Azithromycin in addition to standard of care versus standard of care alone in the treatment of patients admitted to the hospital with severe COVID-19 in Brazil (COALITION II): a randomised clinical trial
Remo H M Furtado, Dr Otavio Berwanger, Henrique A Fonseca, Thiago D Corrêa, Leonardo R Ferraz, Maura G Lapa, Fernando G Zampieri, Viviane C Veiga, Luciano C P Azevedo, Regis G Rosa, Renato D Lopes, Alvaro Avezum, Airton L O Manoel, Felipe M T Piza, Priscilla A Martins, Thiago C Lisboa, Adriano J Pereira, Guilherme B Olivato, Vicente C S Dantas, Eveline P Milan, Otavio C E Gebara, Roberto B Amazonas, Monalisa B Oliveira, Ronaldo V P Soares, Diogo D F Moia, Luciana P A Piano, Kleber Castilho, Roberta G R A P Momesso, Guilherme P P Schettino, Luiz Vicente Rizzo, Ary Serpa Neto, Flávia R Machado, Alexandre B Cavalcanti
The Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31862-6
Background The efficacy and safety of azithromycin in the treatment of COVID-19 remain uncertain. We assessed whether adding azithromycin to standard of care, which included hydroxychloroquine, would improve clinical outcomes of patients admitted to the hospital with severe COVID-19.
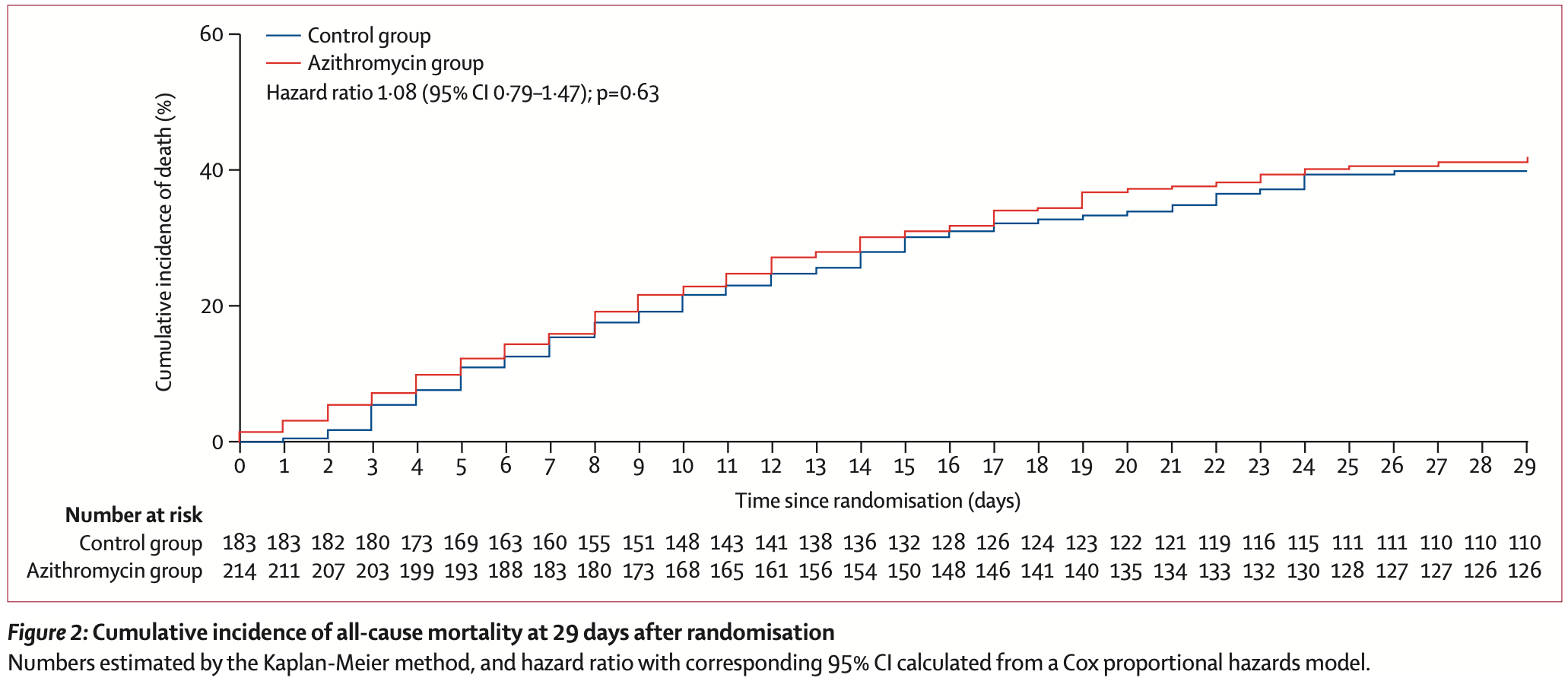
Methods We did an open-label, randomised clinical trial at 57 centres in Brazil. We enrolled patients admitted to hospital with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 and at least one additional severity criteria as follows: use of oxygen supplementation of more than 4 L/min flow; use of high-flow nasal cannula; use of non-invasive mechanical ventilation; or use of invasive mechanical ventilation. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to azithromycin (500 mg via oral, nasogastric, or intravenous administration once daily for 10 days) plus standard of care or to standard of care without macrolides. All patients received hydroxychloroquine (400 mg twice daily for 10 days) because that was part of standard of care treatment in Brazil for patients with severe COVID-19. The primary