The effect of Nigella sativa and vitamin D3 supplementation on the clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Shimaa A Said, Alsayyed Abdulbaset, Amal A El-Kholy, Osama Besckales, Nagwa A Sabri
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522
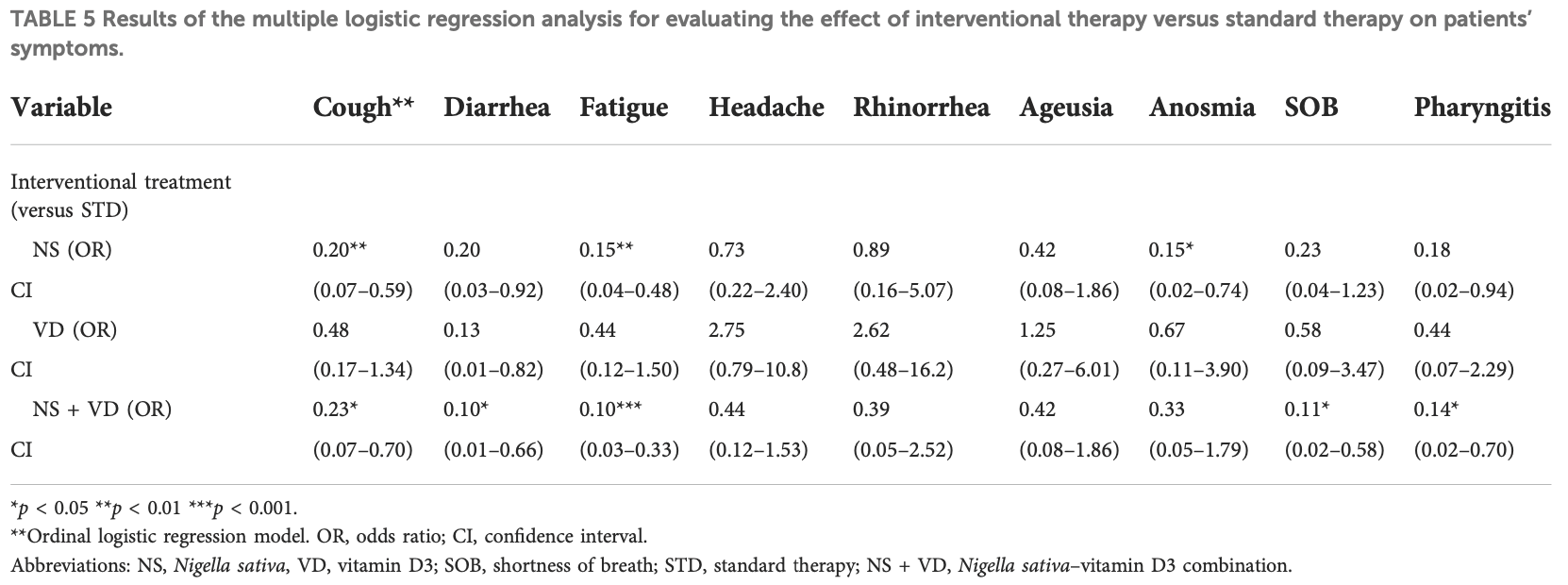
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel coronavirus that causes severe infection in the respiratory system. Since the immune status plays an essential role in combating COVID-19, herbal medicines, which have an immunomodulatory effect, may help prevent and even treat COVID-19. Nigella sativa is one of the herbal medicines with antiviral and immunomodulatory activities, and its therapeutic effectiveness makes it a promising add-on therapy for COVID-19. In addition, vitamin D3 has an immunomodulatory role, but the effect of therapeutic vitamin D3 supplementation in SARS-CoV-2 infection is still not well-known. Objective: This study aims to investigate the effects of Nigella sativa and vitamin D3 as single supplemental therapies and in combination on viral clearance indicated by a negative polymerase chain reaction and the alleviation of symptoms during the study follow-up duration of 14 days. Patients and Methods: The study design was an open-label randomized controlled clinical trial conducted at the Respiratory Hospital at the Kobry El Qobba Armed Forces Medical Complex. In total, 120 COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms were randomly assigned to four groups, with thirty patients each, as follows: Group 1 received an oral dose of 900 mg Nigella sativa through 450 mg soft gelatin capsules twice daily for two weeks; Group 2 received 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 through 1000-IU tablets given as two tablets, once daily; Group 3 received 900 mg of Nigella sativa and 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 in the same manner of dosing as in the previous groups; and Group 4 was the control group. All groups received standard therapy for COVID-19 infections and clinical management of COVID-19's clinical symptoms. Results: The Nigella sativa-vitamin D3 combination in addition to the standard therapy for COVID-19 infections significantly contributed to the alleviation of most COVID-19 symptoms: 50% of patients were free of cough after 7 days,
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ain Shams University, registered at the Egyptian Ministry of Health (MOH). The study was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (NCT ID: NCT04981743).
