SARS-CoV 2 Viral Clearance in 1276 Patients: Associated Factors and the Role of Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin
P Brouqui, D Raoult
Acta Scientific Microbiology, doi:10.31080/asmi.2024.07.1413
Background: The role of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) in lowering the viral load of patients with COVID-19 is controversial.
Methods: In a retrospective observational study of data collected during care, we aimed to compare viral clearance as determined by qPCR in patients who were treated with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and those who were not. As a new feature, we adjusted the data according to the most significant confounding factors (age, initial viral load, and timescale between the onset of symptoms and treatment).
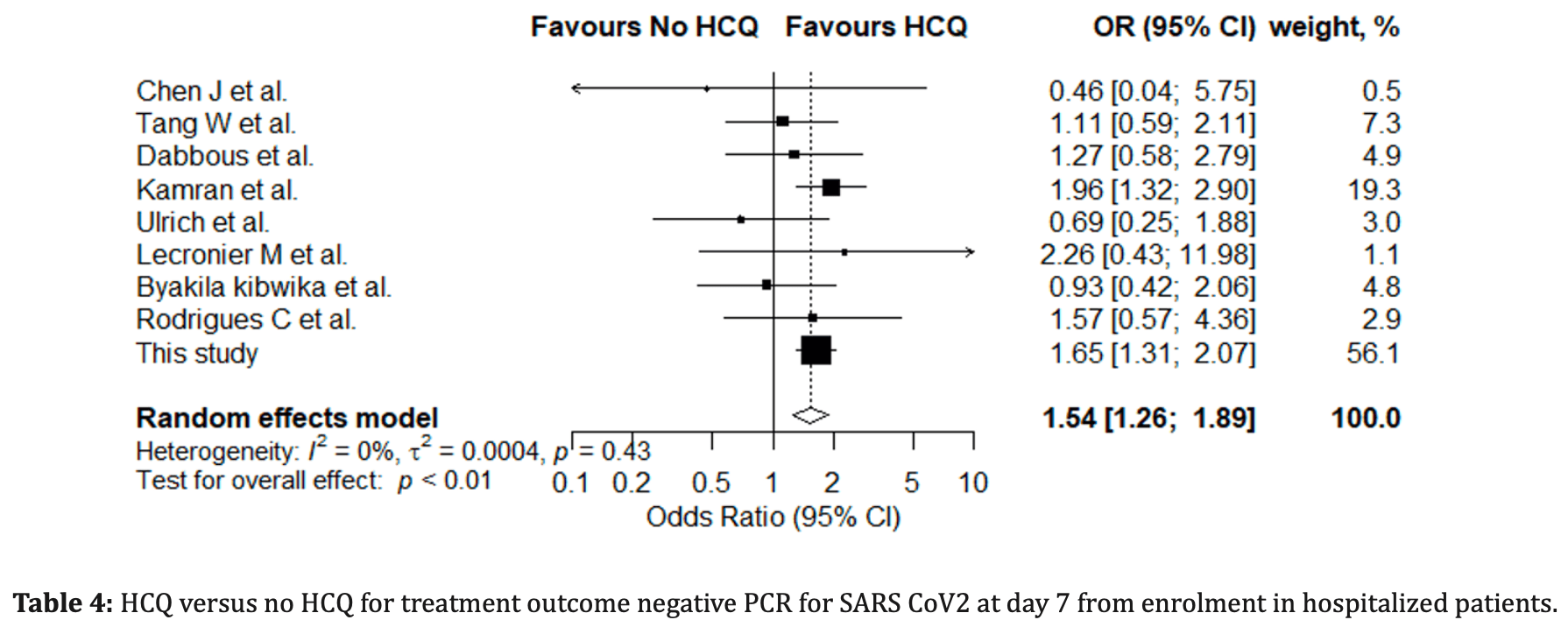
Results: Of the 1 276 patients selected within the hospital database, 776 were treated with HCQ and 500 were not. In the crude analysis, the time from treatment onset to viral clearance was significantly lower in the HCQ group than in the untreated group (logrank test p<.001). When adjusted for age, initial viral load and time from symptom onset to treatment onset, the adjusted hazard ratio of viral clearance for the HCQ group remained statistically significant (hazard ratio 95% CI 1.18 [1.01-1.38], p = .037). We then performed a meta-analysis of 9 similar studies, including this one, collecting a total of 1461 HCQ-treated patients and 958 controls. It showed a shortened SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance in the HCQ group on day 7 and 14, OR 1.54 (95% CI [1.26;1.89]), OR 2.47 (95% CI [0.55;11.17] respectively.
Conclusion: although age, initial viral load, and time to treatment do influence the viral load in patients with COVID-19, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) associated with azithromycin (AZ) still independently significantly lowered viral load more rapidly than other treatments, including azithromycin alone. As the reduction of viral load is associated with the outcome, these data strongly suggest that this treatment would be beneficial in patient with COVID-19.