outcome, assessed by an independent adjudication committee masked to treatment allocation, was clinical status at day 15 after randomisation, assessed by a six-point ordinal scale, with levels ranging from 1 to 6 and higher scores indicating a worse condition (with odds ratio [OR] greater than 1•00 favouring the control group). The primary outcome was assessed in all patients in the intentionto-treat (ITT) population who had severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection confirmed by molecular or serological testing before randomisation (ie, modified ITT [mITT] population). Safety was assessed in all patients according to which treatment they received, regardless of original group assignment. This trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04321278. Findings 447 patients were enrolled from March 28 to May 19, 2020. COVID-19 was confirmed in 397 patients who constituted the mITT population, of whom 214 were assigned to the azithromycin group and 183 to the control group. In the mITT population, the primary endpoint was not significantly different between the azithromycin and control groups (OR 1•36 [95% CI 0•94-1•97], p=0•11). Rates of adverse events, including clinically relevant ventricular arrhythmias, resuscitated cardiac arrest, acute kidney failure, and corrected QT interval prolongation, were not significantly different between groups. Interpretation In patients with severe COVID-19, adding azithromycin to standard of care treatment (which included hydroxychloroquine) did not improve clinical outcomes. Our findings do not support the routine use of azithromycin in combination with hydroxychloroquine in patients with severe COVID-19. Funding COALITION COVID-19 Brazil and EMS.
COVID-19 Brazil. EMS provided partial funding, the study drugs, and coordinated logistics for the trial, but was not involved in the study conduct, analysis, or decision to publish these results. The authors vouch for the integrity and completeness of the data and the fidelity of the trial to the protocol.
