area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0065",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients",
"author": "Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1833",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0070",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0075",
"unstructured": "C.C.-R. Team, Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) - United States, February 12-March 16, 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 69 (2020) 343-346."
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0080",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2020.101205",
"article-title": "Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, immunity and intervention",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0085",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0",
"article-title": "Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "O'Driscoll",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0090",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2021.111423",
"article-title": "Do inflammaging and coagul-aging play a role as conditions contributing to the co-occurrence of the severe hyper-inflammatory state and deadly coagulopathy during COVID-19 in older people?",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Exp Gerontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0095",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study",
"author": "Petrilli",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0100",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.7202",
"article-title": "Characteristics of hospitalized adults with COVID-19 in an integrated health care system in california",
"author": "Myers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2195",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0105",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk and protective factors for COVID-19 morbidity, severity, and mortality",
"author": "Zhang",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Rev Allergy Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0110",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06536-3",
"article-title": "Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients",
"author": "Dessie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "855",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0115",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"article-title": "Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0120",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30633-4",
"article-title": "Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1014",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0125",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.11.012",
"article-title": "Risk factors for COVID-19 progression and mortality in hospitalized patients without pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0130",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104363",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 225 patients with COVID-19 in a tertiary Hospital near Wuhan, China",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0135",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014",
"article-title": "Insulin treatment is associated with increased mortality in patients with COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0140",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2033",
"article-title": "Development and validation of a clinical risk score to predict the occurrence of critical illness in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1081",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101574_b0145",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2352906724002409"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical characteristics and risk factors for in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients in Hubei Province: A multicenter retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "56"
}