Bibliography
References
Asberg, Oral valganciclovir is noninferior to intravenous ganciclovir for the treatment of cytomegalovirus disease in solid organ transplant recipients, American Journal of Transplantation
Balduzzi, How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial, Evidence Based Mental Health
Biber, The effect of ivermectin on the viral load and culture viability in early treatment of nonhospitalized patients with mild COVID-19 -a double-blind, randomized placebocontrolled trial, International Journal of Infectious Disease
Brouqui, Hydroxychloroquine: Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics
Brouqui, Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients, New Microbes New Infectious
Brouqui, Raoult, SARS-CoV 2 Viral Clearance in 1276 Patients: Associated Factors and the Role of Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin Citation, Acta Scientific Microbiology
Byakika-Kibwika, Safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine for treatment of non-severe COVID-19 among adults in Uganda: a randomized open label phase II clinical trial, BMC Infectious Diseases
Chanouzas, Valaciclovir to prevent Cytomegalovirus mediated adverse modulation of the immune system in AN-CA-associated vasculitis (CANVAS): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials
Chen, A multicenter, randomized, open-label, controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of hydroxychloroquine and a retrospective study in adult patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), PLoS One
Chen, A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients with moderate COVID-19, Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban
Dabbous, RETRACTED ARTICLE: Safety and efficacy of favipiravir versus hydroxychloroquine in management of COVID-19: A randomised controlled trial, Scientific Report
Gautret, Effect of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label nonrandomized clinical trial, an update with an intention-to-treat analysis and clinical outcomes, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Gautret, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Hirai, Factors associated with viral clearance periods from patients with COVID-19: A retrospective observational cohort study, Journal of Infectious Chemotherapy
Huang, Preliminary evidence from a multicenter prospective observational study of the safety and efficacy of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19, National Science Review
Jaafar, Correlation between 3790 qPCR positives samples and positive cell cultures including 1941 SARS-CoV-2 isolates, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Kamran, Clearing the fog: Is Hydroxychloroquine effective in reducing Corona virus disease-2019 progression: A randomized controlled trial, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.07.30.20165365v2Lagier, Outcomes of 3,737 COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin and other regimens in Marseille, France: A retrospective analysis, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Lecronier, Comparison of hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir, and standard of care in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: an opportunistic retrospective analysis, Crit Care,
doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03117-9Long, Prolonged viral shedding of SARS-CoV-2 and related factors in symptomatic COVID-19 patients: a prospective study, BMC Infectious Diseases
Maltezou, Association Between Upper Respiratory Tract Viral Load, Comorbidities, Disease Severity, and Outcome of Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Journal of Infectious Disease
Million, Effect of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARS-CoV-2 clearance in COVID-19 patients, a metaanalysis, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Owusu, Persistent SARS-CoV-2 RNA Shedding Without Evidence of Infectiousness: A Cohort Study of Individuals With COVID-19, Journal of Infectious Diseases
Puhach, SARS-CoV-2 viral load and shedding kinetics, Nature Reviews Microbiology
Rodrigues, Hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin early treatment of mild COVID-19 in an outpatient setting: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating viral clearance, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Rojas, Safety and efficacy of convalescent plasma for severe COVID-19: a randomized, single blinded, parallel, controlled clinical study, BMC Infectious Disease
Scola, Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards, European Journal of Clinical
Singh, Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database System Review
Tang, Hydroxychloroquine in patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019: open label, randomised controlled trial, BMJ
Ulrich, Treating COVID-19 With Hydroxychloroquine (TEACH): A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial in Hospitalized Patients, Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Van Wyk, Efficacy and Safety of Switching to Dolutegravir/Lamivudine Fixed-Dose 2-Drug Regimen vs Continuing a Tenofovir Alafenamide-Based 3-or 4-Drug Regimen for Maintenance of Virologic Suppression in Adults Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1: Phase 3, Randomized, Noninferiority TANGO Study, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Ventura-López, Treatment with metformin glycinate reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load: An in vitro model and randomized, double-blind, Phase IIb clinical trial, Biomed Pharmacotherapy
Xu, Factors Associated With Prolonged Viral RNA Shedding in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (CO-VID-19), Clinical Infectious Diseases
Zhang, The clinical utility of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA assays in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: the dawn of a new era?: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 7836 cases, Medicine (Baltimore)
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.31080/asmi.2024.07.1413",
"ISSN": [
"2581-3226"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.31080/ASMI.2024.07.1413",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brouqui",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raoult",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Scientific Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Act Scie Micro",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T10:45:31Z",
"timestamp": 1722941131000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T10:45:48Z",
"timestamp": 1722941148000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-07T00:41:37Z",
"timestamp": 1722991297164
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
]
},
"member": "14742",
"original-title": [],
"page": "136-149",
"prefix": "10.31080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Acta Scientific Publications Pvt. Ltd.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://actascientific.com/ASMI/pdf/ASMI-07-1413.pdf"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV 2 Viral Clearance in 1276 Patients: Associated Factors and the Role of Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin",
"type": "journal-article"
}