Author contributions SS and NS formulated the research question. SS performed all the aspects of the clinical trial including acquiring the investigational agents and randomized the patients into treatment groups, data recording, and quality checks. OB and AA followed up patients and monitored for treatment efficacy and safety of investigational agents and reported study outcomes and clinical endpoints to the principal investigator. NS supervised all aspects of this study and provided guidance. AE-K supervised the quality of data. All the authors contributed equally to writing and revising the manuscript.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdallah, El-Halawany, Darwish, Algandaby, Mohamed et al., Bio-guided isolation of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors from medicinal plants: In vitro assay and molecular dynamics, Plants,
doi:10.3390/PLANTS11151914Ahmadian, Biganeh, Panahi, Guest, Jamialahmadi, None
Alshrari, Hudu, Imran, Asdaq, Ali et al., Innovations and development of COVID-19 vaccines: A patent review, J. Infect. Public Health,
doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.021Asdaq, Rajan, Damodaran, Kamath, Nair et al., None
Ashraf, Ashraf, Akmal, Ashraf, Kalsoom et al., Prophylactic potential of honey and nigella sativa L. Against hospital and community-based SARS-CoV-2 spread: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, medRxiv,
doi:10.1101/2020.10.30.20217364Awodele, Oreagba, Fajemirokun, Samuel, Coulidiaty et al., None
Aziz, Son, Cho, Thymoquinone suppresses IRF-3-mediated expression of type I interferons via suppression of TBK1, Int. J. Mol. Sci,
doi:10.3390/IJMS19051355Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Lazaretti-Castro, Formenti et al., Mechanisms in endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19
Boonstra, Barrat, Crain, Heath, Savelkoulo'garra, 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin d3 has a direct effect on naive CD4(+) T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells, J. Immunol,
doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4974Bouchentouf, Missoum, Identification of compounds from Nigella sativa as new potential inhibitors of 2019 novel coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular docking study,
doi:10.20944/PREPRINTS202004.0079.V1Cascella, Rajnik, Aleem, Dulebohn, Napoli, None
Connelly, Pilot studies, Medsurg Nurs
Erdfelder, Faul, Buchner, Gpower: A general power analysis program, Behav. Res. Methods, Instrum. Comput,
doi:10.3758/BF03203630Fahmy, Sabri, El Hamamsy, El Sawi, Zaki, None
Gandhi, Lynch, Del Rio, Mild or moderate covid-19
Giménez, Sanz, Marón, Ferder, Manucha, Vitamin D-RAAS connection: An integrative standpoint into cardiovascular and neuroinflammatory disorders, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci,
doi:10.2174/1389203721666200606220719Giordo, Zinellu, Eid, Pintus, Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in COVID-19-associated hemostatic disorders, Molecules,
doi:10.3390/molecules26040856Gorman, Tan, Lambert, Scott, Judge, None
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients,
doi:10.3390/nu7064240Haddadi, Pour, Nigeria ; Hannan, Rahman, Sikder, Black cumin (nigella sativa L.): A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, health benefits, molecular pharmacology, and safety, Nutrients,
doi:10.3390/nu13061784Hart, Vitamin D3 deficiency enhances allergen-induced lymphocyte responses in a mouse model of allergic airway disease, Pediatr. Allergy Immunol
Imran, Khan, Alshammari, Alkhaldi, Alshammari et al., Nigella sativa L. and COVID-19: A glance at the anti-COVID-19 chemical constituents, clinical trials, inventions, and patent literature, Molecules,
doi:10.3390/molecules27092750Kim, Jeon, Kang, Kwon, Complementary and alternative medicine for long COVID: Scoping review and bibliometric analysis, Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med,
doi:10.1155/2022/7303393Koshak, Koshak, Mobeireek, Badawi, Wali et al., Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial, Complementary Ther. Med,
doi:10.1016/J.CTIM.2021.102769Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents,
doi:10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.105924Leaf, Ginde, Vitamin D3 to treat COVID-19: Different disease, same answer, Frontiers in Pharmacology frontiersin
Mahdavi, Namazi, Alizadeh, Farajnia, Effects of nigella sativa oil with a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women: A randomized controlled clinical trial, Food Funct,
doi:10.1039/c5fo00316dMalek Mahdavi, A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID-19, Rev. Med. Virol,
doi:10.1002/RMV.2119Martineau, Forouhi, Elassal, Hassany, Shawky et al., Management protocol for COVID-19 patients MoHP protocol for COVID19 November 2020. Cairo Egypt: Ministry of health and population, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol,
doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30268-0Nigella, Black cumin): A promising natural remedy for wide range of illnesses, Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med,
doi:10.1155/2019/1528635Niranjan, Setlur, Karunakaran, Uttarkar, Kumar, None
Phu, Thuan, Nguyen, Posadino, Eid et al., Herbal medicine for slowing aging and aging-associated conditions: Efficacy, mechanisms and safety, Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol,
doi:10.2174/1570161117666190715121939Ramazani, Emami, Tayarani-Najaran, Sahebkar, Tayarani-Najaran, Antiviral plants in view of avicenna's the canon of medicine and modern medicine against common cold, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol,