References
Angus, Optimizing the trade-off between learning and doing in a pandemic, JAMA
Arabi, Deeb, Al-Hameed, Macrolides in critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome, Int J Infect Dis
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cheng, Nie, Chen, The role of macrolide antibiotics in increasing cardiovascular risk, J Am Coll Cardiol
Chorin, Dai, Shulman, The QT interval in patients with COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, Nat Med
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med,
doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436Hraiech, Bourenne, Kuteifan, Lack of viral clearance by the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin or lopinavir and ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2-related acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Intensive Care
Hung, Lung, Tso, Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial, Lancet
Hung, To, Chan, Efficacy of clarithromycinnaproxen-oseltamivir combination in the treatment of patients hospitalized for influenza A(H3N2) infection: an open-label randomized, controlled, phase IIb/III trial, Chest
Kawamura, Ichikado, Takaki, Eguchi, Anan et al., Adjunctive therapy with azithromycin for moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective, propensity score-matching analysis of prospectively collected data at a single center, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Martín-Loeches, Bermejo-Martin, Vallés, Macrolidebased regimens in absence of bacterial co-infection in critically ill H1N1 patients with primary viral pneumonia, Intensive Care Med
Metlay, Waterer, Long, Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Sermo, Largest statistically significant study by 6,200 multi-country physicians on COVID-19 uncovers treatment patterns and puts pandemic in context
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
{ 'indexed': {'date-parts': [[2024, 3, 13]], 'date-time': '2024-03-13T13:05:47Z', 'timestamp': 1710335147470},
'reference-count': 29,
'publisher': 'Elsevier BV',
'issue': '10256',
'license': [ { 'start': { 'date-parts': [[2020, 10, 1]],
'date-time': '2020-10-01T00:00:00Z',
'timestamp': 1601510400000},
'content-version': 'tdm',
'delay-in-days': 0,
'URL': 'https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/'}],
'content-domain': { 'domain': [ 'clinicalkey.fr', 'clinicalkey.jp', 'clinicalkey.com.au', 'clinicalkey.es',
'clinicalkey.com', 'em-consulte.com', 'thelancet.com', 'elsevier.com',
'sciencedirect.com'],
'crossmark-restriction': True},
'published-print': {'date-parts': [[2020, 10]]},
'DOI': '10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31862-6',
'type': 'journal-article',
'created': {'date-parts': [[2020, 9, 6]], 'date-time': '2020-09-06T02:30:36Z', 'timestamp': 1599359436000},
'page': '959-967',
'update-policy': 'http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy',
'source': 'Crossref',
'is-referenced-by-count': 236,
'title': 'Azithromycin in addition to standard of care versus standard of care alone in the treatment of '
'patients admitted to the hospital with severe COVID-19 in Brazil (COALITION II): a randomised '
'clinical trial',
'prefix': '10.1016',
'volume': '396',
'author': [ {'given': 'Remo H M', 'family': 'Furtado', 'sequence': 'first', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Otavio', 'family': 'Berwanger', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Henrique A', 'family': 'Fonseca', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Thiago D', 'family': 'Corrêa', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Leonardo R', 'family': 'Ferraz', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Maura G', 'family': 'Lapa', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Fernando G', 'family': 'Zampieri', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Viviane C', 'family': 'Veiga', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Luciano C P', 'family': 'Azevedo', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Regis G', 'family': 'Rosa', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Renato D', 'family': 'Lopes', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Alvaro', 'family': 'Avezum', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Airton L O', 'family': 'Manoel', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Felipe M T', 'family': 'Piza', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Priscilla A', 'family': 'Martins', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Thiago C', 'family': 'Lisboa', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Adriano J', 'family': 'Pereira', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Guilherme B', 'family': 'Olivato', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Vicente C S', 'family': 'Dantas', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Eveline P', 'family': 'Milan', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Otavio C E', 'family': 'Gebara', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Roberto B', 'family': 'Amazonas', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Monalisa B', 'family': 'Oliveira', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Ronaldo V P', 'family': 'Soares', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Diogo D F', 'family': 'Moia', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Luciana P A', 'family': 'Piano', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Kleber', 'family': 'Castilho', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Roberta G R A P', 'family': 'Momesso', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Guilherme P P', 'family': 'Schettino', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Luiz Vicente', 'family': 'Rizzo', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Ary Serpa', 'family': 'Neto', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Flávia R', 'family': 'Machado', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []},
{'given': 'Alexandre B', 'family': 'Cavalcanti', 'sequence': 'additional', 'affiliation': []}],
'member': '78',
'reference': [ { 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib1',
'series-title': 'Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation report 165',
'year': '2020'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib2',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949',
'article-title': 'Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results '
'of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial',
