Ultrastructural Alteration of Bronchoalveolar Lavage of COVID19 Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients Reveals the Selective Cellular Infectivity, Impact of Hydroxy-Chloroquine, and Syncytial Formation in the Lung
S Yadav, S Chaudhary
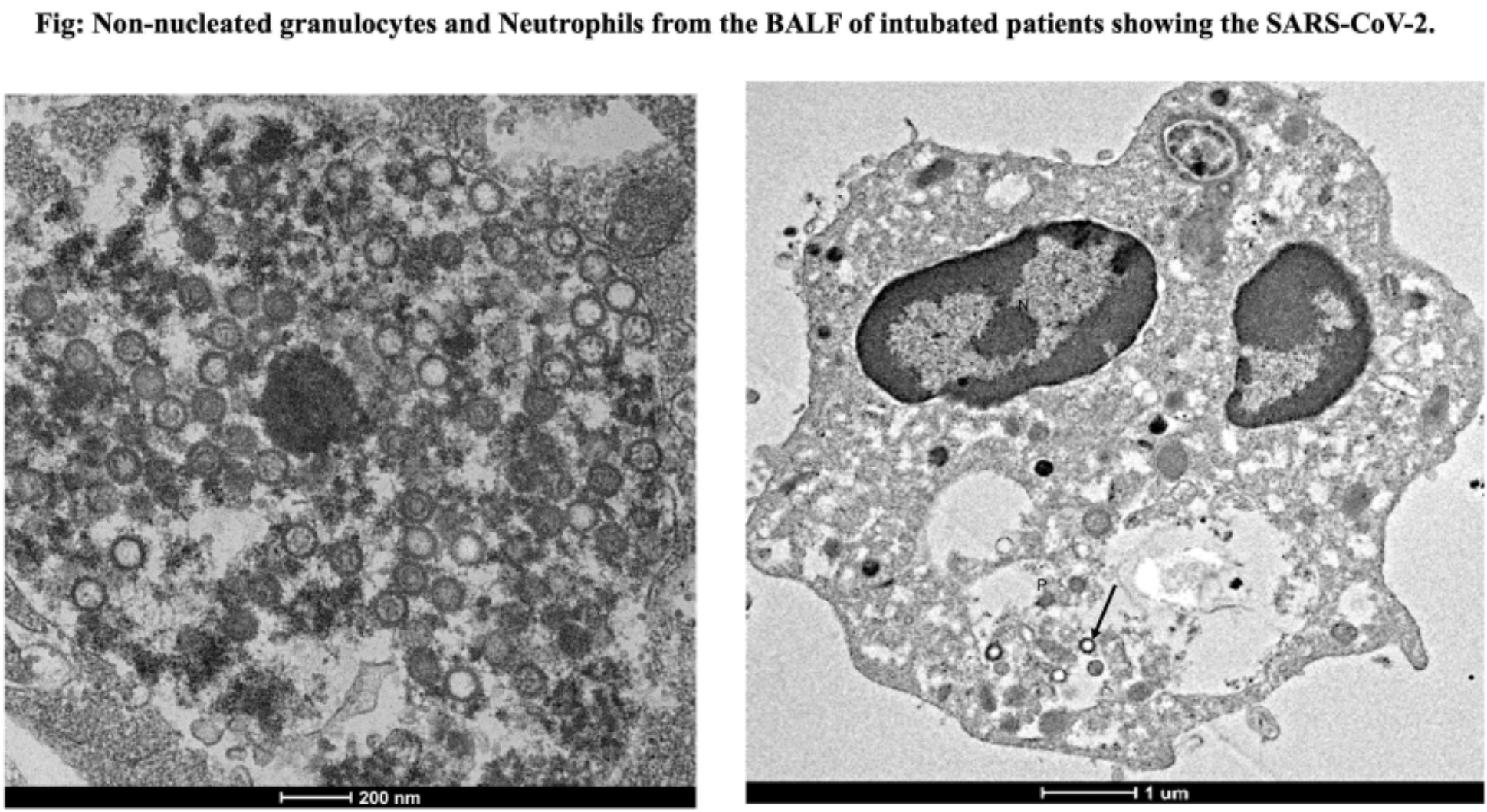
This study investigates the effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on various cell types in the bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF) of intubated COVID-19 patients, focusing on cellular infectivity and ultrastructural changes. We analyzed samples from 79 patients, divided by age (≥60 and <60 years) and common comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, liver and kidney diseases, malignancies). Using light microscopy, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy, we examined ultrastructural changes in cell types such as ciliated epithelium, type II pneumocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and granulocytes. The study revealed that younger patients (<60 years) had higher infection rates and better preservation of subcellular structures than older patients (≥60 years). Patients without comorbidities exhibited a higher viral load than those with comorbidities, with diabetic patients showing the most extensive ultrastructural damage among comorbid cases.We also explored the impact of prophylactic hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on BALF cells in COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Results showed that prophylactic HCQ reduced infection and cellular impairment in ciliated epithelium and type II pneumocytes compared to patients not receiving HCQ, although macrophages and neutrophils were similarly affected in both groups. Granulocytes in the HCQ+ group demonstrated higher phagocytic activity against mature viruses. Immunofluorescence studies revealed high infection levels in syncytial cells. Transmission electron microscopy identified initial fusion of both identical (e.g., neutrophils) and heterotypic (e.g., neutrophils and monocytes) plasma membranes in moderately infected patients. Severe ARDS cases displayed fully mature, large syncytial cells (20-100 µm) originating from neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages.This study highlights the differential impact of SARS-CoV-2 on BALF cell types in relation to age and comorbidities, along with the paradoxical role of HCQ. The findings provide insight into syncytial cell formation, which progresses from homotypic fusion in type II pneumocytes to heterotypic fusion with hematopoietic cells (e.g., monocytes and neutrophils) during the disease's moderate stage (9-16 days). Mature syncytia emerge in later stages, forming large giant cells (40-100 µm).
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.abstracts.a2672",
"ISSN": [
"1073-449X",
"1535-4970"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.Abstracts.A2672",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.Abstracts.A2672"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-05-01"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Electron Microscope Facility, Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Yadav",
"given": "S.C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Electron Microscope Facility, Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, India"
}
],
"family": "Chaudhary",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.atsjournals.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-11T14:47:06Z",
"timestamp": 1746974826000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-11T14:47:18Z",
"timestamp": 1746974838000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-11T15:10:07Z",
"timestamp": 1746976207214,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "Abstracts",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "Abstracts",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.Abstracts.A2672",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "19",
"original-title": [],
"page": "A2672-A2672",
"prefix": "10.1164",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Thoracic Society",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/10.1164/ajrccm.2025.211.Abstracts.A2672"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ultrastructural Alteration of Bronchoalveolar Lavage of COVID19 Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients Reveals the Selective Cellular Infectivity, Impact of Hydroxy-Chloroquine, and Syncytial Formation in the Lung",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1164/crossmarkpolicies",
"volume": "211"
}