doi:10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_7Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled
Sahebkar, Disi, Anwar, Eid, Resveratrol as a probable multiheaded treatment approach for COVID-19, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00323Shaito, Thuan, Phu, Nguyen, Hasan et al., Herbal medicine for cardiovascular diseases: Efficacy, mechanisms, and safety, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00422Shirvani, Rostamkhani, Arabzadeh, Mohammadi, Mohammadi et al., Potential role of Nigella sativa supplementation with physical activity in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A contemporary review, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev,
doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015043Skariyachan, Nugraha, Ridwansyah, Ghozali, Khairani et al., Traditional herbal medicine candidates as complementary treatments for COVID-19: A review of their mechanisms, pros and cons. Evidence-based Complementary, Struct. Chem,
doi:10.1155/2020/2560645Ullah, Munir, Al-Sehemi, Muhammad, Haq et al., Identification of phytochemical inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 protease 3CLpro from selected medicinal plants as per molecular docking, bond energies and amino acid binding energies, Saudi J. Biol. Sci,
doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.03.024Wehbe, Hammoud, Soudani, Zaraket, El-Yazbi et al., Molecular insights into SARS COV-2 interaction with cardiovascular disease: Role of RAAS and MAPK signaling, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00836Wehbe, Wehbe, Iratni, Pintus, Zaraket et al., World Medical Association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA -J. Am. Med. Assoc,
doi:10.1001/jama.2013.281053Yimer, Tuem, Karim, Ur-Rehman, Anwar, None
Younis, Zareef, Al Hassan, Bitar, Eid et al., Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients: Pros and cons, Front. Pharmacol,
doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.597985Zahedipour, Hosseini, Henney, Barreto, Sahebkar, Phytochemicals as inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor alpha and neuroinflammatory responses in neurodegenerative diseases, Frontiers in Pharmacology frontiersin
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel coronavirus that causes severe infection in the respiratory system. Since the immune status plays an essential role in combating COVID-19, herbal medicines, which have an immunomodulatory effect, may help prevent and even treat COVID-19. <jats:italic>Nigella</jats:italic><jats:italic>sativa</jats:italic> is one of the herbal medicines with antiviral and immunomodulatory activities, and its therapeutic effectiveness makes it a promising add-on therapy for COVID-19. In addition, vitamin D3 has an immunomodulatory role, but the effect of therapeutic vitamin D3 supplementation in SARS-CoV-2 infection is still not well-known.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Objective:</jats:bold> This study aims to investigate the effects of <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> and vitamin D3 as single supplemental therapies and in combination on viral clearance indicated by a negative polymerase chain reaction and the alleviation of symptoms during the study follow-up duration of 14 days.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Patients and Methods:</jats:bold> The study design was an open-label randomized controlled clinical trial conducted at the Respiratory Hospital at the Kobry El Qobba Armed Forces Medical Complex. In total, 120 COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms were randomly assigned to four groups, with thirty patients each, as follows: Group 1 received an oral dose of 900 mg <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> through 450 mg soft gelatin capsules twice daily for two weeks; Group 2 received 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 through 1000-IU tablets given as two tablets, once daily; Group 3 received 900 mg of <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> and 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 in the same manner of dosing as in the previous groups; and Group 4 was the control group. All groups received standard therapy for COVID-19 infections and clinical management of COVID-19’s clinical symptoms.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> The <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic>–vitamin D3 combination in addition to the standard therapy for COVID-19 infections significantly contributed to the alleviation of most COVID-19 symptoms: 50% of patients were free of cough after 7 days, 70% showed an absence of fatigue after 4 days, 80% had no headache after 5 days, 90% were free of rhinorrhea after 7 days, and 86.7% of the patients had no dyspnea after 7 days. Moreover, patients in the four studied groups showed a reduced median temperature after 3 days of treatment. Negative results of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test recorded on the 7th and 14th day of therapy were superior in the <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> and vitamin D3 combination arm compared to those of the other studied arms where the value of the odds ratio (OR) on the 7th day was 0.13 with 95% CI: 0.03–0.45 and that of the 14th day was 0.09 with 95% CI: 0.02–0.3.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold> The results of this study showed a promising therapeutic benefit of the administration of <jats:italic>Nigella sativa</jats:italic> and vitamin D3 combination in COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms. Additionally, the remarkable viral clearance in a short time interval and reduction in the severity and progression of symptoms recommended the use of this combination as an add-on therapy for the management of COVID-19 patients.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Clinical Trial Registration:</jats:bold><jats:ext-link>ClinicalTrials.gov</jats:ext-link>, Identifier: NCT04981743.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Said",