'volume': '56',
'author': 'Gautret',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Int J Antimicrob Agents'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib3',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '302',
'DOI': '10.3389/fimmu.2018.00302',
'article-title': 'The immunomodulatory effects of macrolides—a systematic review of the '
'underlying mechanisms',
'volume': '9',
'author': 'Zimmermann',
'year': '2018',
'journal-title': 'Front Immunol'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib4',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '90',
'DOI': '10.1186/1465-9921-11-90',
'article-title': 'Azithromycin attenuates airway inflammation in a mouse model of viral '
'bronchiolitis',
'volume': '11',
'author': 'Beigelman',
'year': '2010',
'journal-title': 'Respir Res'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib5',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '804',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.phrs.2016.07.033',
'article-title': 'Clarithromycin prevents human respiratory syncytial virus-induced '
'airway epithelial responses by modulating activation of interferon '
'regulatory factor-3',
'volume': '111',
'author': 'Yamamoto',
'year': '2016',
'journal-title': 'Pharmacol Res'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib6',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1331',
'DOI': '10.1164/rccm.200402-200OC',
'article-title': 'Azithromycin blocks neutrophil recruitment in Pseudomonas endobronchial '
'infection',
'volume': '170',
'author': 'Tsai',
'year': '2004',
'journal-title': 'Am J Respir Crit Care Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib7',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1033',
'DOI': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0',
'article-title': 'COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression',
'volume': '395',
'author': 'Mehta',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Lancet'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib8',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1881',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa1003833',
'article-title': 'Azithromycin and the risk of cardiovascular death',
'volume': '366',
'author': 'Ray',
'year': '2012',
'journal-title': 'N Engl J Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib9',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'DOI': '10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834',
'article-title': 'Risk of QT interval prolongation associated with use of '
'hydroxychloroquine with or without concomitant azithromycin among '
'hospitalized patients testing positive for coronavirus disease 2019 '
'(COVID-19)',
'author': 'Mercuro',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'JAMA Cardiol'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib10',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '303',
'DOI': '10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048238',
'article-title': 'Cardiovascular toxicities associated with hydroxychloroquine and '
'azithromycin: an analysis of the World Health Organization '
'pharmacovigilance database',
'volume': '142',
'author': 'Nguyen',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Circulation'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib11',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '2493',
'DOI': '10.1001/jama.2020.8630',
'article-title': 'Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with '
'in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State',
'volume': '323',
'author': 'Rosenberg',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'JAMA'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib12',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101738',
'article-title': 'Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and '
'azithromycin: a retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille, '
'France',
'volume': '35',
'author': 'Million',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Travel Med Infect Dis'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib13',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '384',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.006',
'article-title': 'No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical benefit with the '
'combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with '
'severe COVID-19 infection',
'volume': '50',
'author': 'Molina',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Med Mal Infect'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib14',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2019014',
'article-title': 'Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate '
'Covid-19',
'author': 'Cavalcanti',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'N Engl J Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib15',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '269',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0',
'article-title': 'Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged '
'novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro',
'volume': '30',
'author': 'Wang',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Cell Res'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib16',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2007764',
'article-title': 'Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 — preliminary report',
'author': 'Beigel',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'N Engl J Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib17',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1787',
'DOI': '10.1056/NEJMoa2001282',
'article-title': 'A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe '
'Covid-19',
'volume': '382',
'author': 'Cao',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'N Engl J Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib19',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '63',
'DOI': '10.1186/s13613-020-00678-4',
'article-title': 'Lack of viral clearance by the combination of hydroxychloroquine and '
'azithromycin or lopinavir and ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2-related acute '
'respiratory distress syndrome',
'volume': '10',
'author': 'Hraiech',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Ann Intensive Care'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib20',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1069',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.chest.2016.11.012',
'article-title': 'Efficacy of clarithromycin-naproxen-oseltamivir combination in the '
'treatment of patients hospitalized for influenza A(H3N2) infection: an '
'open-label randomized, controlled, phase IIb/III trial',
'volume': '151',
'author': 'Hung',
'year': '2017',
'journal-title': 'Chest'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib21',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '693',
'DOI': '10.1007/s00134-013-2829-8',
'article-title': 'Macrolide-based regimens in absence of bacterial co-infection in '
'critically ill H1N1 patients with primary viral pneumonia',
'volume': '39',
'author': 'Martín-Loeches',
'year': '2013',
'journal-title': 'Intensive Care Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib22',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '184',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.ijid.2019.01.041',
'article-title': 'Macrolides in critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory '
'syndrome',
'volume': '81',
'author': 'Arabi',
'year': '2019',
'journal-title': 'Int J Infect Dis'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib23',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '918',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.02.009',
'article-title': 'Adjunctive therapy with azithromycin for moderate and severe acute '
'respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective, propensity '
'score-matching analysis of prospectively collected data at a single '
'center',
'volume': '51',
'author': 'Kawamura',
'year': '2018',
'journal-title': 'Int J Antimicrob Agents'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib24',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': 'e45',
'DOI': '10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST',
'article-title': 'Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An '
'official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society '
'and Infectious Diseases Society of America',
'volume': '200',
'author': 'Metlay',
'year': '2019',
'journal-title': 'Am J Respir Crit Care Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib25',
'article-title': 'Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—preliminary report',
'author': 'Horby',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'N Engl J Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib26',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1054',
'DOI': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3',
'article-title': 'Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with '
'COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study',
'volume': '395',
'author': 'Zhou',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Lancet'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib27',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '808',
'DOI': '10.1038/s41591-020-0888-2',
'article-title': 'The QT interval in patients with COVID-19 treated with '
'hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin',
'volume': '26',
'author': 'Chorin',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Nat Med'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib28',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '2173',
'DOI': '10.1016/j.jacc.2015.09.029',
'article-title': 'The role of macrolide antibiotics in increasing cardiovascular risk',
'volume': '66',
'author': 'Cheng',
'year': '2015',
'journal-title': 'J Am Coll Cardiol'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib29',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1895',
'DOI': '10.1001/jama.2020.4984',
'article-title': 'Optimizing the trade-off between learning and doing in a pandemic',
'volume': '323',
'author': 'Angus',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'JAMA'},
{ 'key': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6_bib30',
'doi-asserted-by': 'crossref',
'first-page': '1695',
'DOI': '10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4',
'article-title': 'Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and '
'ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with '
'COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial',
'volume': '395',
'author': 'Hung',
'year': '2020',
'journal-title': 'Lancet'}],
'container-title': 'The Lancet',
'original-title': [],
'language': 'en',
'link': [ { 'URL': 'https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673620318626?httpAccept=text/xml',
'content-type': 'text/xml',
'content-version': 'vor',
'intended-application': 'text-mining'},
{ 'URL': 'https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673620318626?httpAccept=text/plain',
'content-type': 'text/plain',
'content-version': 'vor',
'intended-application': 'text-mining'}],
'deposited': { 'date-parts': [[2022, 11, 16]],
'date-time': '2022-11-16T11:06:57Z',
'timestamp': 1668596817000},
'score': 1,
'resource': {'primary': {'URL': 'https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673620318626'}},
'subtitle': [],
'short-title': [],
'issued': {'date-parts': [[2020, 10]]},
'references-count': 29,
'journal-issue': {'issue': '10256', 'published-print': {'date-parts': [[2020, 10]]}},
'alternative-id': ['S0140673620318626'],
'URL': 'http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6',
'relation': { 'has-review': [ { 'id-type': 'doi',
'id': '10.3410/f.738621001.793578689',
'asserted-by': 'object'},
{ 'id-type': 'doi',
'id': '10.3410/f.738621001.793579609',
'asserted-by': 'object'}]},
'ISSN': ['0140-6736'],
'subject': ['General Medicine'],
'container-title-short': 'The Lancet',
'published': {'date-parts': [[2020, 10]]},
'assertion': [ {'value': 'Elsevier', 'name': 'publisher', 'label': 'This article is maintained by'},
{ 'value': 'Azithromycin in addition to standard of care versus standard of care alone in '
'the treatment of patients admitted to the hospital with severe COVID-19 in '
'Brazil (COALITION II): a randomised clinical trial',
'name': 'articletitle',
'label': 'Article Title'},
{'value': 'The Lancet', 'name': 'journaltitle', 'label': 'Journal Title'},
{ 'value': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31862-6',
'name': 'articlelink',
'label': 'CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version'},
{ 'value': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31863-8',
'name': 'associatedlink',
'label': 'CrossRef DOI link to the associated document'},
{'value': 'article', 'name': 'content_type', 'label': 'Content Type'},
{ 'value': '© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.',
'name': 'copyright',
'label': 'Copyright'}]}