"given": "Shimaa A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdulbaset",
"given": "Alsayyed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Kholy",
"given": "Amal A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Besckales",
"given": "Osama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sabri",
"given": "Nagwa A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T07:02:23Z",
"timestamp": 1667890943000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T07:02:31Z",
"timestamp": 1667890951000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T07:41:11Z",
"timestamp": 1667893271435
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667865600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/PLANTS11151914",
"article-title": "Bio-guided isolation of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors from medicinal plants: In vitro assay and molecular dynamics",
"author": "Abdallah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1914",
"journal-title": "Plants",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_29",
"article-title": "Resveratrol as a probable multiheaded treatment approach for COVID-19",
"author": "Ahmadian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "441",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "1328",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2015.00323",
"article-title": "Anti-hypertensive herbs and their mechanisms of action: Part I",
"author": "Al Disi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "323",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.021",
"article-title": "Innovations and development of COVID-19 vaccines: A patent review",
"author": "Alshrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2016.00050",
"article-title": "Anti-hypertensive herbs and their mechanisms of action: Part II",
"author": "Anwar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics10111308",
"article-title": "Identifying mucormycosis severity in Indian COVID-19 patients: A nano-based diagnosis and the necessity for critical therapeutic intervention",
"author": "Asdaq",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1308",
"journal-title": "Antibiotics",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05510-3",
"article-title": "Prophylactic potential of honey and nigella sativa L. Against hospital and community-based SARS-CoV-2 spread: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Ashraf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "618",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.30.20217364",
"article-title": "Efficacy of honey and nigella sativa against COVID-19: HNS-COVID-PK trial",
"author": "Ashraf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "A multi-center placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial",
"key": "B8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Herbal medicines use : Remedies or risks",
"author": "Awodele",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "West Afr. J. Pharm.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/IJMS19051355",
"article-title": "Thymoquinone suppresses IRF-3-mediated expression of type I interferons via suppression of TBK1",
"author": "Aziz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1355",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"article-title": "Mechanisms in endocrinology: Vitamin D and COVID-19",
"author": "Bilezikian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R133",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Endocrinol.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.167.9.4974",
"article-title": "1alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin d3 has a direct effect on naive CD4(+) T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells",
"author": "Boonstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4974",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/PREPRINTS202004.0079.V1",
"article-title": "Identification of compounds from Nigella sativa as new potential inhibitors of 2019 novel coronasvirus (Covid-19): Molecular docking study",
"author": "Bouchentouf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B14",
"unstructured": "Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19)\n CascellaM.\n RajnikM.\n AleemA.\n DulebohnS. C.\n Di NapoliR.\n 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.830990",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and its combination with repurposed drugs as COVID-19 therapeutics",
"author": "Chatterjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "830990",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Pilot studies",
"author": "Connelly",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "Medsurg Nurs.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3758/BF03203630",
"article-title": "Gpower: A general power analysis program",
"author": "Erdfelder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Behav. Res. Methods, Instrum. Comput.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.7(3).1043-49",
"article-title": "Vitamin D intake and sun exposure in autistic children",
"author": "Fahmy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1043",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMCP2009249",
"article-title": "Mild or moderate covid-19",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1757",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389203721666200606220719",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-RAAS connection: An integrative standpoint into cardiovascular and neuroinflammatory disorders",
"author": "Giménez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "948",
"journal-title": "Curr. Protein Pept. Sci.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26040856",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in COVID-19-associated hemostatic disorders",
"author": "Giordo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/J.1399-3038.2011.01146.X",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 deficiency enhances allergen-induced lymphocyte responses in a mouse model of allergic airway disease",
"author": "Gorman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Allergy Immunol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"article-title": "Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D",
"author": "Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4240",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "Haddadi",
"key": "B24",
"volume-title": "IRCT approved: International and national patent: Herbal medicine for the treatment of COVID-19/PCT: WO2022009236A1/139950140003003167",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061784",
"article-title": "Black cumin (nigella sativa L.): A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, health benefits, molecular pharmacology, and safety",
"author": "Hannan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1784",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27092750",
"article-title": "Nigella sativa L. and COVID-19: A glance at the anti-COVID-19 chemical constituents, clinical trials, inventions, and patent literature",
"author": "Imran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2750",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/9632034",
"article-title": "Medicinal plants and zinc: Impact on COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Jalal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9632034",
"journal-title": "Sci. World J.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/CLINMED.2020-0301",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Kenneth Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E107",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13880209.2021.1931353",
"article-title": "Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19",
"author": "Khazdair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Biol.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/7303393",
"article-title": "Complementary and alternative medicine for long COVID: Scoping review and bibliometric analysis",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7303393",
"journal-title": "Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.CTIM.2021.102769",
"article-title": "Nigella sativa for the treatment of COVID-19: An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Koshak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102769",
"journal-title": "Complementary Ther. Med.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/J.IJANTIMICAG.2020.105924",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105924",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMA.2020.26850",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 to treat COVID-19: Different disease, same answer",
"author": "Leaf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1047",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c5fo00316d",
"article-title": "Effects of nigella sativa oil with a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women: A randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Mahdavi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2041",
"journal-title": "Food Funct.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/RMV.2119",
"article-title": "A brief review of interplay between vitamin D and angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2: Implications for a potential treatment for COVID‐19",
"author": "Malek Mahdavi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2119",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30268-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D for COVID-19: A case to answer?",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Masoud",
"key": "B36",
"volume-title": "Management protocol for COVID-19 patients MoHP protocol for COVID19 November 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2019722",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2",
"article-title": "Vitamin-D and COVID-19: Do deficient risk a poorer outcome?",
"author": "Mitchell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "570",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Muhammad",
"key": "B38",
"volume-title": "SPECIFIC AIMS Fitra30 COVID-19 protocol",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/JAMA.2020.26848",
"article-title": "Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11224-022-02020-z",
"article-title": "Scope of repurposed drugs against the potential targets of the latest variants of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Niranjan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1585",
"journal-title": "Struct. Chem.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/2560645",
"article-title": "Traditional herbal medicine candidates as complementary treatments for COVID-19: A review of their mechanisms, pros and cons",
"author": "Nugraha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Evidence-based Complementary Altern. Med.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1570161117666190715121939",
"article-title": "Herbal medicine for slowing aging and aging-associated conditions: Efficacy, mechanisms and safety",
"author": "Phu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_7",
"article-title": "Antiviral plants in view of avicenna's the canon of medicine and modern medicine against common cold",
"author": "Ramazani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "1328",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31080/ASPS.2022.06.0883",
"article-title": "Microbiota in the era of COVID-19. Correlation and benefits",
"author": "Raslan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Act. Scie. Pharma.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "6",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.31080/asps.2022.06.0872",
"article-title": "The significance of COVID-19 vaccine booster dose. A comparative review",
"author": "Raslan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "03",
"journal-title": "Act. Scie. Pharma.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "6",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/POSTGRADMEDJ-2020-139065",
"article-title": "Short term, high-dose vitamin D supplementation for COVID-19 disease: A randomised, placebo-controlled, study (SHADE study)",
"author": "Rastogi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1381612828666220802121014",
"article-title": "Herbal medicines as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Rostami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2375",
"journal-title": "Curr. Pharm. Des.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_19",
"article-title": "Role of herbal medicines in the management of brain injury",
"author": "Safdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "1328",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.steroids.2022.109102",
"article-title": "Corticosteroids: A boon or bane for COVID-19 patients?",
"author": "Sen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109102",
"journal-title": "Steroids",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00422",
"article-title": "Herbal medicine for cardiovascular diseases: Efficacy, mechanisms, and safety",
"author": "Shaito",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "422",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11332-021-00787-y",
"article-title": "Potential role of Nigella sativa supplementation with physical activity in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A contemporary review",
"author": "Shirvani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "849",
"journal-title": "Sport Sci. Health",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD015043",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: A living systematic review",
"author": "Stroehlein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "CD015043",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.03.024",
"article-title": "Identification of phytochemical inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 protease 3CLpro from selected medicinal plants as per molecular docking, bond energies and amino acid binding energies",
"author": "Ullah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103274",
"journal-title": "Saudi J. Biol. Sci.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00836",
"article-title": "Molecular insights into SARS COV-2 interaction with cardiovascular disease: Role of RAAS and MAPK signaling",
"author": "Wehbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "836",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.663586",
"article-title": "Repurposing ivermectin for COVID-19: Molecular aspects and therapeutic possibilities",
"author": "Wehbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "663586",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"article-title": "World Medical Association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2191",
"journal-title": "JAMA - J. Am. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "310",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/1528635",
"article-title": "Nigella sativa L. (Black cumin): A promising natural remedy for wide range of illnesses",
"author": "Yimer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1528635",
"journal-title": "Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med.",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.597985",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients: Pros and cons",
"author": "Younis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597985",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1673-5374.332128",
"article-title": "Phytochemicals as inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor alpha and neuroinflammatory responses in neurodegenerative diseases",
"author": "Zahedipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1675",
"journal-title": "Neural Regen. Res.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 61,
"references-count": 61,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.1011522/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The effect of Nigella sativa and vitamin D3 supplementation on the clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}